6.24. SQL Join
Combine records from two or more tables in a database
Combining fields from two tables by using values common to each
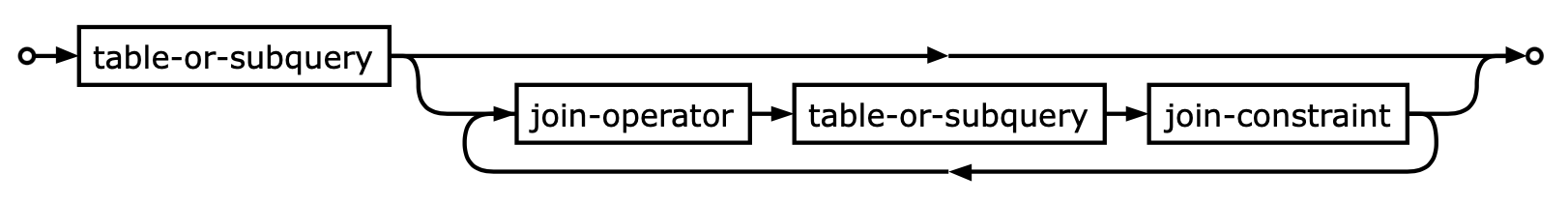
The SQL Joins clause is used to combine records from two or more tables in a database. A JOIN is a means for combining fields from two tables by using values common to each. [1]
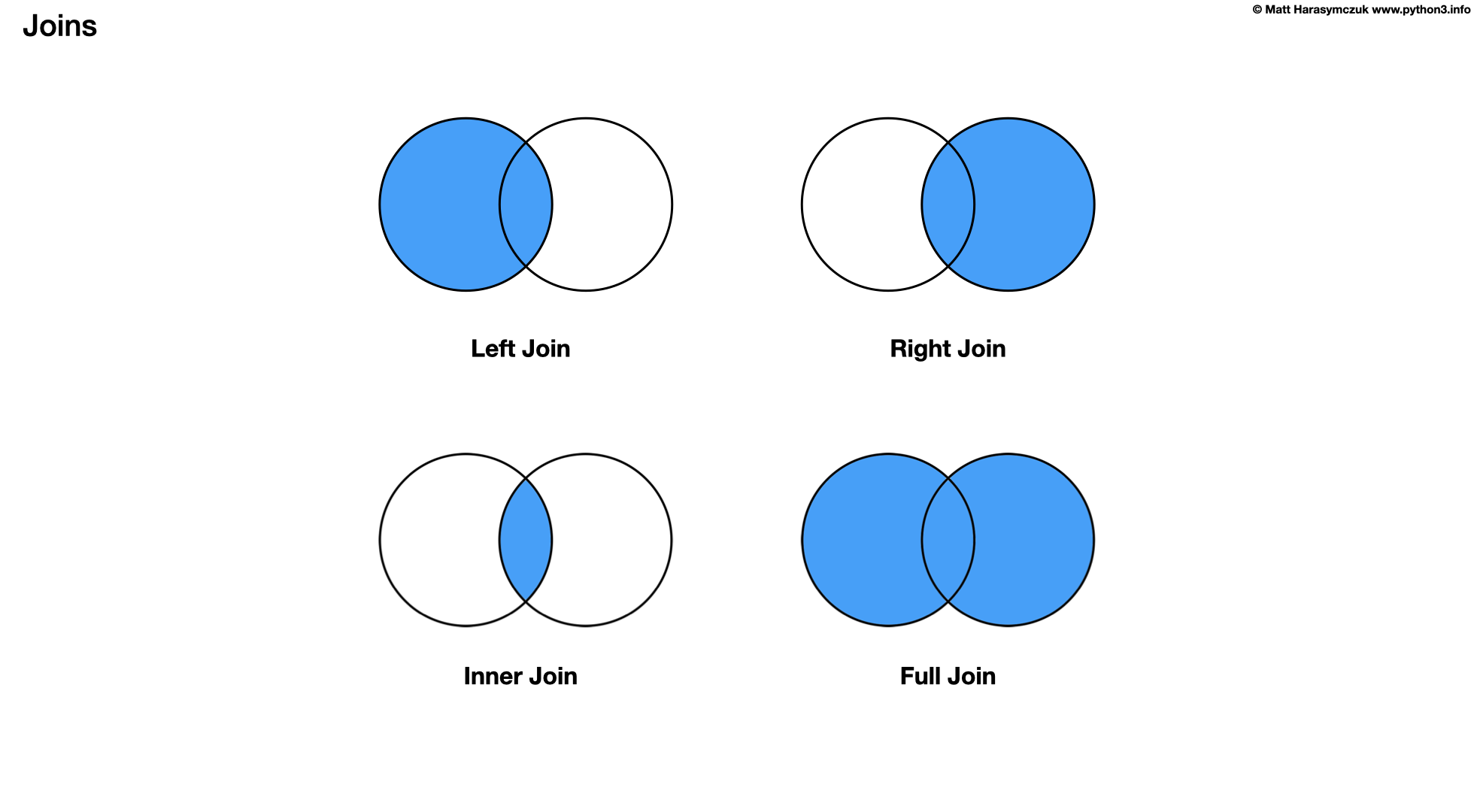
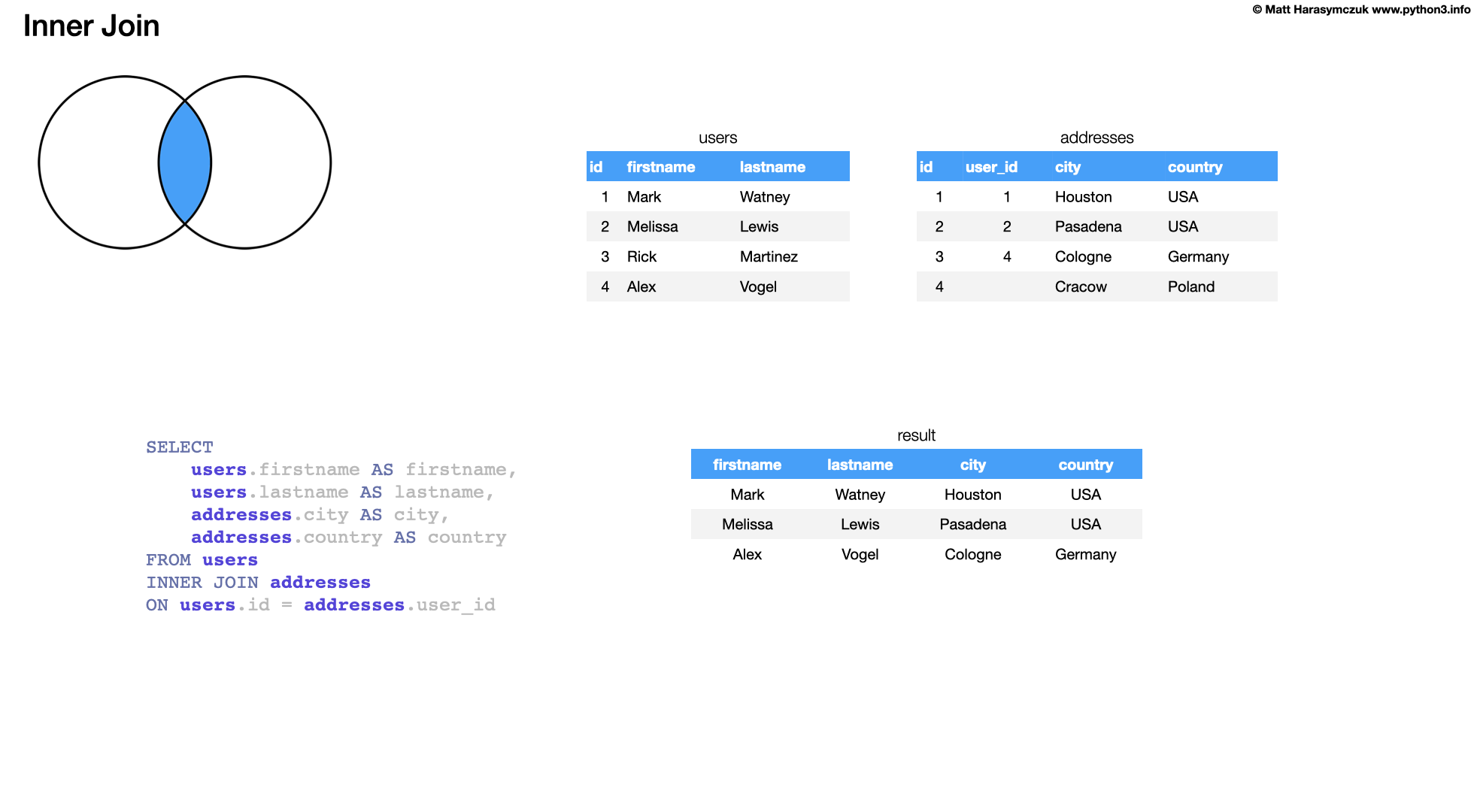
6.24.1. INNER JOIN
Returns rows when there is a match in both tables
The most important and frequently used of the joins
The INNER JOIN creates a new result table by combining column values of two tables (table1 and table2) based upon the join-predicate. The query compares each row of table1 with each row of table2 to find all pairs of rows which satisfy the join-predicate. When the join-predicate is satisfied, column values for each matched pair of rows of A and B are combined into a result row. [7]
SELECT
users.firstname AS firstname,
users.lastname AS lastname,
addresses.city AS city,
addresses.country AS country
FROM users
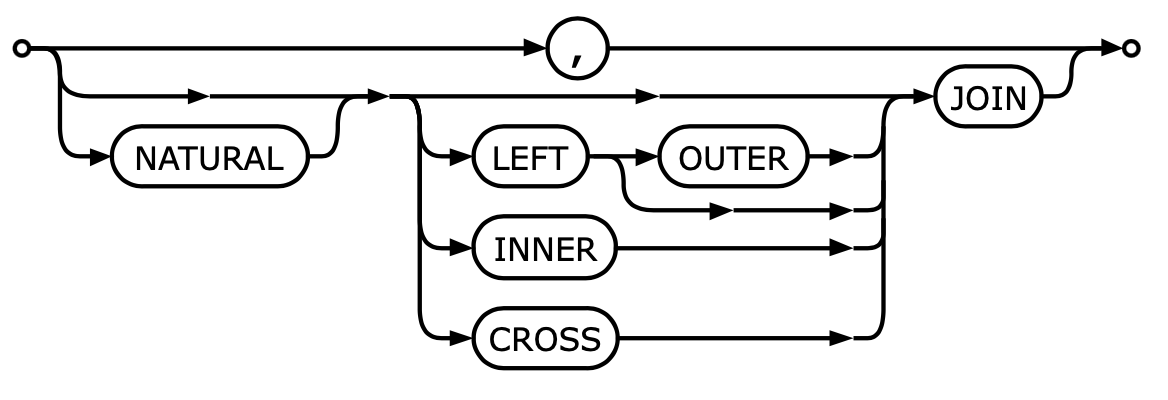
INNER JOIN addresses
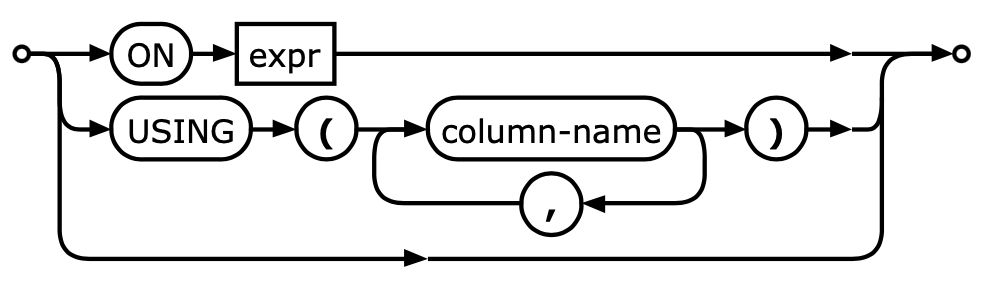
ON users.id = addresses.user_id
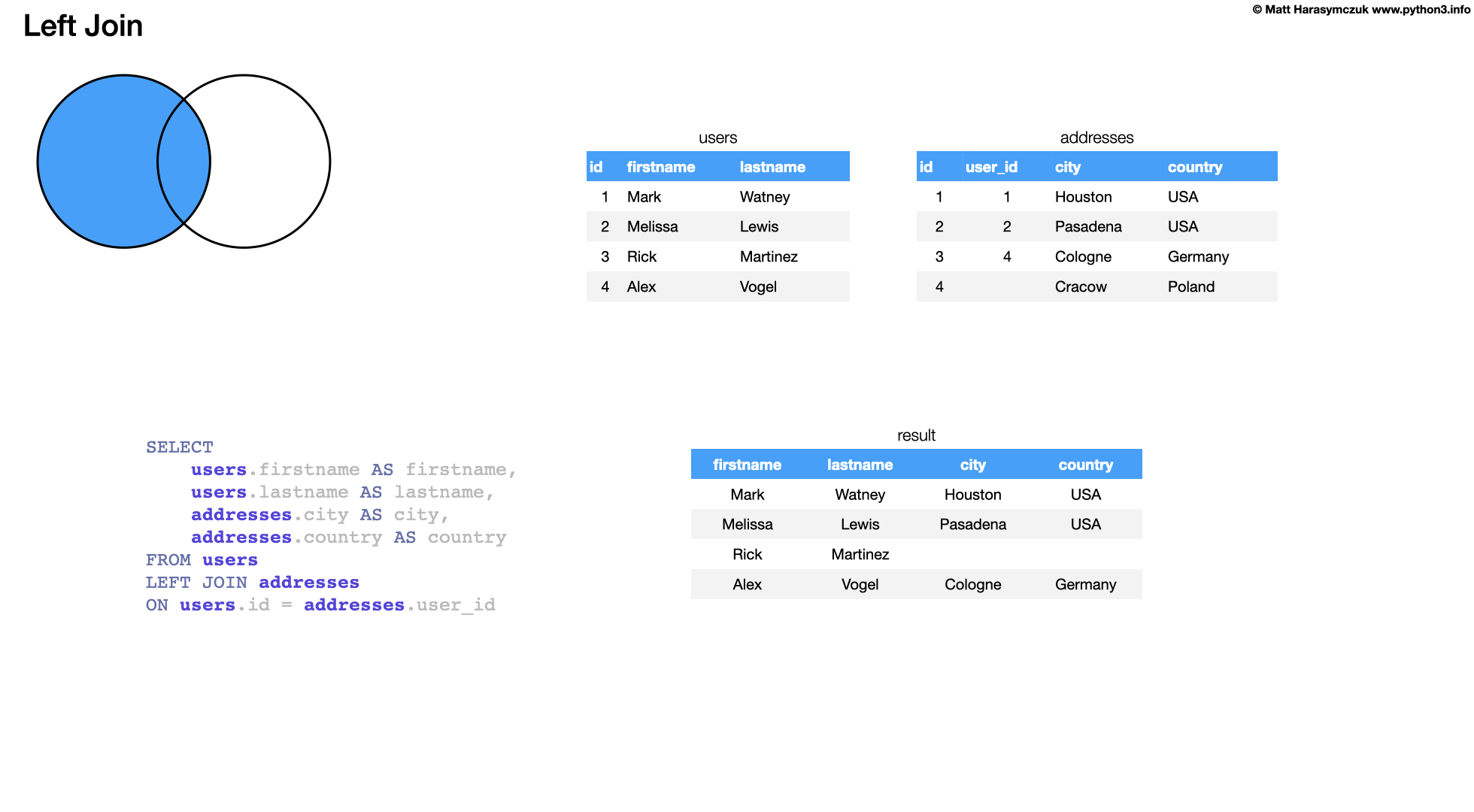
6.24.2. LEFT JOIN
Returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table
This means that if the ON clause matches 0 (zero) records in the right table; the join will still return a row in the result, but with NULL in each column from the right table. [2]
This means that a left join returns all the values from the left table, plus matched values from the right table or NULL in case of no matching join predicate. [2]
SELECT
users.firstname AS firstname,
users.lastname AS lastname,
addresses.city AS city,
addresses.country AS country
FROM users
LEFT JOIN addresses
ON users.id = addresses.user_id
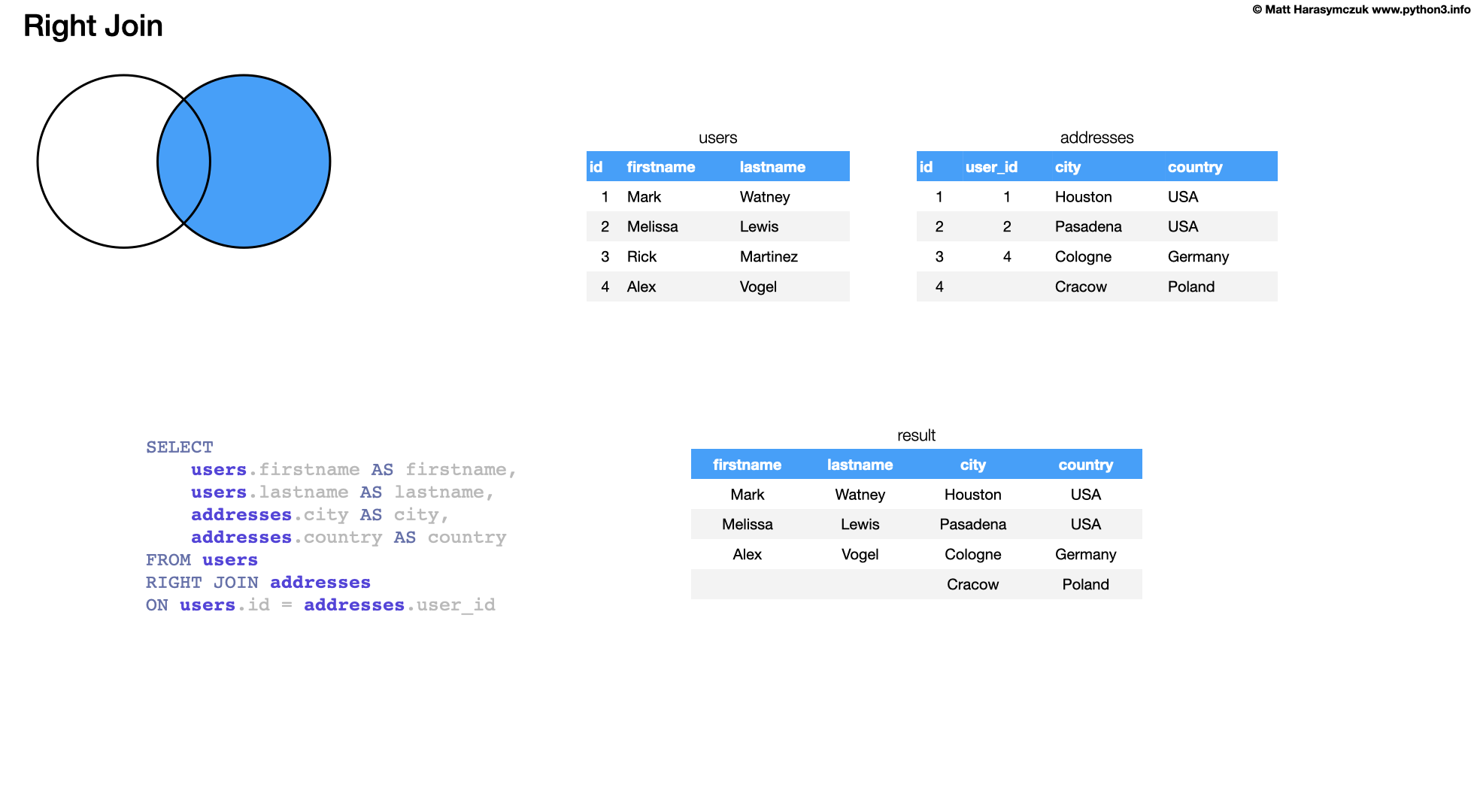
6.24.3. RIGHT JOIN
Returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table
This means that if the ON clause matches 0 (zero) records in the left table; the join will still return a row in the result, but with NULL in each column from the left table. [3]
This means that a right join returns all the values from the right table, plus matched values from the left table or NULL in case of no matching join predicate. [3]
SELECT
users.firstname AS firstname,
users.lastname AS lastname,
addresses.city AS city,
addresses.country AS country
FROM users
RIGHT JOIN addresses
ON users.id = addresses.user_id
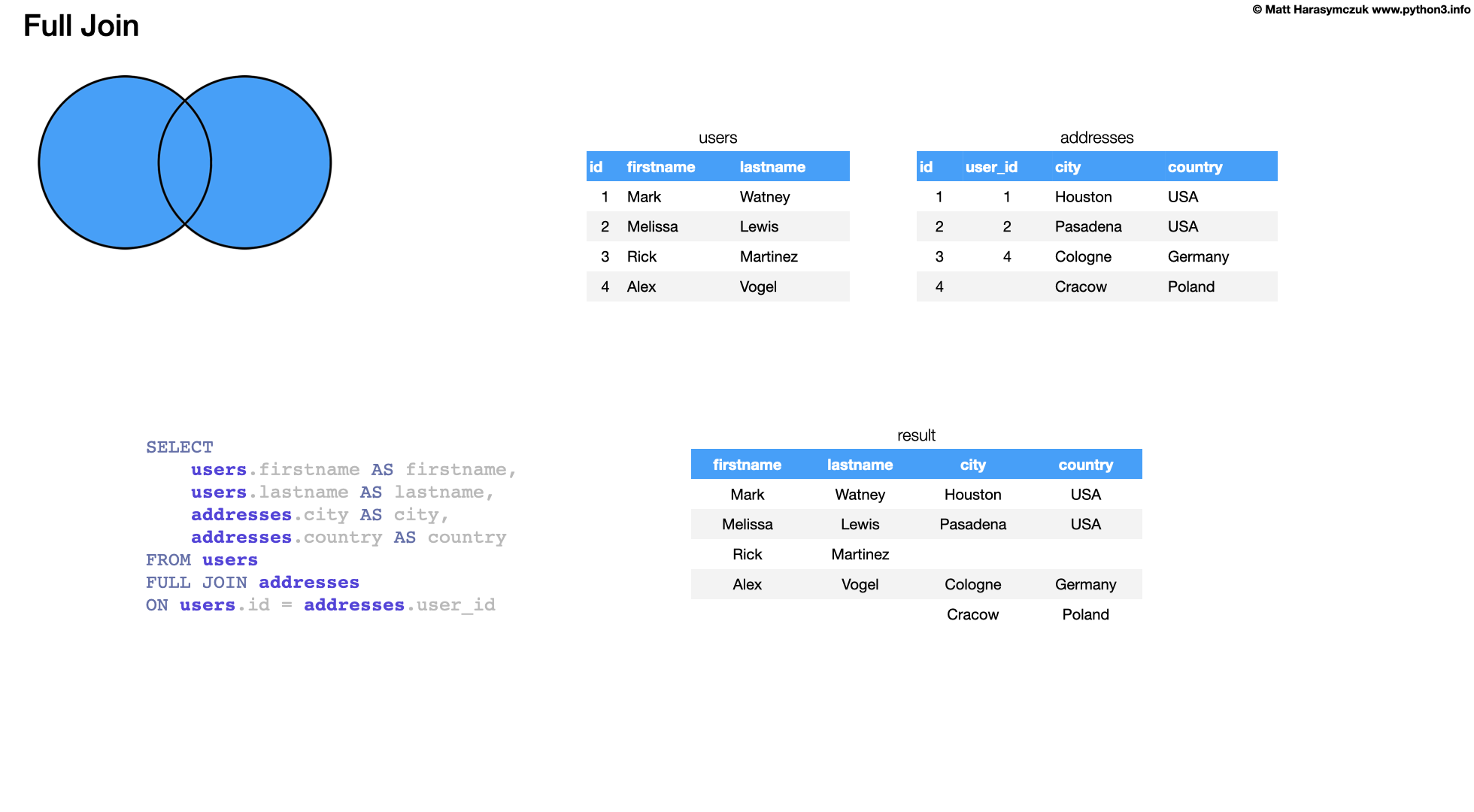
6.24.4. FULL JOIN
Combines the results of both left and right outer joins
The joined table will contain all records from both the tables and fill in NULLs for missing matches on either side. [4]
SELECT
users.firstname AS firstname,
users.lastname AS lastname,
addresses.city AS city,
addresses.country AS country
FROM users
FULL JOIN addresses
ON users.id = addresses.user_id
6.24.5. SELF JOIN
Is used to join a table to itself as if the table were two tables
Temporarily renaming at least one table in the SQL statement
SELECT a.city, a.country
FROM addresses AS a, addresses AS b
WHERE a.id != b.id
AND a.country = b.country
6.24.6. CARTESIAN JOIN
Also known as
CROSS JOINReturns the Cartesian product of the sets of records from the two or more joined tables.
Thus, it equates to an inner join where the join-condition always evaluates to either True or where the join-condition is absent from the statement. [6]
SELECT users.firstname,
users.lastname,
addresses.city,
addresses.country
FROM users, addresses
6.24.7. References
6.24.8. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Database Join Left
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Write SQL query to select data:
# - table: `users`, `addresses`
# - column: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - what: merge data from both tables
# - use: LEFT JOIN
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Napisz zapytanie SQL aby wybrać dane:
# - tabela: `users`, `addresses`
# - kolumny: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - co: scal dane z obu tabel
# - użyj: LEFT JOIN
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> import sqlite3
>>> database = Path(__file__).parent.parent / 'shop.db'
>>> with sqlite3.connect(database) as db:
... db.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
... data = map(dict, db.execute(result).fetchall())
>>> pprint(list(data), sort_dicts=False, width=250)
[{'firstname': 'Chris', 'lastname': 'Beck', 'street': '4800 Oak Grove Dr', 'city': 'Pasadena', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Beth', 'lastname': 'Johanssen', 'street': '2825 E Ave P', 'city': 'Palmdale', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Melissa', 'lastname': 'Lewis', 'street': 'Kamienica Pod św. Janem Kapistranem', 'city': 'Cracow', 'country': 'Poland'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Baikonur Cosmodrome', 'city': 'Baikonur', 'country': 'Kazakhstan'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Chkalovskoye Shosse', 'city': 'Zvyozdny Gorodok', 'country': 'Russia'},
{'firstname': 'Alex', 'lastname': 'Vogel', 'street': 'Linder Hoehe', 'city': 'Cologne', 'country': 'Germany'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': '2101 E NASA Pkwy', 'city': 'Houston', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': 'Kennedy Space Center', 'city': 'Merritt Island', 'country': 'USA'}]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: str
# %% Data
# %% Result
result = """
-- replace this comment
-- with your sql query
"""
# %% About
# - Name: Database Join Right
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Write SQL query to select data:
# - table: `users`, `addresses`
# - column: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - what: merge data from both tables
# - use: RIGHT JOIN
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Napisz zapytanie SQL aby wybrać dane:
# - tabela: `users`, `addresses`
# - kolumny: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - co: scal dane z obu tabel
# - użyj: RIGHT JOIN
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> import sqlite3
>>> database = Path(__file__).parent.parent / 'shop.db'
>>> with sqlite3.connect(database) as db:
... db.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
... data = map(dict, db.execute(result).fetchall())
>>> pprint(list(data), sort_dicts=False, width=250)
[{'firstname': 'Chris', 'lastname': 'Beck', 'street': '4800 Oak Grove Dr', 'city': 'Pasadena', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Beth', 'lastname': 'Johanssen', 'street': '2825 E Ave P', 'city': 'Palmdale', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Melissa', 'lastname': 'Lewis', 'street': 'Kamienica Pod św. Janem Kapistranem', 'city': 'Cracow', 'country': 'Poland'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Chkalovskoye Shosse', 'city': 'Zvyozdny Gorodok', 'country': 'Russia'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Baikonur Cosmodrome', 'city': 'Baikonur', 'country': 'Kazakhstan'},
{'firstname': 'Alex', 'lastname': 'Vogel', 'street': 'Linder Hoehe', 'city': 'Cologne', 'country': 'Germany'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': '2101 E NASA Pkwy', 'city': 'Houston', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': 'Kennedy Space Center', 'city': 'Merritt Island', 'country': 'USA'}]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: str
# %% Data
# %% Result
result = """
-- replace this comment
-- with your sql query
"""
# %% About
# - Name: Database Join Inner
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Write SQL query to select data:
# - table: `users`, `addresses`
# - column: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - what: merge data from both tables
# - use: INNER JOIN
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Napisz zapytanie SQL aby wybrać dane:
# - tabela: `users`, `addresses`
# - kolumny: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - co: scal dane z obu tabel
# - użyj: INNER JOIN
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> import sqlite3
>>> database = Path(__file__).parent.parent / 'shop.db'
>>> with sqlite3.connect(database) as db:
... db.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
... data = map(dict, db.execute(result).fetchall())
>>> pprint(list(data), sort_dicts=False, width=250)
[{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': '2101 E NASA Pkwy', 'city': 'Houston', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': 'Kennedy Space Center', 'city': 'Merritt Island', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Melissa', 'lastname': 'Lewis', 'street': 'Kamienica Pod św. Janem Kapistranem', 'city': 'Cracow', 'country': 'Poland'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Chkalovskoye Shosse', 'city': 'Zvyozdny Gorodok', 'country': 'Russia'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Baikonur Cosmodrome', 'city': 'Baikonur', 'country': 'Kazakhstan'},
{'firstname': 'Alex', 'lastname': 'Vogel', 'street': 'Linder Hoehe', 'city': 'Cologne', 'country': 'Germany'},
{'firstname': 'Beth', 'lastname': 'Johanssen', 'street': '2825 E Ave P', 'city': 'Palmdale', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Chris', 'lastname': 'Beck', 'street': '4800 Oak Grove Dr', 'city': 'Pasadena', 'country': 'USA'}]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: str
# %% Data
# %% Result
result = """
-- replace this comment
-- with your sql query
"""
# %% About
# - Name: Database Join Full
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Write SQL query to select data:
# - table: `users`, `addresses`
# - column: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - what: merge data from both tables
# - use: FULL JOIN
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Napisz zapytanie SQL aby wybrać dane:
# - tabela: `users`, `addresses`
# - kolumny: `firstname`, `lastname`, `street`, `city`, `country
# - co: scal dane z obu tabel
# - użyj: FULL JOIN
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> import sqlite3
>>> database = Path(__file__).parent.parent / 'shop.db'
>>> with sqlite3.connect(database) as db:
... db.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
... data = map(dict, db.execute(result).fetchall())
>>> pprint(list(data), sort_dicts=False, width=250)
[{'firstname': 'Chris', 'lastname': 'Beck', 'street': '4800 Oak Grove Dr', 'city': 'Pasadena', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Beth', 'lastname': 'Johanssen', 'street': '2825 E Ave P', 'city': 'Palmdale', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Melissa', 'lastname': 'Lewis', 'street': 'Kamienica Pod św. Janem Kapistranem', 'city': 'Cracow', 'country': 'Poland'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Chkalovskoye Shosse', 'city': 'Zvyozdny Gorodok', 'country': 'Russia'},
{'firstname': 'Rick', 'lastname': 'Martinez', 'street': 'Baikonur Cosmodrome', 'city': 'Baikonur', 'country': 'Kazakhstan'},
{'firstname': 'Alex', 'lastname': 'Vogel', 'street': 'Linder Hoehe', 'city': 'Cologne', 'country': 'Germany'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': '2101 E NASA Pkwy', 'city': 'Houston', 'country': 'USA'},
{'firstname': 'Mark', 'lastname': 'Watney', 'street': 'Kennedy Space Center', 'city': 'Merritt Island', 'country': 'USA'}]
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
result: str
# %% Data
# %% Result
result = """
-- replace this comment
-- with your sql query
"""