6.15. DataFrame Statistics
.count().value_counts().nunique().sum().cumsum().prod().cumprod().min().idxmin().cummin().max().idxmax().cummax().mean().median().mode().rolling(window=3).mean().abs().std().mad()- Mean absolute deviation (PL: Odchylenie bezwzględne).sem()- Standard Error of the Mean (SEM) (PL: błąd standardowy średniej).skew()- Skewness - 3rd moment (PL: skośność).kurt()- Kurtosis - 4th moment (PL: kurtoza).quantile(.33)- Sample quantile (value at %). Quantile also known as Percentile.quantile([.25, .5, .75]).var().corr().describe().nsmallest().values().rank()- Compute numerical data ranks (1 through n) along axis.
6.15.1. SetUp
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>>
>>>
>>> df = pd.DataFrame(
... columns = ['Morning', 'Noon', 'Evening', 'Midnight'],
... index = pd.date_range('1999-12-30', periods=7),
... data = np.random.randn(7, 4))
>>>
>>> df
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357
2000-01-01 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274
2000-01-02 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
2000-01-03 1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096
2000-01-04 -2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165
2000-01-05 2.269755 -1.454366 0.045759 -0.187184
6.15.2. Count
Number of non-null observations:
>>> df.count()
Morning 7
Noon 7
Evening 7
Midnight 7
dtype: int64
>>> df.value_counts()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
-2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165 1
-0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274 1
0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674 1
1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096 1
1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893 1
1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357 1
2.269755 -1.454366 0.045759 -0.187184 1
Name: count, dtype: int64
>>> df.nunique()
Morning 7
Noon 7
Evening 7
Midnight 7
dtype: int64
6.15.3. Sum
Sum of values:
df.sum() Morning 5.500273 Noon -1.050752 Evening 3.739996 Midnight 2.094039 dtype: float64
Cumulative sum:
>>> df.cumsum()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 3.631610 -0.577121 1.928826 2.089536
2000-01-01 3.528391 -0.166522 2.072870 3.543809
2000-01-02 4.289429 -0.044847 2.516733 3.877484
2000-01-03 5.783508 -0.250005 2.829801 3.023388
2000-01-04 3.230518 0.403613 3.694237 2.281223
2000-01-05 5.500273 -1.050752 3.739996 2.094039
6.15.4. Product
Product of values:
>>> df.prod()
Morning 2.240538
Noon -0.003810
Evening 0.000736
Midnight 0.019528
dtype: float64
Cumulative product:
>>> df.cumprod()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 3.294470 -0.391065 0.929888 -0.339175
2000-01-01 -0.340051 -0.160571 0.133944 -0.493254
2000-01-02 -0.258792 -0.019537 0.059453 -0.164586
2000-01-03 -0.386656 0.004008 0.018613 0.140572
2000-01-04 0.987128 0.002620 0.016090 -0.104328
2000-01-05 2.240538 -0.003810 0.000736 0.019528
6.15.5. Extremes
Minimum, index of minimum and cumulative minimum:
>>> df.min()
Morning -2.552990
Noon -1.454366
Evening 0.045759
Midnight -0.854096
dtype: float64
>>> df.idxmin()
Morning 2000-01-04
Noon 2000-01-05
Evening 2000-01-05
Midnight 2000-01-03
dtype: datetime64[ns]
>>> df.cummin()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 1.764052 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357
2000-01-01 -0.103219 -0.977278 0.144044 -0.151357
2000-01-02 -0.103219 -0.977278 0.144044 -0.151357
2000-01-03 -0.103219 -0.977278 0.144044 -0.854096
2000-01-04 -2.552990 -0.977278 0.144044 -0.854096
2000-01-05 -2.552990 -1.454366 0.045759 -0.854096
Maximum, index of maximum and cumulative maximum:
>>> df.max()
Morning 2.269755
Noon 0.653619
Evening 0.978738
Midnight 2.240893
dtype: float64
>>> df.idxmax()
Morning 2000-01-05
Noon 2000-01-04
Evening 1999-12-30
Midnight 1999-12-30
dtype: datetime64[ns]
>>> df.cummax()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 1.867558 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
2000-01-01 1.867558 0.410599 0.978738 2.240893
2000-01-02 1.867558 0.410599 0.978738 2.240893
2000-01-03 1.867558 0.410599 0.978738 2.240893
2000-01-04 1.867558 0.653619 0.978738 2.240893
2000-01-05 2.269755 0.653619 0.978738 2.240893
6.15.6. Average
Arithmetic mean of values:
>>> df.mean()
Morning 0.785753
Noon -0.150107
Evening 0.534285
Midnight 0.299148
dtype: float64
Arithmetic median of values:
>>> df.median()
Morning 1.494079
Noon 0.121675
Evening 0.443863
Midnight -0.151357
dtype: float64
Mode:
>>> df.mode()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
0 -2.552990 -1.454366 0.045759 -0.854096
1 -0.103219 -0.977278 0.144044 -0.742165
2 0.761038 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.187184
3 1.494079 0.121675 0.443863 -0.151357
4 1.764052 0.400157 0.864436 0.333674
5 1.867558 0.410599 0.950088 1.454274
6 2.269755 0.653619 0.978738 2.240893
Rolling Average:
>>> df.rolling(window=30)
Rolling [window=30,center=False,axis=0,method=single]
>>>
>>> df.rolling(window=3).mean()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-31 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-01 1.176130 -0.055507 0.690957 1.181270
2000-01-02 0.841792 -0.148335 0.512665 0.545530
2000-01-03 0.717299 0.109038 0.300325 0.311284
2000-01-04 -0.099291 0.190045 0.540456 -0.420862
2000-01-05 0.403615 -0.335302 0.407754 -0.594482
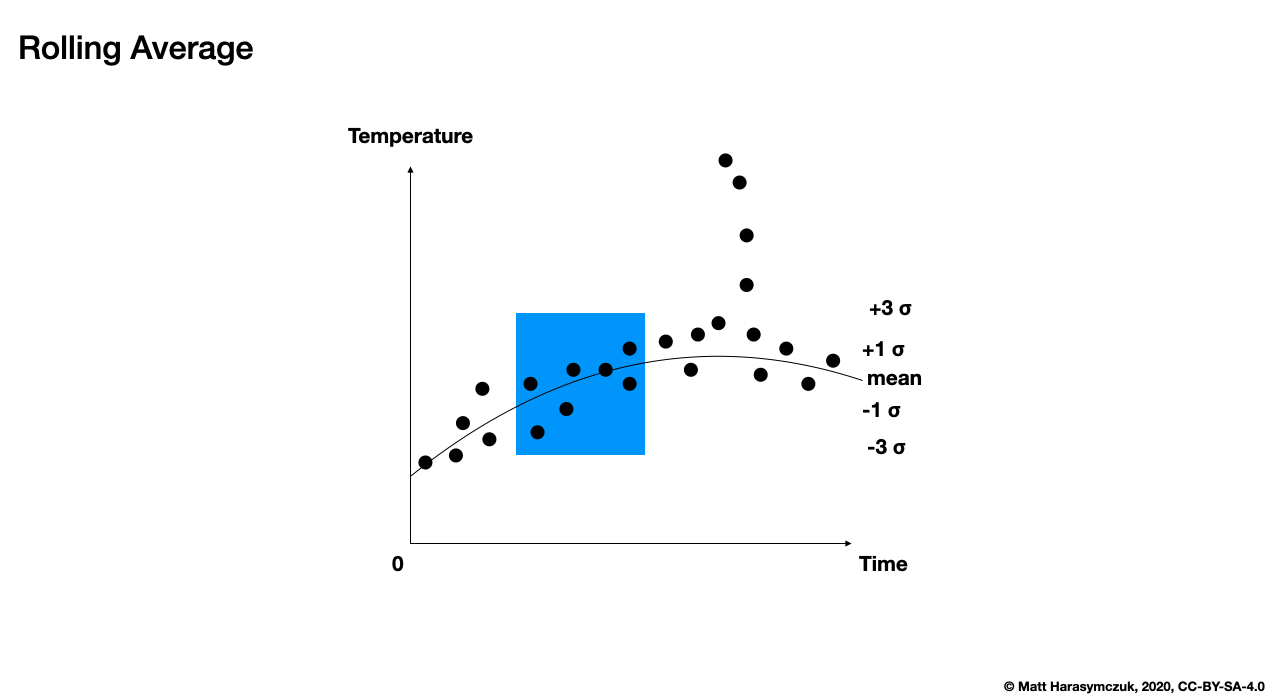
Figure 6.10. Rolling Average
6.15.7. Distribution
Absolute value:
>>> df.abs()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-30 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-31 1.867558 0.977278 0.950088 0.151357
2000-01-01 0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274
2000-01-02 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
2000-01-03 1.494079 0.205158 0.313068 0.854096
2000-01-04 2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 0.742165
2000-01-05 2.269755 1.454366 0.045759 0.187184
Standard deviation:
>>> df.std()
Morning 1.671798
Noon 0.787967
Evening 0.393169
Midnight 1.151785
dtype: float64
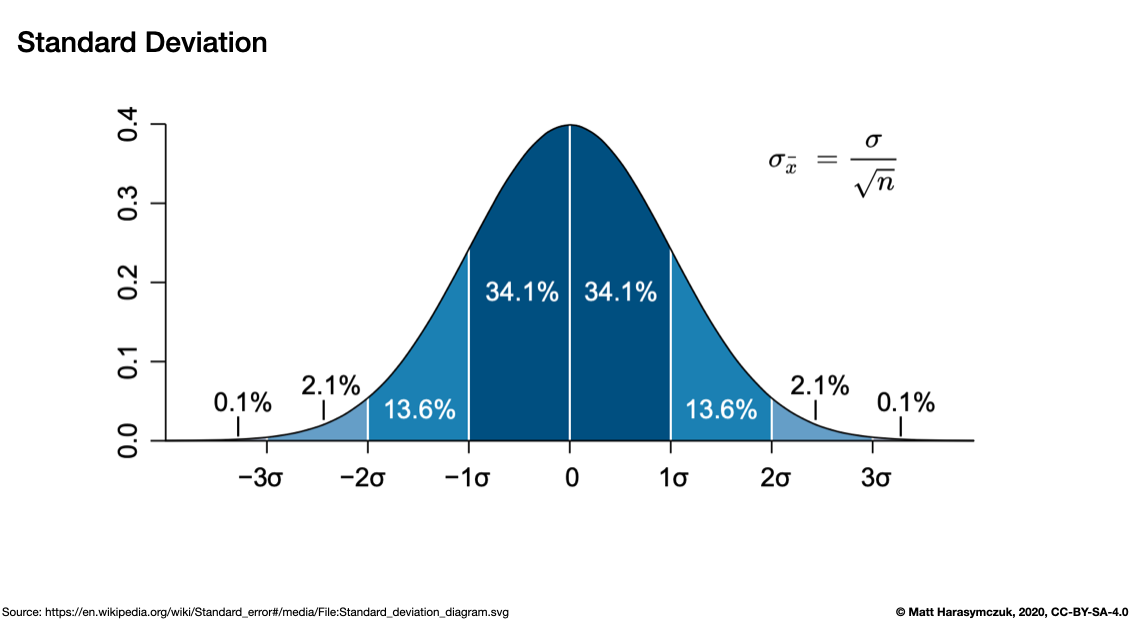
Figure 6.11. Standard Deviation
Standard Error of the Mean (SEM):
>>> df.sem()
Morning 0.631880
Noon 0.297824
Evening 0.148604
Midnight 0.435334
dtype: float64
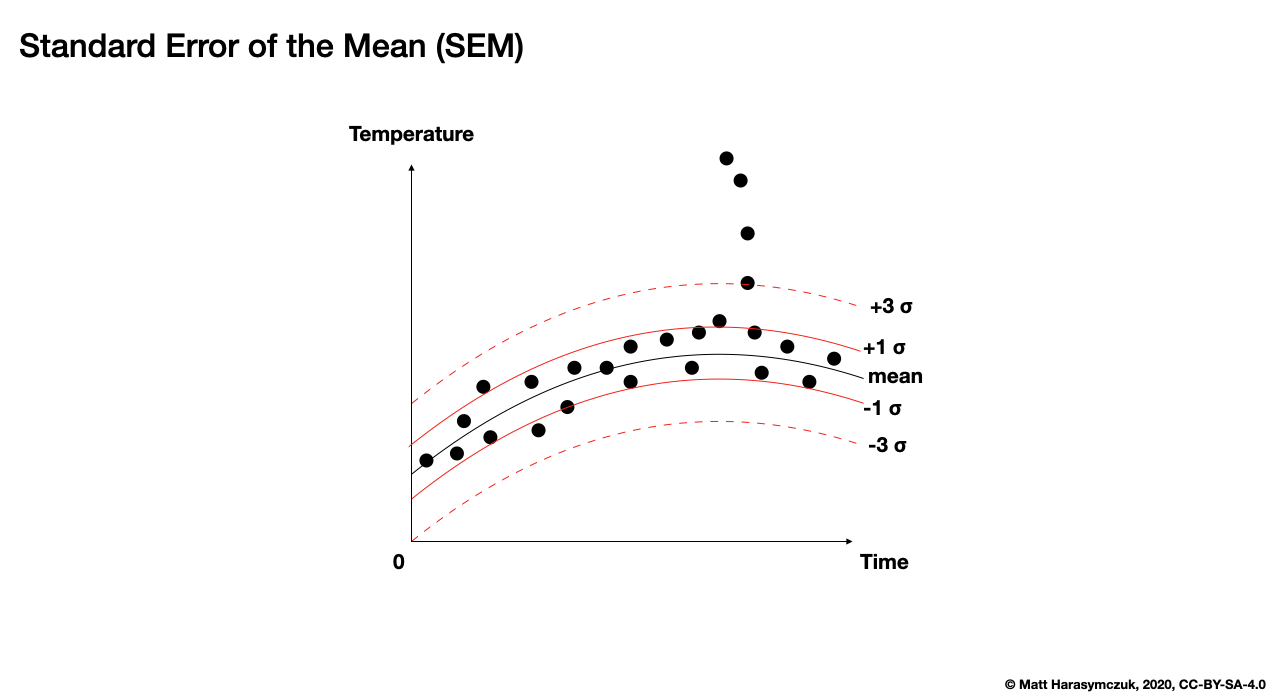
Figure 6.12. Standard Error of the Mean (SEM)
Skewness (3rd moment):
>>> df.skew()
Morning -1.602706
Noon -0.907414
Evening 0.031047
Midnight 0.915190
dtype: float64
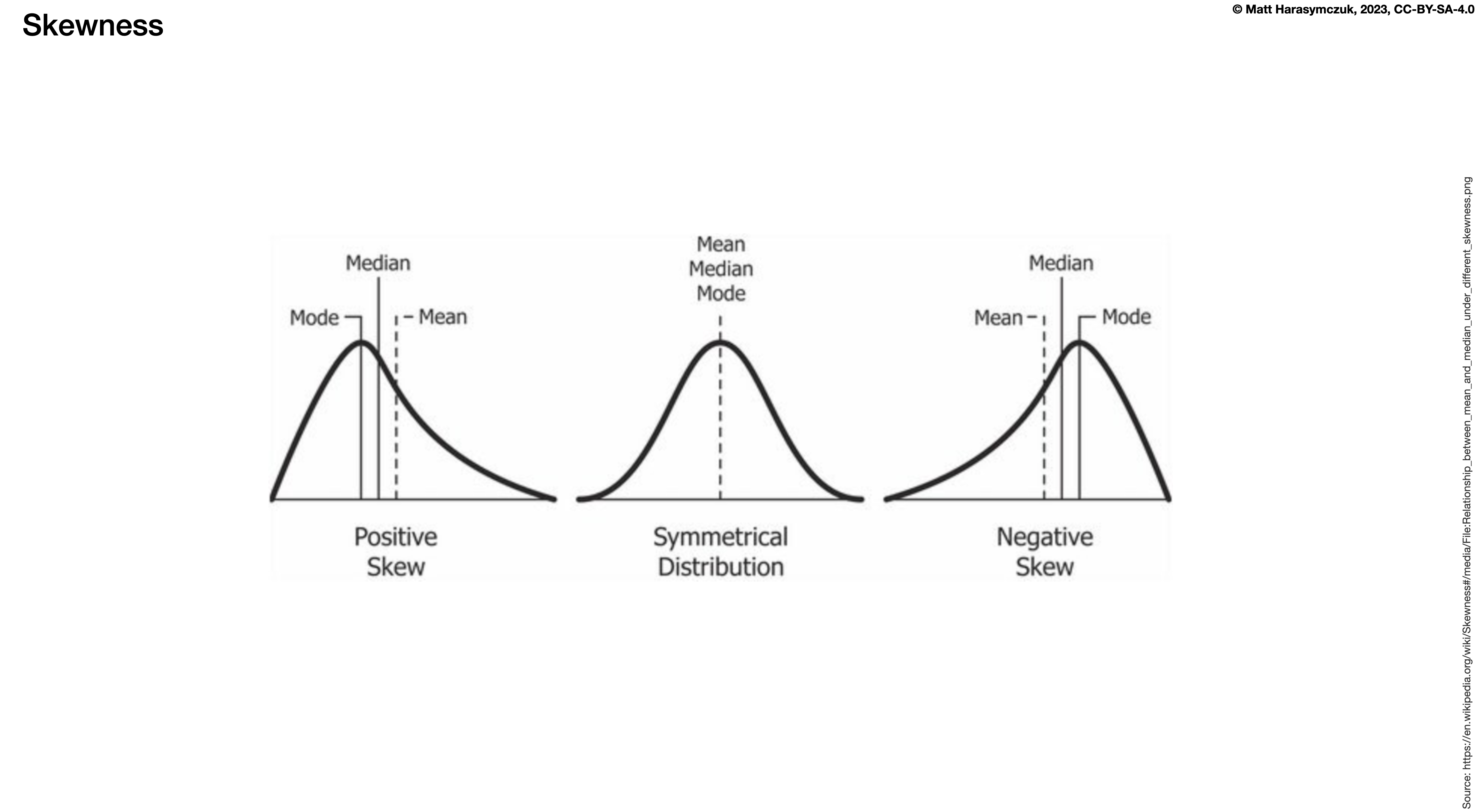
Figure 6.13. Skewness
Kurtosis (4th moment):
>>> df.kurt()
Morning 2.502051
Noon -0.588010
Evening -2.208781
Midnight -0.351782
dtype: float64
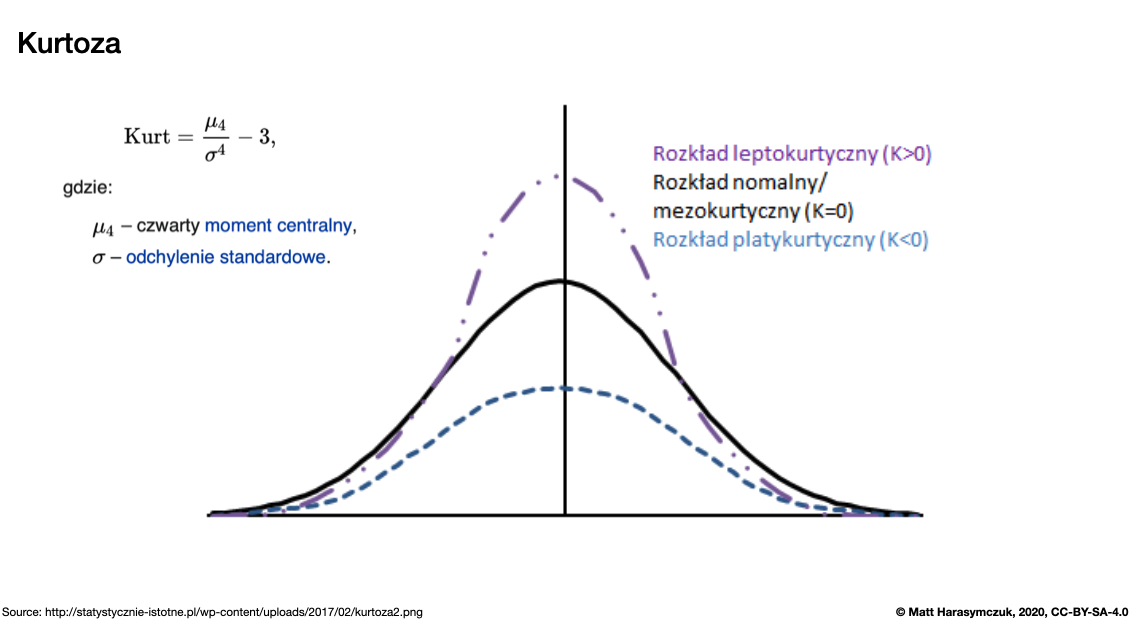
Figure 6.14. Kurtosis
Sample quantile (value at %). Quantile also known as Percentile:
>>> df.quantile(.33)
Morning 0.743753
Noon -0.220601
Evening 0.309687
Midnight -0.198283
Name: 0.33, dtype: float64
>>> df.quantile([.25, .5, .75])
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
0.25 0.328909 -0.591218 0.228556 -0.464674
0.50 1.494079 0.121675 0.443863 -0.151357
0.75 1.815805 0.405378 0.907262 0.893974
Variance:
>>> df.var()
Morning 2.794907
Noon 0.620892
Evening 0.154582
Midnight 1.326610
dtype: float64
Correlation Coefficient:
>>> df.corr()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
Morning 1.000000 -0.698340 -0.190219 0.201034
Noon -0.698340 1.000000 0.307686 0.359761
Evening -0.190219 0.307686 1.000000 0.136436
Midnight 0.201034 0.359761 0.136436 1.000000
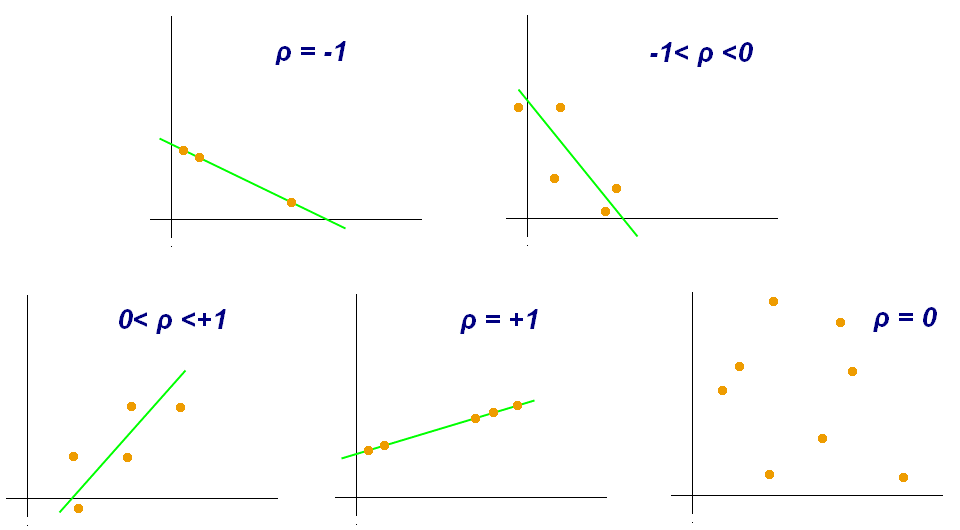
Figure 6.15. Correlation Coefficient
6.15.8. Describe
>>> df.describe()
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
count 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000 7.000000
mean 0.785753 -0.150107 0.534285 0.299148
std 1.671798 0.787967 0.393169 1.151785
min -2.552990 -1.454366 0.045759 -0.854096
25% 0.328909 -0.591218 0.228556 -0.464674
50% 1.494079 0.121675 0.443863 -0.151357
75% 1.815805 0.405378 0.907262 0.893974
max 2.269755 0.653619 0.978738 2.240893
6.15.9. Examples
>>> import pandas as pd
>>>
>>>
>>> DATA = 'https://python3.info/_static/phones-en.csv'
>>>
>>> df = pd.read_csv(DATA, parse_dates=['date'])
>>> df.drop(columns='index', inplace=True)
- date
The date and time of the entry
- duration
The duration (in seconds) for each call, the amount of data (in MB) for each data entry, and the number of texts sent (usually 1) for each sms entry
- item
A description of the event occurring – can be one of call, sms, or data
- month
The billing month that each entry belongs to – of form
YYYY-MM- network
The mobile network that was called/texted for each entry
- network_type
Whether the number being called was a mobile, international ('world'), voicemail, landline, or other ('special') number.
Source [1]
How many rows the dataset:
>>> df['item'].count()
np.int64(830)
What was the longest phone call / data entry?:
>>> df['duration'].max()
np.float64(10528.0)
How many seconds of phone calls are recorded in total?:
>>> df.loc[ df['item'] == 'call' ]['duration'].sum()
np.float64(92321.0)
How many entries are there for each month?:
>>> df['month'].value_counts()
month
2014-11 230
2015-01 205
2014-12 157
2015-02 137
2015-03 101
Name: count, dtype: int64
Number of non-null unique network entries:
>>> df['network'].nunique()
9
6.15.10. Other
.nsmallest()
.values()
.rank()
6.15.11. References
6.15.12. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: DataFrame Statistics
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Save basic descriptive statistics to `result: pd.DataFrame`
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Zapisz podstawowe statystyki opisowe do `result: pd.DataFrame`
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Hints
# - `DataFrame.describe()`
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> pd.set_option('display.width', 500)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 10)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)
>>> pd.set_option('display.precision', 4)
>>> assert 'result' in globals(), \
'Variable `result` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result) is pd.DataFrame, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid type; expected: `pd.DataFrame`.'
>>> result # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
mileage consumption
count 50.0000 50.0000
mean 110421.0200 9.3200
std 53170.2433 6.2448
min 7877.0000 0.0000
25% 71239.7500 4.0000
50% 115186.0000 9.0000
75% 154889.0000 14.7500
max 199827.0000 20.0000
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result: pd.DataFrame
# %% Data
np.random.seed(0)
df = pd.DataFrame({
'mileage': np.random.randint(0, 200_000, size=50),
'consumption': np.random.randint(0, 21, size=50),
})
# %% Result
result = ...