4.6. Protocol Descriptor¶
Add managed attributes to objects
Outsource functionality into specialized classes
Descriptors:
classmethod,staticmethod,property, functions in general__del__(self)is reserved when object is being deleted by garbage collector (destructor)__set_name()After class creation, Python default metaclass will call it with cls and classname
4.6.1. Protocol¶
__get__(self, cls, *args) -> self__set__(self, cls, value) -> None__delete__(self, cls) -> None__set_name__(self)
If any of those methods are defined for an object, it is said to be a descriptor.
—Raymond Hettinger
>>> class Descriptor:
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... return ...
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... ...
...
... def __delete__(self, cls):
... ...
...
... def __set_name__(self, cls, attrname):
... ...
4.6.2. Example¶
>>> class MyField:
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... print('Getter')
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... print('Setter')
...
... def __delete__(self, cls):
... print('Deleter')
>>>
>>>
>>> class MyClass:
... value = MyField()
>>>
>>>
>>> my = MyClass()
>>>
>>> my.value = 'something'
Setter
>>>
>>> my.value
Getter
>>>
>>> del my.value
Deleter
4.6.3. Property vs Reflection vs Descriptor¶
Property:
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin = property()
... _value: float
...
... @kelvin.setter
... def myattribute(self, value):
... if value < 0:
... raise ValueError
... else:
... self._value = value
Reflection:
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin: float
...
... def __setattr__(self, attrname, value):
... if attrname == 'kelvin' and value < 0:
... raise ValueError
... else:
... super().__setattr__(attrname, value)
Descriptor:
>>> class Kelvin:
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if value < 0:
... raise ValueError
... else:
... cls._value = value
>>>
>>>
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin = Kelvin()
... _value: float
4.6.4. Inheritance¶
4.6.5. Function Descriptor¶
Function are Descriptors too
>>> def hello():
... pass
>>>
>>>
>>> type(hello)
<class 'function'>
>>> hasattr(hello, '__get__')
True
>>> hasattr(hello, '__set__')
False
>>> hasattr(hello, '__delete__')
False
>>> hasattr(hello, '__set_name__')
False
>>> dir(hello)
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__call__', '__class__', '__closure__',
'__code__', '__defaults__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__',
'__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__get__', '__getattribute__',
'__getstate__', '__globals__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__',
'__init_subclass__', '__kwdefaults__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__',
'__name__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__qualname__', '__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__',
'__subclasshook__', '__type_params__']
>>> class Astronaut:
... def hello(self):
... pass
>>>
>>> type(Astronaut.hello)
<class 'function'>
>>> hasattr(Astronaut.hello, '__get__')
True
>>> hasattr(Astronaut.hello, '__set__')
False
>>> hasattr(Astronaut.hello, '__delete__')
False
>>> hasattr(Astronaut.hello, '__set_name__')
False
>>> dir(Astronaut.hello)
['__annotations__', '__builtins__', '__call__', '__class__',
'__closure__', '__code__', '__defaults__', '__delattr__', '__dict__',
'__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__get__',
'__getattribute__', '__getstate__', '__globals__', '__gt__', '__hash__',
'__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__kwdefaults__', '__le__', '__lt__',
'__module__', '__name__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__qualname__', '__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__',
'__subclasshook__', '__type_params__']
>>> class Astronaut:
... def hello(self):
... pass
>>>
>>> mark = Astronaut()
>>>
>>> type(mark.hello)
<class 'method'>
>>> hasattr(mark.hello, '__get__')
True
>>> hasattr(mark.hello, '__set__')
False
>>> hasattr(mark.hello, '__delete__')
False
>>> hasattr(mark.hello, '__set_name__')
False
>>> dir(mark.hello)
['__call__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__',
'__format__', '__func__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getstate__',
'__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__',
'__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__self__',
'__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__']
4.6.6. Use Case - 0x01¶
Kelvin Temperature Validator
>>> class KelvinValidator:
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if value < 0.0:
... raise ValueError('Cannot set negative Kelvin')
... cls._value = value
>>>
>>>
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin = KelvinValidator()
...
... def __init__(self):
... self._value = None
>>>
>>>
>>> t = Temperature()
>>> t.kelvin = -1
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Cannot set negative Kelvin
4.6.7. Use Case - 0x02¶
Temperature Conversion
>>> class Kelvin:
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... return round(cls._value, 2)
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... cls._value = value
>>>
>>>
>>> class Celsius:
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... value = cls._value - 273.15
... return round(value, 2)
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... cls._value = value + 273.15
>>>
>>>
>>> class Fahrenheit:
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... value = (cls._value - 273.15) * 9 / 5 + 32
... return round(value, 2)
...
... def __set__(self, cls, fahrenheit):
... cls._value = (fahrenheit - 32) * 5 / 9 + 273.15
>>>
>>>
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin = Kelvin()
... celsius = Celsius()
... fahrenheit = Fahrenheit()
...
... def __init__(self):
... self._value = 0.0
>>>
>>>
>>> t = Temperature()
>>>
>>> t.kelvin = 273.15
>>> print(t.kelvin)
273.15
>>> print(t.celsius)
0.0
>>> print(t.fahrenheit)
32.0
>>>
>>> t.fahrenheit = 100
>>> print(t.kelvin)
310.93
>>> print(t.celsius)
37.78
>>> print(t.fahrenheit)
100.0
>>>
>>> t.celsius = 100
>>> print(t.kelvin)
373.15
>>> print(t.celsius)
100.0
>>> print(t.fahrenheit)
212.0
4.6.8. Use Case - 0x03¶
Value Range Descriptor
>>> class Between:
... def __init__(self, min, max):
... self.min = min
... self.max = max
...
... def __set_name__(self, cls, attrname):
... self.attrname = f'_{attrname}'
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if not self.min <= value <= self.max:
... field = self.attrname.removeprefix('_')
... raise ValueError(f'Value of field "{field}" is not between {self.min} and {self.max}')
... setattr(cls, self.attrname, value)
...
... def __get__(self, cls, clstype):
... return getattr(cls, self.attrname)
...
... def __delete__(self, cls):
... setattr(cls, self.attrname, None)
>>>
>>>
>>> class Astronaut:
... firstname: str
... lastname: str
... age = Between(30, 50)
... height = Between(150, 210)
... weight = Between(50, 90)
>>> mark = Astronaut()
>>>
>>> mark.firstname = 'Mark'
>>> mark.lastname = 'Watney'
>>> mark.age = 42
>>> mark.height = 178.0
>>> mark.weight = 75.5
>>> mark.age = 18
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Value of field "age" is not between 30 and 50
>>>
>>> mark.weight = 100
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Value of field "weight" is not between 50 and 90
>>>
>>> mark.height = 220
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Value of field "height" is not between 150 and 210
4.6.9. Use Case - 0x04¶
>>> import re
>>>
>>>
>>> class Validator:
... def __set_name__(self, cls, attribute_name):
... self.attrname_short = f'_{attribute_name}'
... self.attrname_full = f'{cls.__name__}.{attribute_name}'
...
... def __get__(self, cls, cls_type):
... return getattr(cls, self.attrname_short)
...
... def __delete__(self, cls):
... setattr(cls, self.attrname_short, None)
>>>
>>>
>>> class Between(Validator):
... def __init__(self, min, max):
... self.min = min
... self.max = max
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if self.min <= value < self.max:
... setattr(cls, self.attrname_short, value)
... else:
... raise ValueError(f'{self.attrname_full} value: {value} '
... f'is not between {self.min} and {self.max}')
>>>
>>>
>>> class MaxLength(Validator):
... def __init__(self, max_length):
... self.max_length = max_length
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if len(value) <= self.max_length:
... setattr(cls, self.attrname_short, value)
... else:
... raise ValueError(f'{self.attrname_full} value: {value} '
... f'is longer than {self.max_length}')
>>>
>>> class MatchesRegex(Validator):
... def __init__(self, pattern):
... self.pattern = pattern
... self.regex = re.compile(pattern)
...
... def __set__(self, cls, value):
... if self.regex.match(value):
... setattr(cls, self.attrname_short, value)
... else:
... raise ValueError(f'{self.attrname_full} value: {value} '
... f'does not match pattern: {self.pattern}')
>>>
>>>
>>> class Astronaut:
... firstname: str = MaxLength(20)
... lastname: str = MaxLength(30)
... age: int = Between(30, 50)
... height: float = Between(150, 210)
... weight: float = Between(50, 90)
... email: str = MatchesRegex('^[a-z]+@nasa.gov$')
>>> mark = Astronaut()
>>>
>>> mark.firstname = 'Mark'
>>> mark.lastname = 'Watney'
>>> mark.age = 42
>>> mark.height = 178.0
>>> mark.weight = 75.5
>>> mark.email = 'mwatney@nasa.gov'
>>> mark.firstname = 'MarkMarkMarkMarkMarkMark'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.firstname value: MarkMarkMarkMarkMarkMark is longer than 20
>>> mark.lastname = 'WatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatney'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.lastname value: WatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatney is longer than 30
>>> mark.age = 60
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.age value: 60 is not between 30 and 50
>>> mark.height = 220
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.height value: 220 is not between 150 and 210
>>> mark.weight = 100
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.weight value: 100 is not between 50 and 90
>>> mark.email = 'invalid-email@nasa.gov'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Astronaut.email value: invalid-email@nasa.gov does not match pattern: ^[a-z]+@nasa.gov$
4.6.10. Use Case - 0x05¶
>>> import re
>>> from abc import ABC, abstractmethod, abstractproperty
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass, InitVar
>>>
>>>
>>> class Validator(ABC):
... attrname: str
...
... @abstractproperty
... def error_message(self) -> str: ...
...
... def __set_name__(self, owner, attrname):
... self.attrname = f'_{attrname}'
...
... def __get__(self, instance, owner):
... return getattr(instance, self.attrname)
...
... def __set__(self, instance, value):
... if self.is_valid(value):
... setattr(instance, self.attrname, value)
... else:
... raise ValueError(self.error_message.format(**vars(self)))
...
... @abstractmethod
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... raise NotImplementedError
>>>
>>>
>>> @dataclass
... class MaxLength(Validator):
... maxlength: int
... error_message: str = ('Attribute {attrname} is invalid. '
... 'Value is longer than {maxlength}')
...
... def is_valid(self, value):
... return len(value) <= self.maxlength
>>>
>>>
>>> @dataclass
... class Between(Validator):
... min: int
... max: int
... error_message: str = ('Attribute {attrname} is invalid. '
... 'Value not between {min} and {max}.')
...
... def is_valid(self, value):
... return self.min <= value < self.max
>>>
>>> @dataclass
... class Matches(Validator):
... pattern: InitVar[str]
... regex: re.Pattern | None = None
... error_message: str = ('Attribute {attrname} is invalid. '
... 'Value does not match pattern `{regex.pattern}`')
...
... def __post_init__(self, pattern):
... self.regex = re.compile(pattern)
...
... def is_valid(self, value):
... return self.regex.match(value)
>>>
>>>
>>> @dataclass
... class Astronaut:
... firstname: str = MaxLength(50)
... lastname: str = MaxLength(50)
... age: int = Between(min=30, max=50)
... height: float = Between(min=150, max=210)
... weight: float = Between(min=50, max=90)
... email: str = Matches('^[a-z]+@nasa.gov$')
>>> mark = Astronaut(
... firstname = 'Mark',
... lastname = 'Watney',
... age = 42,
... height = 178.0,
... weight = 75.5,
... email = 'mwatney@nasa.gov',
... )
4.6.11. Use Case - 0x06¶
>>> from abc import ABC, abstractmethod, abstractproperty
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass, InitVar
>>> import re
>>> from typing import ClassVar
...
...
>>> @dataclass
... class Validator(ABC):
... attrname: str | None = None
...
... def __set_name__(self, owner, name):
... self.attrname = f'_{name}'
...
... def __get__(self, instance, owner):
... return getattr(instance, self.attrname)
...
... def __delete__(self, instance):
... delattr(instance, self.attrname, None)
...
... def __set__(self, instance, value):
... if not self.is_valid(value):
... raise ValueError(self.ERROR_MSG.format(value=value, **self.__dict__))
... setattr(instance, self.attrname, value)
...
... @abstractmethod
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... ...
...
... @abstractproperty
... def ERROR_MSG(self) -> str:
... ...
...
...
>>> @dataclass
... class String(Validator):
... max_length: int = 30
... ERROR_MSG: ClassVar[str] = '{attrname} {value} is longer than {max_length}'
...
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... return len(value) <= self.max_length
...
...
>>> @dataclass
... class Email(Validator):
... domain: str = ''
... ERROR_MSG: ClassVar[str] = '{attrname} value "{value}" is not in domain {domain}'
...
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... return value.endswith(self.domain)
...
...
>>> @dataclass
... class Integer(Validator):
... min: int = 0
... max: int = 256
... ERROR_MSG: ClassVar[str] = '{attrname} value "{value}" is not between {min} and {max}'
...
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... return self.min <= value < self.max
...
...
>>> @dataclass
... class Phone(Validator):
... regex: InitVar[str] = r'.*'
... pattern: re.Pattern | None = None
... ERROR_MSG: ClassVar[str] = '{attrname} value "{value}" does not match {pattern}'
...
... def __post_init__(self, regex):
... self.pattern = re.compile(regex)
...
... def is_valid(self, value) -> bool:
... return True if self.pattern.match(value) else False
>>> class Astronaut:
... firstname: str = String(max_length=20)
... lastname: str = String(max_length=30)
... email: str = Email(domain='@nasa.gov')
... phone: str = Phone(regex=r'^\+48 \d{3} \d{3} \d{3}$')
... age: int = Integer(min=30, max=50)
>>> mark = Astronaut()
>>> mark.firstname = 'Mark'
>>> mark.lastname = 'Watney'
>>> mark.age = 42
>>> mark.email = 'mwantey@nasa.gov'
>>> mark.phone = '+48 123 456 789'
>>> mark.firstname = 'WatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatney'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _firstname WatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatneyWatney is longer than 20
>>> mark.age = 20
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _age value "20" is not between 30 and 50
>>> mark.age = 60
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _age value "60" is not between 30 and 50
>>> mark.phone = '+48 12 3456 789'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _phone value "+48 12 3456 789" does not match re.compile('^\\+48 \\d{3} \\d{3} \\d{3}$')
>>> mark.phone = '+49 123 456 789'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _phone value "+49 123 456 789" does not match re.compile('^\\+48 \\d{3} \\d{3} \\d{3}$')
>>> mark.email = 'mwantey@nasa.com'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _email value "mwantey@nasa.com" is not in domain @nasa.gov
>>> mark.email = 'mwantey@nasa.gov.pl'
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: _email value "mwantey@nasa.gov.pl" is not in domain @nasa.gov
>>> vars(mark)
{'_firstname': 'Mark',
'_lastname': 'Watney',
'_age': 42,
'_email': 'mwantey@nasa.gov',
'_phone': '+48 123 456 789'}
>>> vars(Astronaut)
mappingproxy({'__module__': '__main__',
'__annotations__': {'firstname': <class 'str'>,
'lastname': <class 'str'>,
'email': <class 'str'>,
'phone': <class 'str'>,
'age': <class 'int'>},
'firstname': String(attrname='_firstname', max_length=20),
'lastname': String(attrname='_lastname', max_length=30),
'email': Email(attrname='_email', domain='@nasa.gov'),
'phone': Phone(attrname='_phone', pattern=re.compile('^\\+48 \\d{3} \\d{3} \\d{3}$')),
'age': Integer(attrname='_age', min=30, max=50),
'__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'Astronaut' objects>,
'__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'Astronaut' objects>,
'__doc__': None})
4.6.12. Use Case - 0x07¶
Timezone Converter Descriptor
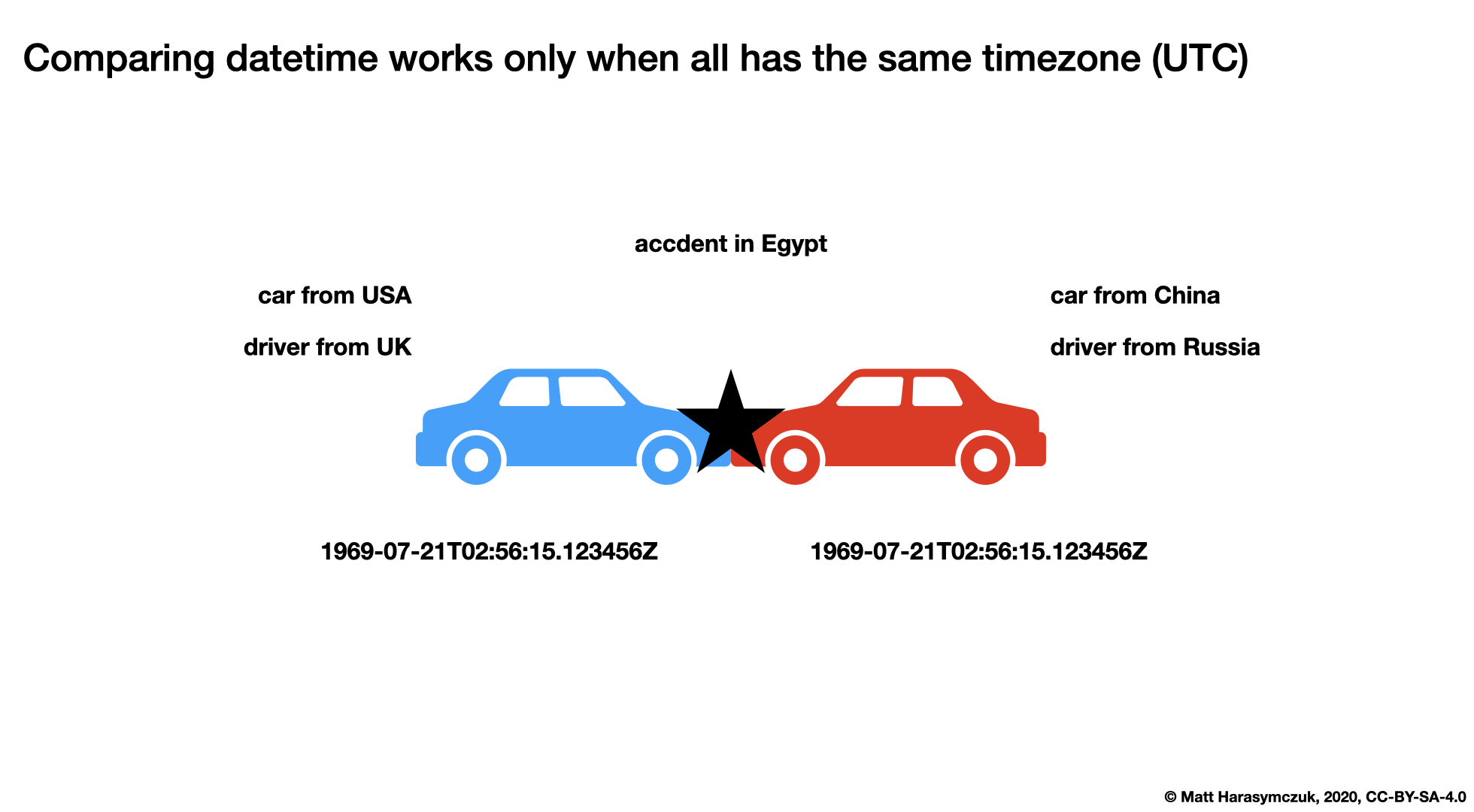
Figure 4.16. Comparing datetime works only when all has the same timezone (UTC). More information in Stdlib Datetime Timezone¶
Descriptor Timezone Converter:
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> from zoneinfo import ZoneInfo
>>>
>>>
>>> class Timezone:
... def __init__(self, name):
... self.timezone = ZoneInfo(name)
...
... def __get__(self, cls, *args):
... utc = cls.utc.replace(tzinfo=ZoneInfo('UTC'))
... return utc.astimezone(self.timezone)
...
... def __set__(self, cls, new_datetime):
... local_time = new_datetime.replace(tzinfo=self.timezone)
... cls.utc = local_time.astimezone(ZoneInfo('UTC'))
>>>
>>>
>>> @dataclass
... class Time:
... utc = datetime.now(tz=ZoneInfo('UTC'))
... warsaw = Timezone('Europe/Warsaw')
... eastern = Timezone('America/New_York')
... pacific = Timezone('America/Los_Angeles')
>>>
>>>
>>> t = Time()
>>>
>>> # Gagarin's launch to space
>>> t.utc = datetime(1961, 4, 12, 6, 7)
>>>
>>> print(t.utc)
1961-04-12 06:07:00
>>> print(t.warsaw)
1961-04-12 07:07:00+01:00
>>> print(t.eastern)
1961-04-12 01:07:00-05:00
>>> print(t.pacific)
1961-04-11 22:07:00-08:00
>>>
>>>
>>> # Armstrong's first Lunar step
>>> t.warsaw = datetime(1969, 7, 21, 3, 56, 15)
>>>
>>> print(t.utc)
1969-07-21 02:56:15+00:00
>>> print(t.warsaw)
1969-07-21 03:56:15+01:00
>>> print(t.eastern)
1969-07-20 22:56:15-04:00
>>> print(t.pacific)
1969-07-20 19:56:15-07:00
4.6.13. Assignments¶
"""
* Assignment: Protocol Descriptor Simple
* Complexity: easy
* Lines of code: 9 lines
* Time: 5 min
English:
1. Define descriptor class `Kelvin`
2. Temperature must always be positive
3. Use descriptors to check boundaries at each value modification
4. All tests must pass
5. Run doctests - all must succeed
Polish:
1. Zdefiniuj klasę deskryptor `Kelvin`
2. Temperatura musi być zawsze być dodatnia
3. Użyj deskryptorów do sprawdzania zakresów przy każdej modyfikacji
4. Wszystkie testy muszą przejść
5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
Tests:
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> class Temperature:
... kelvin = Kelvin()
>>> t = Temperature()
>>> t.kelvin = 1
>>> t.kelvin
1
>>> t.kelvin = -1
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Negative temperature
"""
"""
* Assignment: Protocol Descriptor ValueRange
* Complexity: easy
* Lines of code: 9 lines
* Time: 13 min
English:
1. Define descriptor class `ValueRange` with attributes:
a. `name: str`
b. `min: float`
c. `max: float`
d. `value: float`
2. Define class `User` with attributes:
a. `age = ValueRange('Age', min=28, max=42)`
b. `height = ValueRange('Height', min=150, max=200)`
3. Setting `User` attribute should invoke boundary check of `ValueRange`
4. Run doctests - all must succeed
Polish:
1. Zdefiniuj klasę-deskryptor `ValueRange` z atrybutami:
a. `name: str`
b. `min: float`
c. `max: float`
d. `value: float`
2. Zdefiniuj klasę `User` z atrybutami:
a. `age = ValueRange('Age', min=28, max=42)`
b. `height = ValueRange('Height', min=150, max=200)`
3. Ustawianie atrybutu `User` powinno wywołać sprawdzanie zakresu z `ValueRange`
6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
Tests:
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> mark = User('Mark Watney', 36, 170)
>>> melissa = User('Melissa Lewis', 44, 170)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Age is not between 28 and 42
>>> alex = User('Alex Vogel', 40, 201)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Height is not between 150 and 200
"""
class ValueRange:
name: str
min: float
max: float
def __init__(self, name, min, max):
pass
class User:
name: str
age = ValueRange('Age', min=28, max=42)
height = ValueRange('Height', min=150, max=200)
def __init__(self, name, age, height):
self.name = name
self.height = height
self.age = age
def __repr__(self):
name = self.name
age = self.age.value
height = self.height.value
return f'User({name=}, {age=}, {height=})'
"""
* Assignment: Protocol Descriptor Inheritance
* Complexity: medium
* Lines of code: 17 lines
* Time: 21 min
English:
1. Define class `GeographicCoordinate`
2. Use descriptors to check value boundaries
3. Run doctests - all must succeed
Polish:
1. Zdefiniuj klasę `GeographicCoordinate`
2. Użyj deskryptory do sprawdzania wartości brzegowych
3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
Tests:
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> place1 = GeographicCoordinate(50, 120, 8000)
>>> place1
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=50, longitude=120, elevation=8000)
>>> place2 = GeographicCoordinate(22, 33, 44)
>>> place2
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=22, longitude=33, elevation=44)
>>> place1.latitude = 1
>>> place1.longitude = 2
>>> place1
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=1, longitude=2, elevation=8000)
>>> place2
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=22, longitude=33, elevation=44)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(90, 0, 0)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=90, longitude=0, elevation=0)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(-90, 0, 0)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=-90, longitude=0, elevation=0)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, +180, 0)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=0, longitude=180, elevation=0)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, -180, 0)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=0, longitude=-180, elevation=0)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, 0, +8848)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=0, longitude=0, elevation=8848)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, 0, -10994)
GeographicCoordinate(latitude=0, longitude=0, elevation=-10994)
>>> GeographicCoordinate(-91, 0, 0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
>>> GeographicCoordinate(+91, 0, 0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, -181, 0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, +181, 0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, 0, -10995)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
>>> GeographicCoordinate(0, 0, +8849)
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Out of bounds
"""
from dataclasses import dataclass
from abc import ABC, abstractproperty
class GEOProperty(ABC):
pass
class Latitude(GEOProperty):
MIN: float = -90.0
MAX: float = +90.0
class Longitude(GEOProperty):
MIN: float = -180.0
MAX: float = +180.0
class Elevation(GEOProperty):
MIN: float = -10994.0
MAX: float = +8848.0
@dataclass
class GeographicCoordinate:
latitude: float = Latitude()
longitude: float = Longitude()
elevation: float = Elevation()