2.5. Datasets
2.5.1. Skąd wziąć dane testowe?
2.5.2. Iris Flower Dataset
The Iris flower data set or Fisher's Iris data set is a multivariate data set introduced by the British statistician and biologist Ronald Fisher in his 1936 paper The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems as an example of linear discriminant analysis.

The data set consists of 50 samples from each of three species of Iris (Iris setosa, Iris virginica and Iris versicolor). Four features were measured from each sample: the length and the width of the sepals and petals, in centimetres. Based on the combination of these four features, Fisher developed a linear discriminant model to distinguish the species from each other.
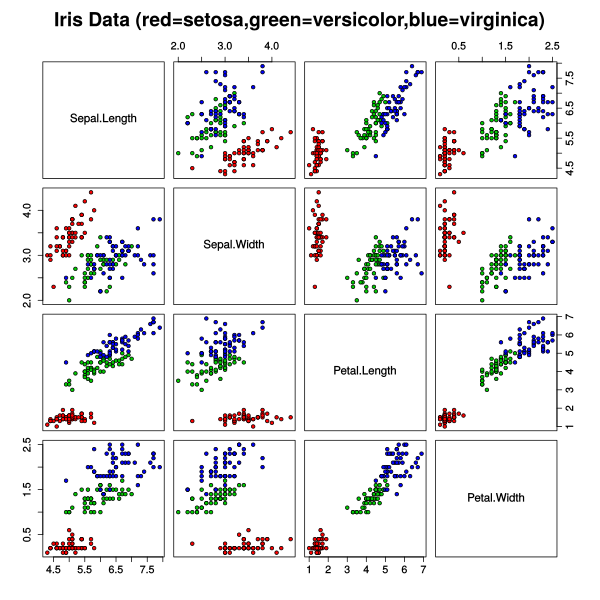
Figure 2.26. Scatterplot of the Iris data set
Based on Fisher's linear discriminant model, this data set became a typical test case for many statistical classification techniques in machine learning such as support vector machines.
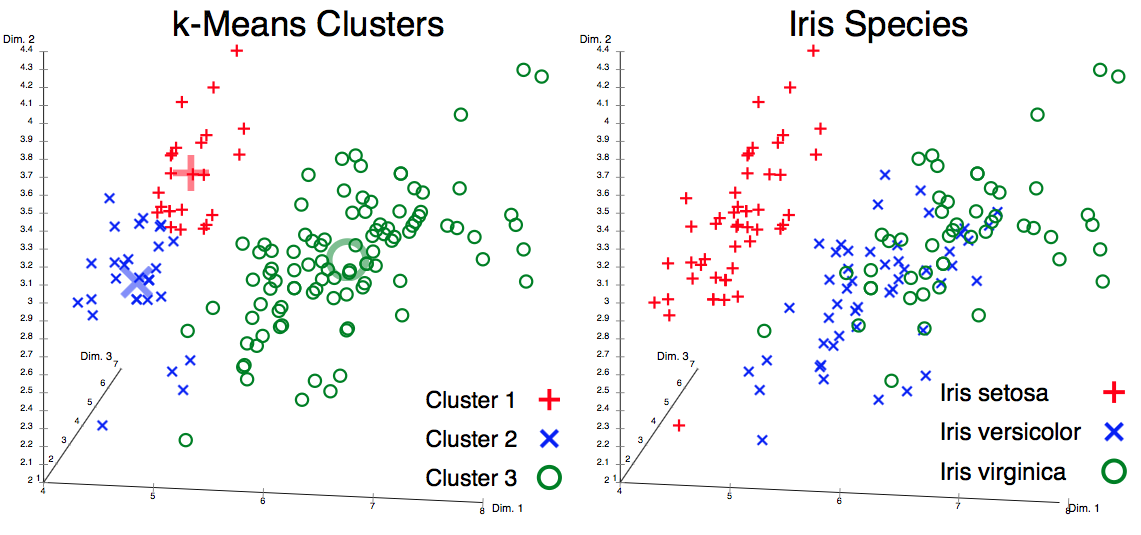
Figure 2.27. Unsatisfactory k-means clustering result (the data set does not cluster into the known classes) and actual species visualized using ELKI
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
iris = load_iris()
iris.feature_names
# ['sepal_length (cm)', 'sepal_width (cm)', 'petal_length (cm)', 'petal_width (cm)']
iris.target_names
# ['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
iris.data[0]
# [5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2]
print(iris.target[0]
# 0
2.5.3. Pima Indians Diabetes problem
Dataset:
This problem is comprised of 768 observations of medical details for Pima indians patents. The records describe instantaneous measurements taken from the patient such as their age, the number of times pregnant and blood workup. All patients are women aged 21 or older. All attributes are numeric, and their units vary from attribute to attribute.
Number of times pregnant
Plasma glucose concentration a 2 hours in an oral glucose tolerance test
Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg)
Triceps skin fold thickness (mm)
2-Hour serum insulin (mu U/ml)
Body mass index (weight in kg/(height in m)^2)
Diabetes pedigree function
Age (years)
Class variable (0 or 1)
Each record has a class value that indicates whether the patient suffered an onset of diabetes within 5 years of when the measurements were taken (1) or not (0).
This is a standard dataset that has been studied a lot in machine learning literature. A good prediction accuracy is 70%-76%.
2.5.4. Wisconsin Breast Cancer Database
- URL:
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/
- Struktura:
#
Attribute
Domain
Sample code number
id number
Clump Thickness
1 - 10
Uniformity of Cell Size
1 - 10
Uniformity of Cell Shape
1 - 10
Marginal Adhesion
1 - 10
Single Epithelial Cell Size
1 - 10
Bare Nuclei
1 - 10
Bland Chromatin
1 - 10
Normal Nucleoli
1 - 10
Mitoses
1 - 10
Class:
(2 for benign, 4 for malignant)
2.5.5. Quandl
Quandl is a platform for financial, economic, and alternative data that serves investment professionals. Quandl sources data from over 500 publishers. All Quandl data are accessible via an API. API access is possible through packages for multiple programming languages including R, Python, Matlab, Maple (software) and Stata.
An Excel add-in allows access to data, including stock price information.
Package for quandl API access https://www.quandl.com/topics
2.5.6. SPAM Dataset
https://inclass.kaggle.com/c/adcg-ss14-challenge-02-spam-mails-detection/data
http://www.aclweb.org/aclwiki/index.php?title=Spam_filtering_datasets
http://opendata.stackexchange.com/questions/1776/publicly-available-spam-dataset-of-social-networks
https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/doing-data-science/9781449363871/ch04.html
https://www2.stat.duke.edu/courses/Spring13/sta102.001/Lab/Lab13.pdf
http://www.nargund.com/gsu/mgs8040/Sample%20Project%201%20-%20Restrepo%20Gies%20Labbe.pdf
2.5.7. SCI-Kit Datasets
The sklearn.datasets package embeds some small toy datasets. To evaluate the impact of the scale of the dataset (n_samples and n_features) while controlling the statistical properties of the data (typically the correlation and informativeness of the features), it is also possible to generate synthetic data.
This package also features helpers to fetch larger datasets commonly used by the machine learning community to benchmark algorithm on data that comes from the 'real world'.
'clear_data_home',
'dump_svmlight_file',
'fetch_20newsgroups',
'fetch_20newsgroups_vectorized',
'fetch_lfw_pairs',
'fetch_lfw_people',
'fetch_mldata',
'fetch_olivetti_faces',
'fetch_species_distributions',
'fetch_california_housing',
'fetch_covtype',
'fetch_rcv1',
'fetch_kddcup99',
'get_data_home',
'load_boston',
'load_diabetes',
'load_digits',
'load_files',
'load_iris',
'load_breast_cancer',
'load_linnerud',
'load_mlcomp',
'load_sample_image',
'load_sample_images',
'load_svmlight_file',
'load_svmlight_files',
'load_wine',
'make_biclusters',
'make_blobs',
'make_circles',
'make_classification',
'make_checkerboard',
'make_friedman1',
'make_friedman2',
'make_friedman3',
'make_gaussian_quantiles',
'make_hastie_10_2',
'make_low_rank_matrix',
'make_moons',
'make_multilabel_classification',
'make_regression',
'make_s_curve',
'make_sparse_coded_signal',
'make_sparse_spd_matrix',
'make_sparse_uncorrelated',
'make_spd_matrix',
'make_swiss_roll',
'mldata_filename'
2.5.8. Eurostat datasets
2.5.9. ML Data
mldata.org is a public repository for machine learning data, supported by the PASCAL network.
The sklearn.datasets package is able to directly download data sets from the repository using the function sklearn.datasets.fetch_mldata.
For example, to download the MNIST digit recognition database:
>>> from sklearn.datasets import fetch_mldata
>>> mnist = fetch_mldata('MNIST original', data_home=custom_data_home)
2.5.10. PASCAL
PASCAL is a Network of Excellence funded by the European Union. It has established a distributed institute that brings together researchers and students across Europe, and is now reaching out to countries all over the world.
PASCAL is developing the expertise and scientific results that will help create new technologies such as intelligent interfaces and adaptive cognitive systems. To achieve this, it supports and encourages collaboration between experts in Machine Learning, Statistics and Optimization. It also promotes the use of machine learning in many relevant application domains such as:
Machine Vision
Speech
Haptics
Brain-Computer Interface
User-modeling for computer human interaction
Multimodal integration
Natural Language Processing
Information Retrieval
Textual Information Access
2.5.11. Kaggle
dane raka płuc
konkursy ML