11.1. Polynomial About
11.1.1. SetUp
>>> import numpy as np
11.1.2. Defining
Polynomial of degree three:
Ax^3 + Bx^2 + Cx^1 + D = 0
1x^3 + 2x^2 + 3x^1 + 4 = 0
>>> np.poly1d([1, 2, 3, 4])
poly1d([1, 2, 3, 4])
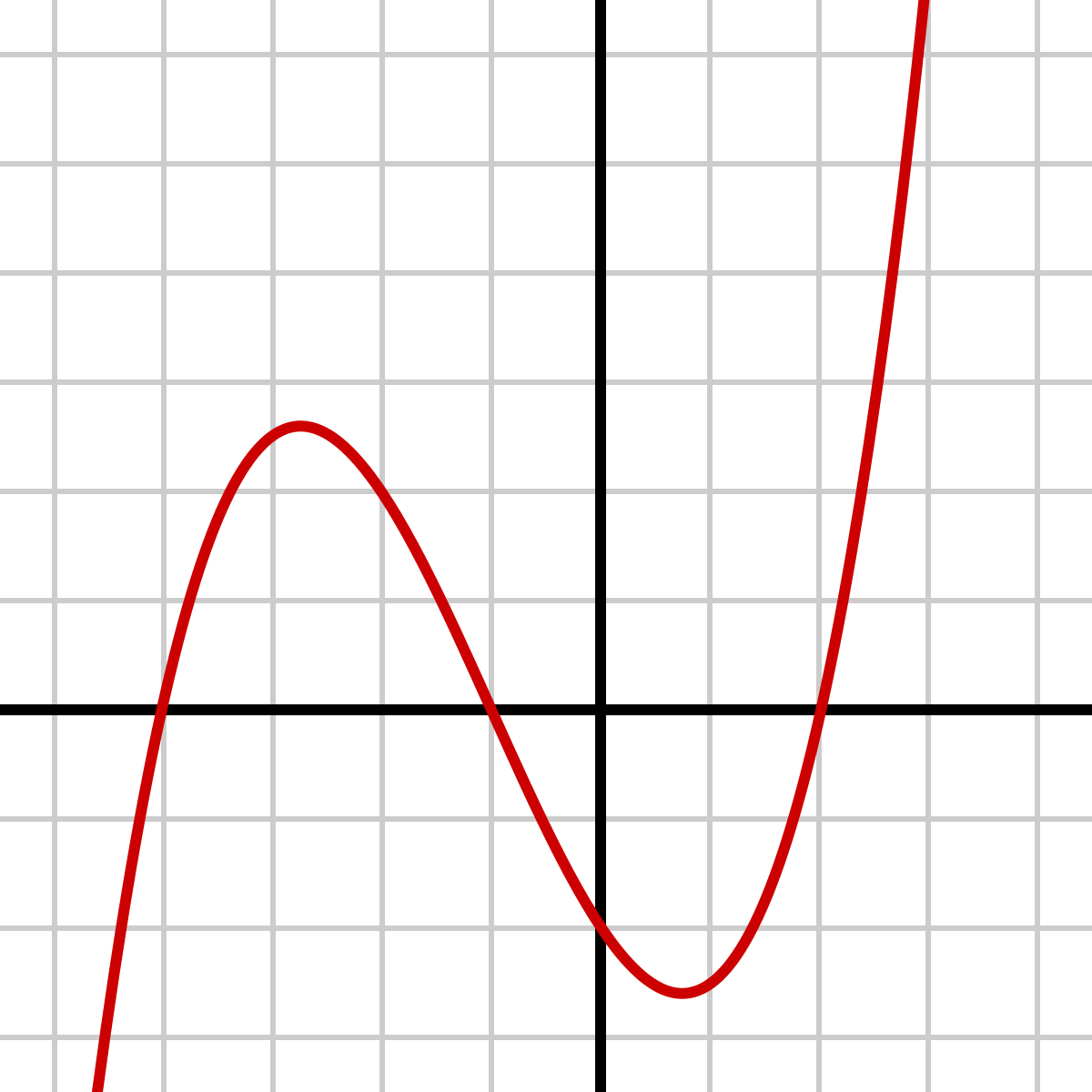
Figure 11.1. Polynomial of degree three Ax^3 + Bx^2 + Cx^1 + D = 0 [1]
Polynomial of degree six:
Ax^6 + Bx^5 + Cx^4 + Dx^3 + Ex^2 + Fx + G = 0
1x^6 + 2x^5 + 3x^4 + 4x^3 + 5x^2 + 6x + 7 = 0
>>> np.poly1d([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
poly1d([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
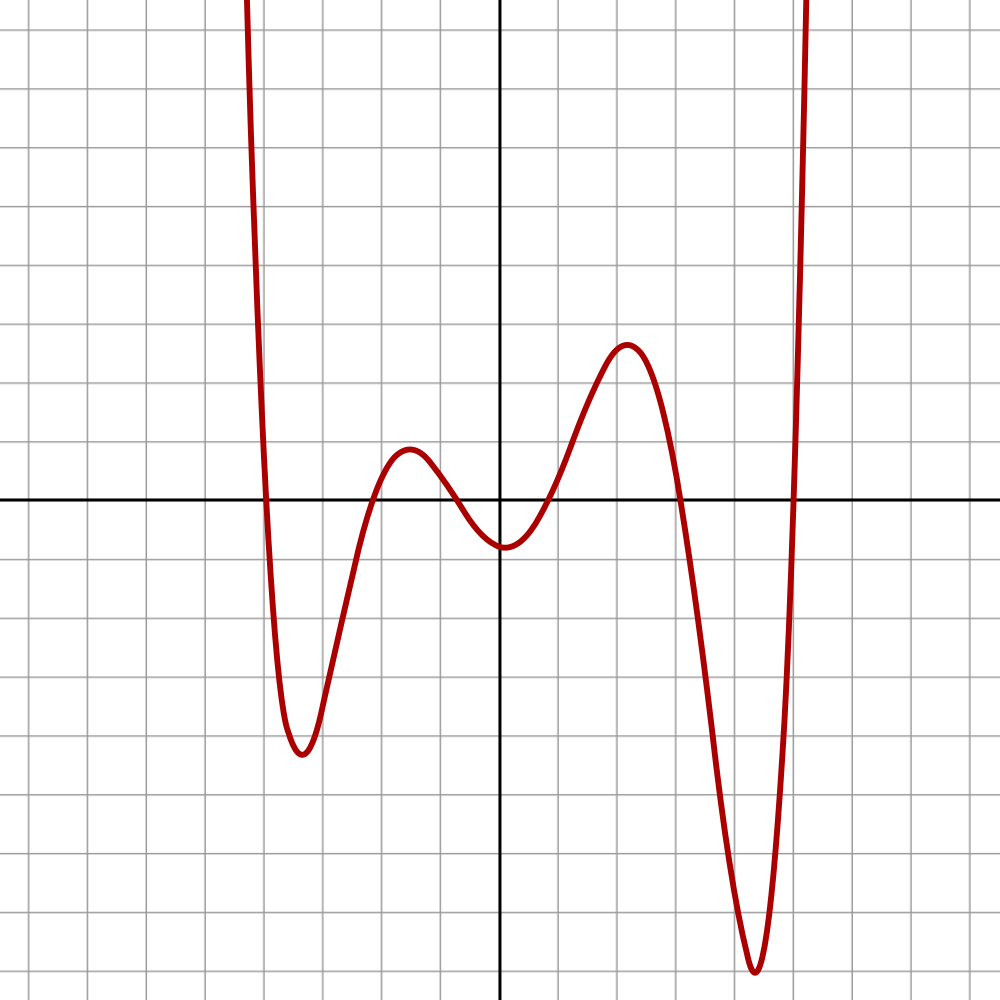
Figure 11.2. Polynomial of degree six Ax^6 + Bx^5 + Cx^4 + Dx^3 + Ex^2 + Fx + G = 0 [1]
11.1.3. Find Coefficients
Find the coefficients of a polynomial with the given sequence of roots
Specifying the roots of a polynomial still leaves one degree of freedom, typically represented by an undetermined leading coefficient.
>>> np.poly([0, 0, 0])
array([1., 0., 0., 0.])
>>> np.poly([1, 2])
array([ 1., -3., 2.])
>>> np.poly([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
array([ 1.0000e+00, -2.8000e+01, 3.2200e+02, -1.9600e+03, 6.7690e+03,
-1.3132e+04, 1.3068e+04, -5.0400e+03])
11.1.4. Roots
Return the roots of a polynomial
>>> np.roots([1, 2])
array([-2.])
>>> np.roots([0, 1, 3])
array([-3.])
>>> np.roots([1, 4, -2, 3]).round(4)
array([-4.5797+0.j , 0.2899+0.7557j, 0.2899-0.7557j])
>>> np.roots([ 1, -11, 9, 11, -10]).round(4)
array([10., -1., 1., 1.])
11.1.5. Derivative of a Polynomial
>>> np.polyder([1/4, 1/3, 1/2, 1, 0])
array([1., 1., 1., 1.])
>>> np.polyder([0.25, 0.33333333, 0.5, 1, 0]).round(4)
array([1., 1., 1., 1.])
>>> np.polyder([1, 2, 3, 4])
array([3, 4, 3])
11.1.6. Antiderivative (indefinite integral) of a polynomial
Return an antiderivative (indefinite integral) of a polynomial
>>> np.polyint([1, 1, 1, 1]).round(4)
array([0.25 , 0.3333, 0.5 , 1. , 0. ])
>>> np.polyint([16, 9, 4, 2])
array([4., 3., 2., 2., 0.])
11.1.7. Evaluate a Polynomial at Specific Values
Compute polynomial values
Horner's scheme is used to evaluate the polynomial
>>> np.polyval([1, -2, 0, 2], 4)
np.int64(34)
11.1.8. Least Squares Polynomial Fit
Least squares polynomial fit
>>> x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> y = [0, 2, 1, 3, 7, 10, 11, 19]
>>>
>>> np.polyfit(x, y, 2).round(4)
array([ 0.375 , -0.8869, 1.0536])
11.1.9. Polynomial Arithmetic
np.polyadd()np.polysub()np.polymul()np.polydiv()
11.1.10. Sum of Two Polynomials
>>> a = [1, 2]
>>> b = [9, 5, 4]
>>>
>>> np.polyadd(a, b)
array([9, 6, 6])
11.1.11. References
11.1.12. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Polyfit
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 4
# - Minutes: 8
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Given are points coordinates in Cartesian system
# 2. Separate first row (header) from data
# 3. Calculate coefficients of best approximating polynomial of 3rd degree
# 4. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Dane są koordynaty punktów w układzie kartezjańskim
# 2. Odseparuj pierwszy wiersz (nagłówek) do danych
# 3. Oblicz współczynniki najlepiej dopasowanego wielomianu 3 stopnia
# 4. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert 'result' in globals(), \
'Variable `result` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> result
array([ 0.25, 0.75, -1.5 , -2. ])
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result: np.ndarray
# %% Data
DATA = [
('x', 'y'),
(-4.0, 0.0),
(-3.0, 2.5),
(-2.0, 2.0),
(0.0, -2.0),
(2.0, 0.0),
(3.0, 7.0),
]
# %% Result
result = ...