6.22. DataFrame Join
pd.concat().merge().join().melt()- stack columns
Warning
DataFrame.append() and Series.append() have been deprecated and will be removed in Pandas 2.0. Use pandas.concat() instead [1]
6.22.1. SetUp
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.random.seed(0)
>>>
>>> pd.set_option('display.width', 250)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 20)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 30)
>>>
>>>
>>> df1999 = pd.DataFrame(
... columns = ['Morning', 'Noon', 'Evening', 'Midnight'],
... index = pd.date_range('1999-12-29', periods=3),
... data = np.random.randn(3, 4))
>>>
>>> df2000 = pd.DataFrame(
... columns = ['Morning', 'Noon', 'Evening', 'Midnight'],
... index = pd.date_range('2000-01-01', periods=3),
... data = np.random.randn(3, 4))
>>>
>>> df1999
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-29 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-30 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357
1999-12-31 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274
>>>
>>> df2000
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
2000-01-01 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
2000-01-02 1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096
2000-01-03 -2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165
6.22.2. Concatenate
Useful for merging data from two files or datasources
>>> pd.concat([df1999, df2000])
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
1999-12-29 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
1999-12-30 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357
1999-12-31 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274
2000-01-01 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
2000-01-02 1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096
2000-01-03 -2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165
6.22.3. Merge
Merge DataFrame or named Series objects with a database-style join.
The join is done on columns or indexes.
If joining columns on columns, the DataFrame indexes will be ignored.
Otherwise if joining indexes on indexes or indexes on a column or columns, the index will be passed on.
>>> firstnames = pd.DataFrame({
... 'id': [1, 2, 3, 4],
... 'firstname': ['Mark', 'Melissa', 'Rick', 'Beth']})
>>>
>>> lastnames = pd.DataFrame({
... 'id': [1, 2, 3, 4],
... 'lastname': ['Watney', 'Lewis', 'Martinez', 'Johanssen']})
>>>
>>> firstnames
id firstname
0 1 Mark
1 2 Melissa
2 3 Rick
3 4 Beth
>>>
>>> lastnames
id lastname
0 1 Watney
1 2 Lewis
2 3 Martinez
3 4 Johanssen
>>>
>>> firstnames.merge(lastnames)
id firstname lastname
0 1 Mark Watney
1 2 Melissa Lewis
2 3 Rick Martinez
3 4 Beth Johanssen
>>>
>>> firstnames.merge(lastnames, on='id')
id firstname lastname
0 1 Mark Watney
1 2 Melissa Lewis
2 3 Rick Martinez
3 4 Beth Johanssen
>>>
>>> firstnames.merge(lastnames, left_on='id', right_on='id')
id firstname lastname
0 1 Mark Watney
1 2 Melissa Lewis
2 3 Rick Martinez
3 4 Beth Johanssen
>>>
>>> firstnames.merge(lastnames).set_index('id')
firstname lastname
id
1 Mark Watney
2 Melissa Lewis
3 Rick Martinez
4 Beth Johanssen
>>> df1999.merge(df2000)
Empty DataFrame
Columns: [Morning, Noon, Evening, Midnight]
Index: []
>>>
>>> df1999.merge(df2000, right_index=True, left_index=True, how='left', suffixes=('_1999', '_2000'))
Morning_1999 Noon_1999 Evening_1999 Midnight_1999 Morning_2000 Noon_2000 Evening_2000 Midnight_2000
1999-12-29 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-30 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-31 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274 NaN NaN NaN NaN
>>>
>>> df1999.merge(df2000, how='outer')
Morning Noon Evening Midnight
0 -2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165
1 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274
2 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
3 1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096
4 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893
5 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357
6.22.4. Join
Join columns of another DataFrame.
Join columns with other DataFrame either on index or on a key column.
Efficiently join multiple DataFrame objects by index at once by passing a list.
rfuffix- If two columns has the same name, add suffix to rightlfuffix- If two columns has the same name, add suffix to left
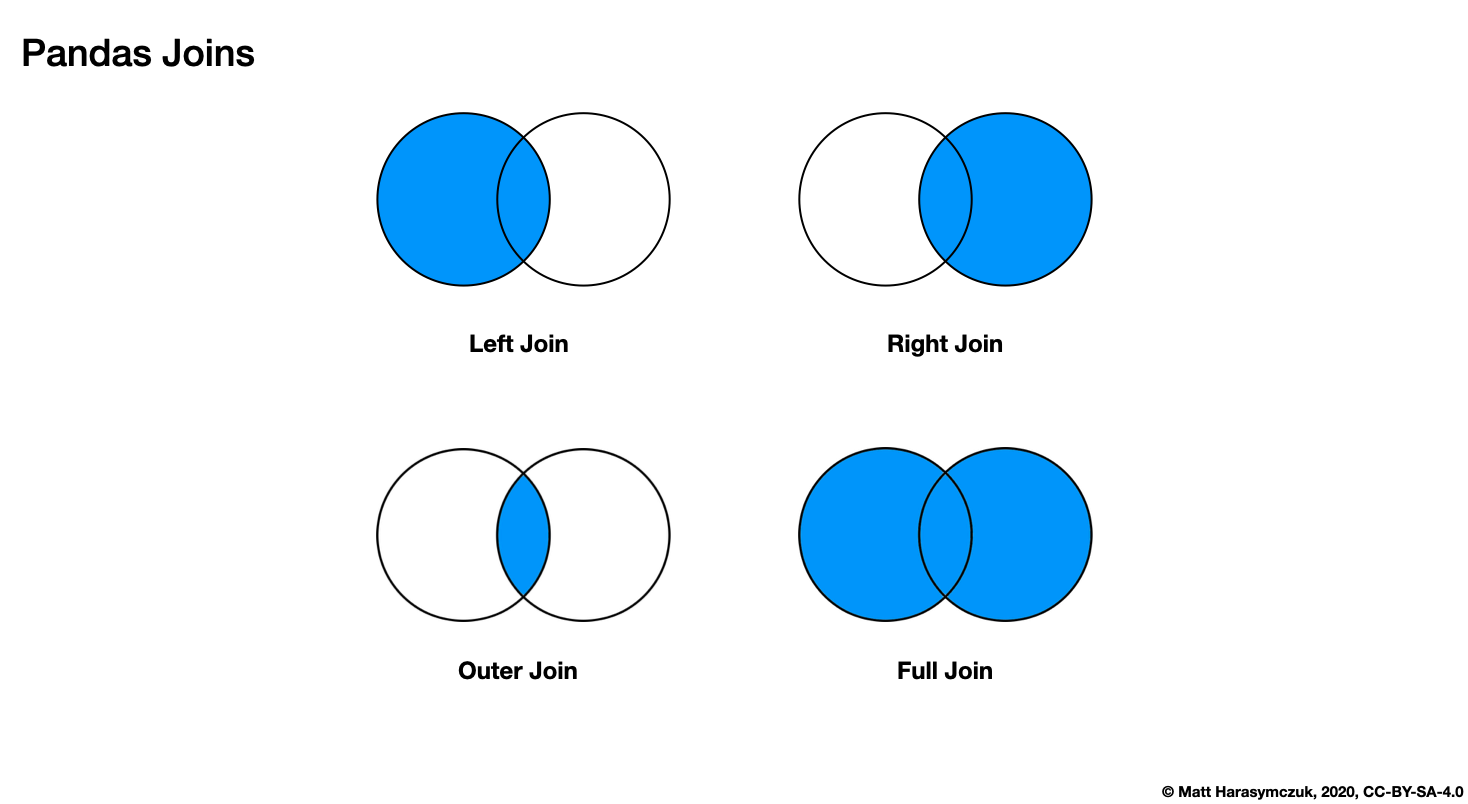
Figure 6.17. Pandas DataFrame Joins
>>> firstnames = pd.DataFrame({
... 'id': [1, 2, 3, 4],
... 'firstname': ['Mark', 'Melissa', 'Rick', 'Beth']})
>>>
>>> lastnames = pd.DataFrame({
... 'id': [1, 2, 3, 4],
... 'lastname': ['Watney', 'Lewis', 'Martinez', 'Johanssen']})
>>>
>>> firstnames
id firstname
0 1 Mark
1 2 Melissa
2 3 Rick
3 4 Beth
>>>
>>> lastnames
id lastname
0 1 Watney
1 2 Lewis
2 3 Martinez
3 4 Johanssen
Join DataFrames using their indexes:
>>> firstnames.join(lastnames, lsuffix='_fname', rsuffix='_lname')
id_fname firstname id_lname lastname
0 1 Mark 1 Watney
1 2 Melissa 2 Lewis
2 3 Rick 3 Martinez
3 4 Beth 4 Johanssen
>>>
>>> firstnames.set_index('id').join(lastnames.set_index('id'))
firstname lastname
id
1 Mark Watney
2 Melissa Lewis
3 Rick Martinez
4 Beth Johanssen
This method preserves the original DataFrame's index in the result:
>>> firstnames.join(lastnames.set_index('id'), on='id')
id firstname lastname
0 1 Mark Watney
1 2 Melissa Lewis
2 3 Rick Martinez
3 4 Beth Johanssen
>>>
>>> df1999.join(df2000, how='left', lsuffix='_1999', rsuffix='_2000')
Morning_1999 Noon_1999 Evening_1999 Midnight_1999 Morning_2000 Noon_2000 Evening_2000 Midnight_2000
1999-12-29 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-30 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-31 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274 NaN NaN NaN NaN
>>>
>>> df1999.join(df2000, how='outer', lsuffix='_1999', rsuffix='_2000')
Morning_1999 Noon_1999 Evening_1999 Midnight_1999 Morning_2000 Noon_2000 Evening_2000 Midnight_2000
1999-12-29 1.764052 0.400157 0.978738 2.240893 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-30 1.867558 -0.977278 0.950088 -0.151357 NaN NaN NaN NaN
1999-12-31 -0.103219 0.410599 0.144044 1.454274 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-01 NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.761038 0.121675 0.443863 0.333674
2000-01-02 NaN NaN NaN NaN 1.494079 -0.205158 0.313068 -0.854096
2000-01-03 NaN NaN NaN NaN -2.552990 0.653619 0.864436 -0.742165
6.22.5. References
6.22.6. Assignments
# FIXME: za trudne zadanie, przenieść je do case study
# FIXME: Write solution
# FIXME: Write tests
# FIXME: English translation
# %% About
# - Name: DataFrame Join
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 25
# - Minutes: 21
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# %% Polish
# 1. Na podstawie podanych URL:
# - https://www.worldspaceflight.com/bios/eva/eva.php
# - https://www.worldspaceflight.com/bios/eva/eva2.php
# - https://www.worldspaceflight.com/bios/eva/eva3.php
# - https://www.worldspaceflight.com/bios/eva/eva4.php
# 2. Scrape'uj stronę wykorzystując `pandas.read_html()`
# 3. Połącz dane wykorzystując `pd.concat`
# 4. Przygotuj plik `CSV` z danymi dotyczącymi spacerów kosmicznych
# 5. Zapisz dane do pliku
# 6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> pd.set_option('display.width', 500)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 10)
>>> pd.set_option('display.max_rows', 10)
# >>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
# 'Variable `result` is empty; assign your result to it.'
# >>> assert type(result) is pd.DataFrame, \
# 'Variable `result` must be a `pd.DataFrame` type'
>>> result # doctest: +NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE
Ellipsis
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import pandas as pd
# %% Types
result: pd.DataFrame
# %% Data
# %% Result
result = ...