10.2. Math Linear Algebra
Linear Algebra
Logarithms
np.sign()np.abs()np.sqrt()np.power()np.log()np.log10()np.exp()
>>> import numpy as np
10.2.1. Vector and matrix mathematics
10.2.2. Determinant of a square matrix
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>>
>>> np.linalg.det(a)
np.float64(-9.51619735392994e-16)
>>> a = np.array([[4, 2, 0],
... [9, 3, 7],
... [1, 2, 1]])
>>>
>>> np.linalg.det(a)
np.float64(-48.00000000000003)
10.2.3. Inner product
Compute inner product of two vectors
np.inner()Ordinary inner product of vectors for 1-D arrays (without complex conjugation)
In higher dimensions a sum product over the last axes
Ordinary inner product for vectors:
>>> a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
>>> b = np.array([0, 1, 0])
>>>
>>> np.inner(a, b)
np.int64(2)
Multidimensional example:
>>> a = np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
>>> b = np.arange(4)
>>>
>>> np.inner(a, b)
array([[ 14, 38, 62],
[ 86, 110, 134]])
10.2.4. Outer product
np.outer()
Compute the outer product of two vectors
>>> a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
>>> b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
>>>
>>> np.outer(a, b)
array([[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 8, 10, 12],
[12, 15, 18]])
10.2.5. Cross product
np.cross()
The cross product of a and b in R^3 is a vector perpendicular to both a and b
Vector cross-product:
>>> a = [1, 2, 3]
>>> b = [4, 5, 6]
>>>
>>> np.cross(a, b)
array([-3, 6, -3])
One vector with dimension 2:
>>> a = [1, 2]
>>> b = [4, 5, 6]
>>>
>>> np.cross(a, b)
array([12, -6, -3])
10.2.6. Eigenvalues and vectors of a square matrix
Each of a set of values of a parameter for which a differential equation has a nonzero solution (an eigenfunction) under given conditions. Any number such that a given matrix minus that number times the identity matrix has a zero determinant.
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>>
>>> vals, vecs = np.linalg.eig(a)
>>>
>>> vals
array([ 1.61168440e+01, -1.11684397e+00, -9.75918483e-16])
>>>
>>> vecs
array([[-0.23197069, -0.78583024, 0.40824829],
[-0.52532209, -0.08675134, -0.81649658],
[-0.8186735 , 0.61232756, 0.40824829]])
10.2.7. Inverse of a square matrix
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>>
>>> np.linalg.inv(a)
array([[-4.50359963e+15, 9.00719925e+15, -4.50359963e+15],
[ 9.00719925e+15, -1.80143985e+16, 9.00719925e+15],
[-4.50359963e+15, 9.00719925e+15, -4.50359963e+15]])
>>> a = np.array([[4, 2, 0],
... [9, 3, 7],
... [1, 2, 1]])
>>>
>>> b = np.linalg.inv(a)
>>> b
array([[ 0.22916667, 0.04166667, -0.29166667],
[ 0.04166667, -0.08333333, 0.58333333],
[-0.3125 , 0.125 , 0.125 ]])
>>>
>>> np.dot(a, b)
array([[1.00000000e+00, 5.55111512e-17, 0.00000000e+00],
[0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00, 2.22044605e-16],
[2.77555756e-17, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]])
10.2.8. Singular value decomposition of a matrix
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>>
>>> U, s, Vh = np.linalg.svd(a)
>>>
>>> U
array([[-0.21483724, 0.88723069, 0.40824829],
[-0.52058739, 0.24964395, -0.81649658],
[-0.82633754, -0.38794278, 0.40824829]])
>>>
>>> s
array([1.68481034e+01, 1.06836951e+00, 3.33475287e-16])
>>>
>>> Vh
array([[-0.47967118, -0.57236779, -0.66506441],
[-0.77669099, -0.07568647, 0.62531805],
[-0.40824829, 0.81649658, -0.40824829]])
10.2.9. Linear Algebra
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
norm |
Vector or matrix norm |
inv |
Inverse of a square matrix |
solve |
Solve a linear system of equations |
det |
Determinant of a square matrix |
slogdet |
Logarithm of the determinant of a square matrix |
lstsq |
Solve linear least-squares problem |
pinv |
Pseudo-inverse (Moore-Penrose) calculated using a singular value decomposition |
matrix_power |
Integer power of a square matrix |
matrix_rank |
Calculate matrix rank using an SVD-based method |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
eig |
Eigenvalues and vectors of a square matrix |
eigh |
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a Hermitian matrix |
eigvals |
Eigenvalues of a square matrix |
eigvalsh |
Eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix |
qr |
QR decomposition of a matrix |
svd |
Singular value decomposition of a matrix |
cholesky |
Cholesky decomposition of a matrix |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
tensorsolve |
Solve a linear tensor equation |
tensorinv |
Calculate an inverse of a tensor |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
LinAlgError |
Indicates a failed linear algebra operation |
10.2.10. Assignments
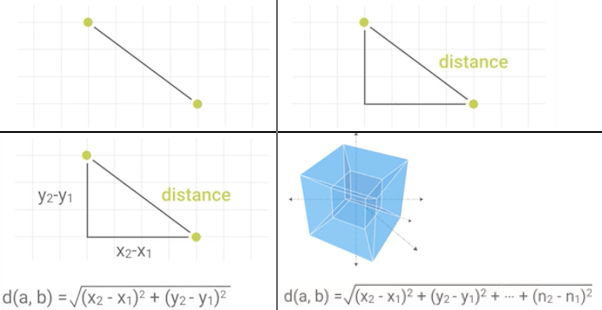
Figure 10.5. Calculate Euclidean distance in Cartesian coordinate system
\(distance(a, b) = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\)
\(distance(a, b) = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2 + ... + (n_2 - n_1)^2}\)
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Algebra Euclidean 2D
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 6
# - Minutes: 5
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Given are two points `a: tuple[int, int]` and `b: tuple[int, int]`
# 2. Coordinates are in cartesian system
# 3. Points `a` and `b` are in two dimensional space
# 4. Calculate distance between points using Euclidean algorithm
# 5. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Dane są dwa punkty `a: tuple[int, int]` i `b: tuple[int, int]`
# 2. Koordynaty są w systemie kartezjańskim
# 3. Punkty `a` i `b` są w dwuwymiarowej przestrzeni
# 4. Oblicz odległość między nimi wykorzystując algorytm Euklidesa
# 5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert result((0,0), (0,0)) is not Ellipsis, \
'Function `euclidean_distance` is invalid; write your solution to it'
>>> a = (1, 0)
>>> b = (0, 1)
>>> result(a, b)
1.4142135623730951
>>> result((0,0), (1,0))
1.0
>>> result((0,0), (1,1))
1.4142135623730951
>>> result((0,1), (1,1))
1.0
>>> result((0,10), (1,1))
9.055385138137417
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
from math import sqrt
# %% Types
from typing import Callable
type point = tuple[int,int]
result: Callable[[point, point], point]
# %% Data
# %% Result
def result(a, b):
...
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Algebra Euclidean Ndim
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 7
# - Minutes: 8
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Given are two points `a: Sequence[int]` and `b: Sequence[int]`
# 2. Coordinates are in cartesian system
# 3. Points `a` and `b` are in n-dimensional space
# 4. Points `a` and `b` must be in the same space
# 5. Calculate distance between points using Euclidean algorithm
# 6. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Dane są dwa punkty `a: Sequence[int]` i `b: Sequence[int]`
# 2. Koordynaty są w systemie kartezjańskim
# 3. Punkty `a` i `b` są w n-wymiarowej przestrzeni
# 4. Punkty `b` i `b` muszą być w tej samej przestrzeni
# 5. Oblicz odległość między nimi wykorzystując algorytm Euklidesa
# 6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Hints
# - `for n1,n2 in zip(a,b)`
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert result((0,0), (0,0)) is not Ellipsis, \
'Assign result to function: `euclidean_distance`'
>>> result((0,0,1,0,1), (1,1))
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: Points must be in the same dimensions
>>> result((0,0,0), (0,0,0))
0.0
>>> result((0,0,0), (1,1,1))
1.7320508075688772
>>> result((0,1,0,1), (1,1,0,0))
1.4142135623730951
>>> result((0,0,1,0,1), (1,1,0,0,1))
1.7320508075688772
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
from math import sqrt
# %% Types
from typing import Callable
type point = tuple[int,int]
result: Callable[[point, point], point]
# %% Data
# %% Result
def result(a, b):
...