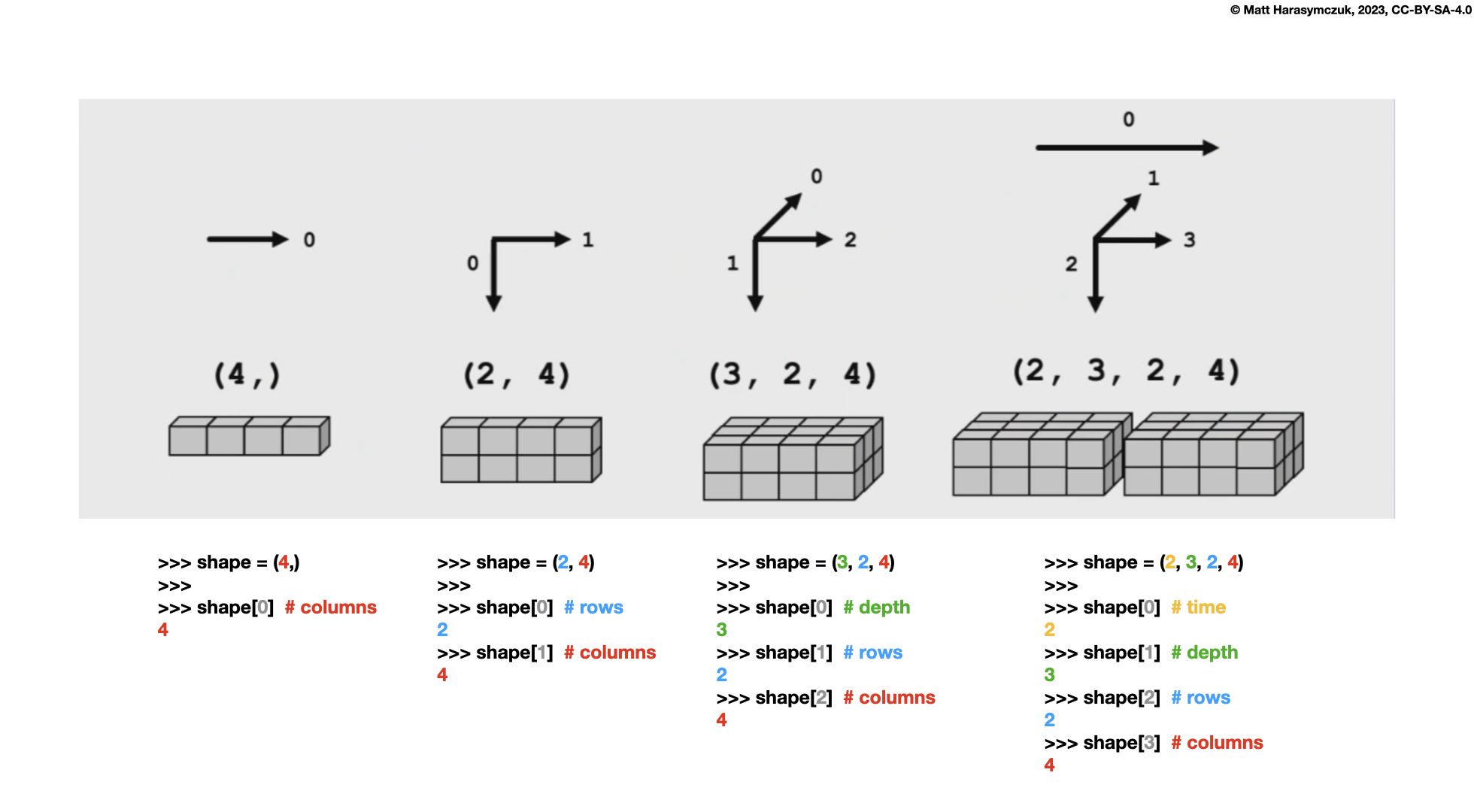
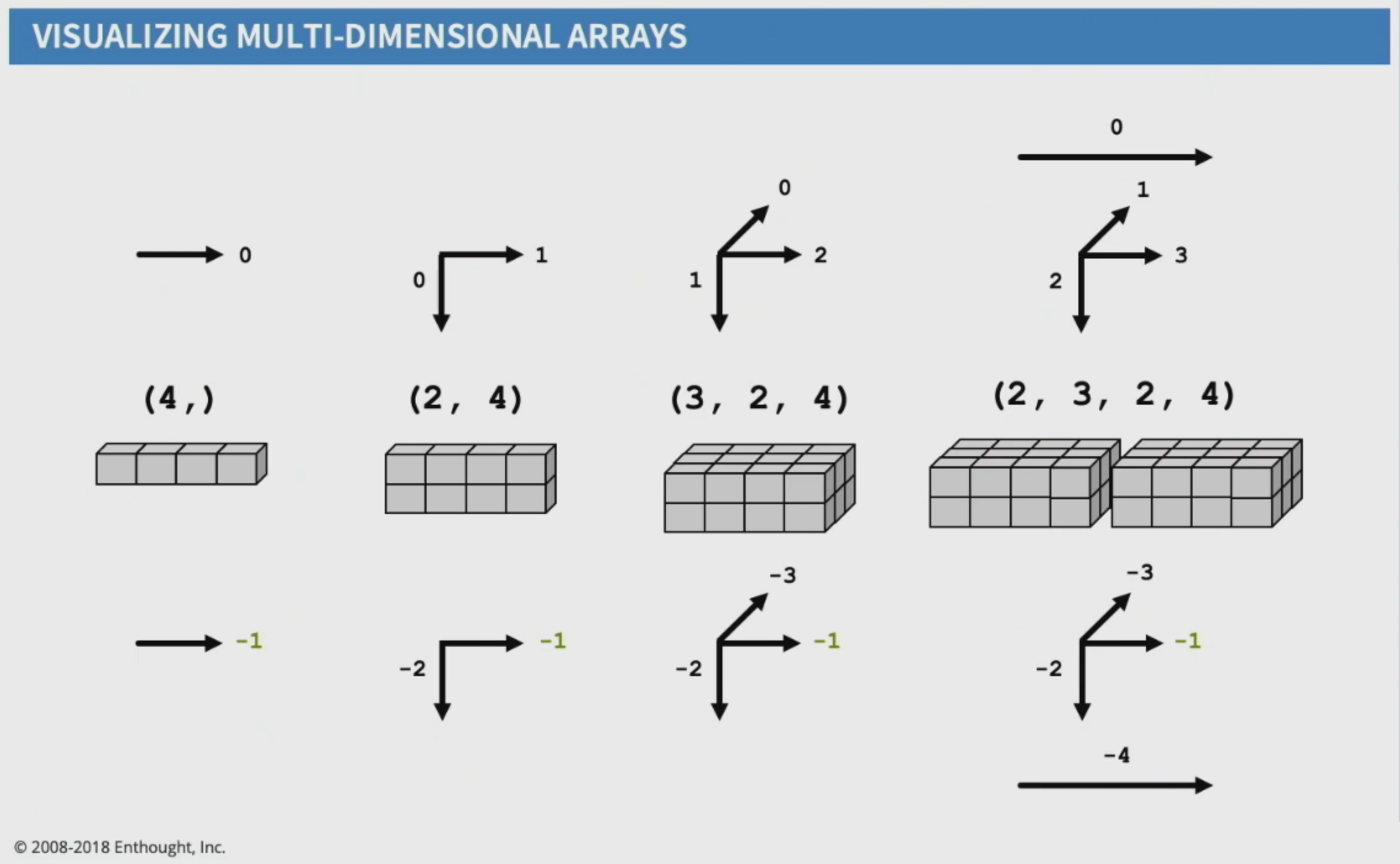
6.3. Indexing Axis
axisis an index ina.shapeColumns are always last

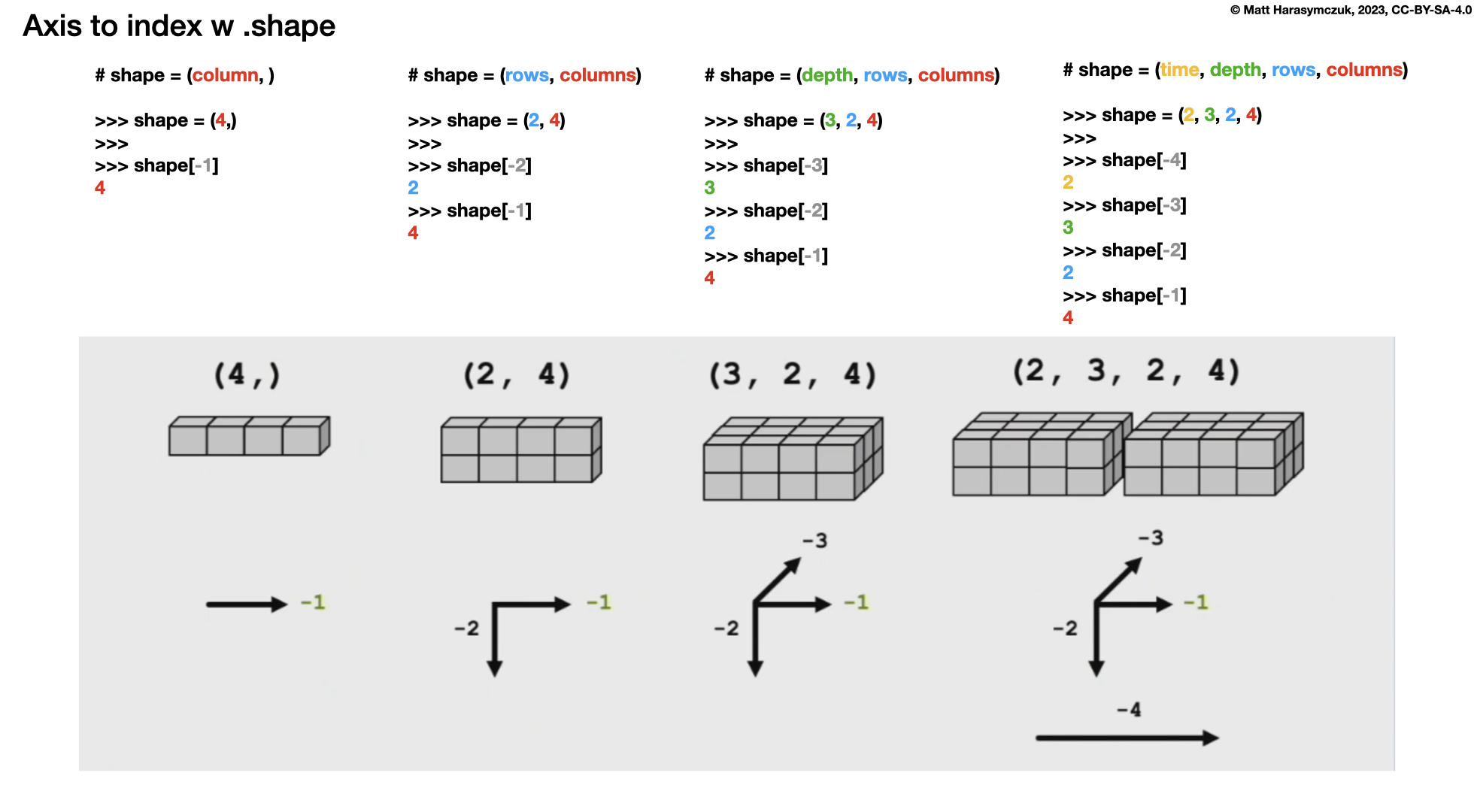

6.3.1. SetUp
>>> import numpy as np
6.3.2. Axis
New dimensions are added at the beginning of
shapeOld axes numbers are pushed to the right
One Dimensions:
>>> a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(3,)
>>>
>>> a.ndim
1
axis=0 # columns
axis=-0 # columns
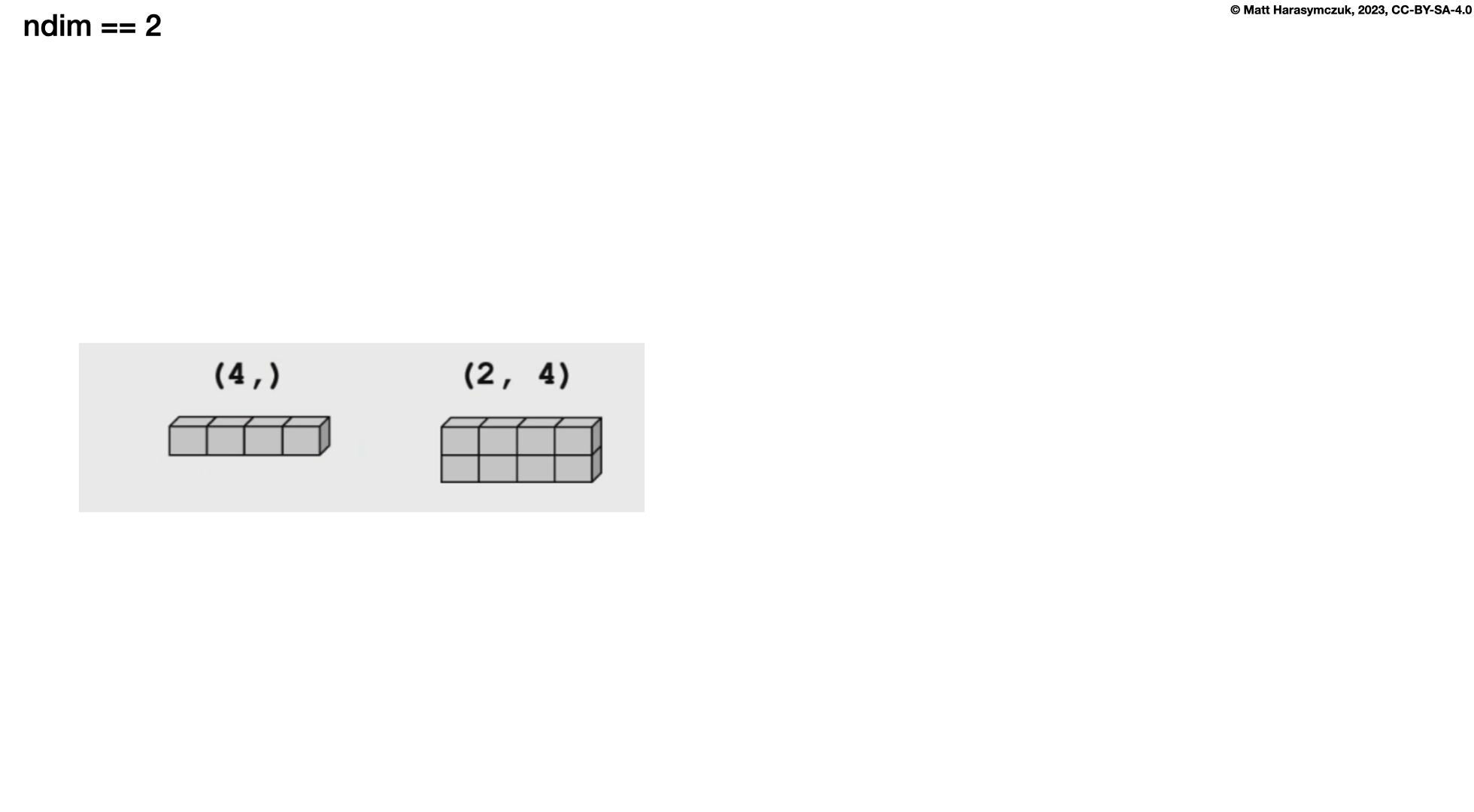
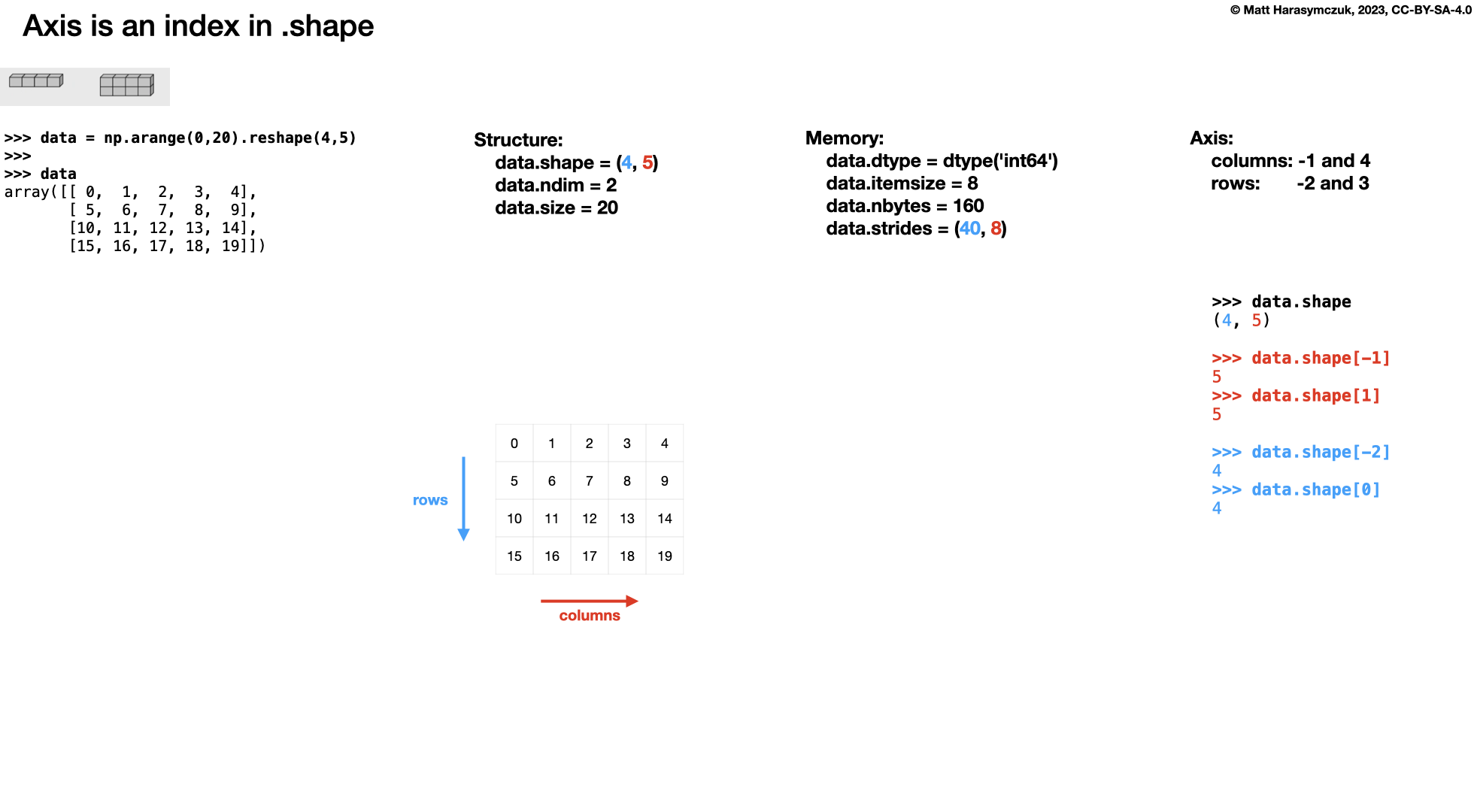
Two Dimensions:
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6]])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(2, 3)
>>>
>>> a.ndim
2
axis=0 # rows
axis=1 # columns
axis=-0 # rows
axis=-1 # columns
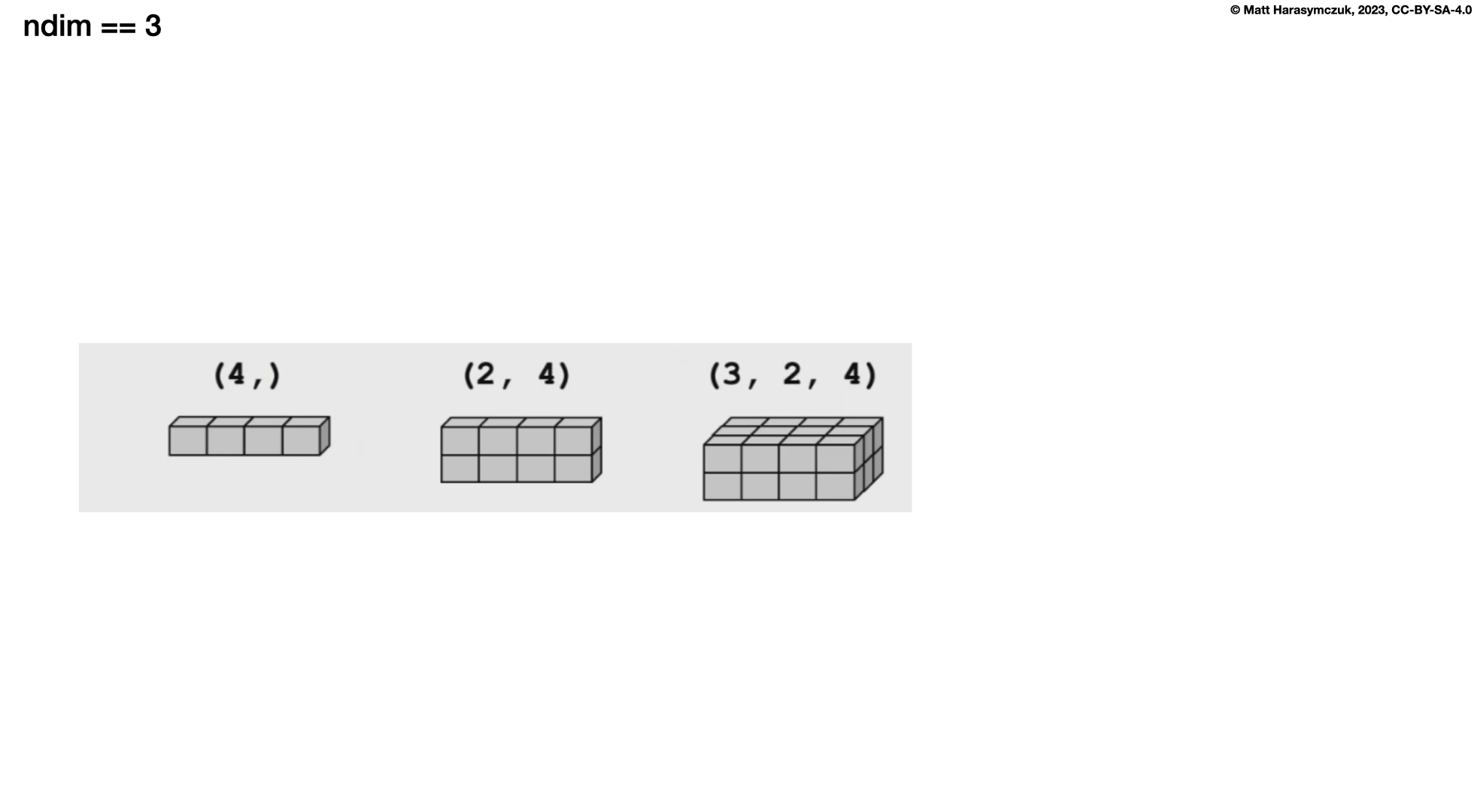
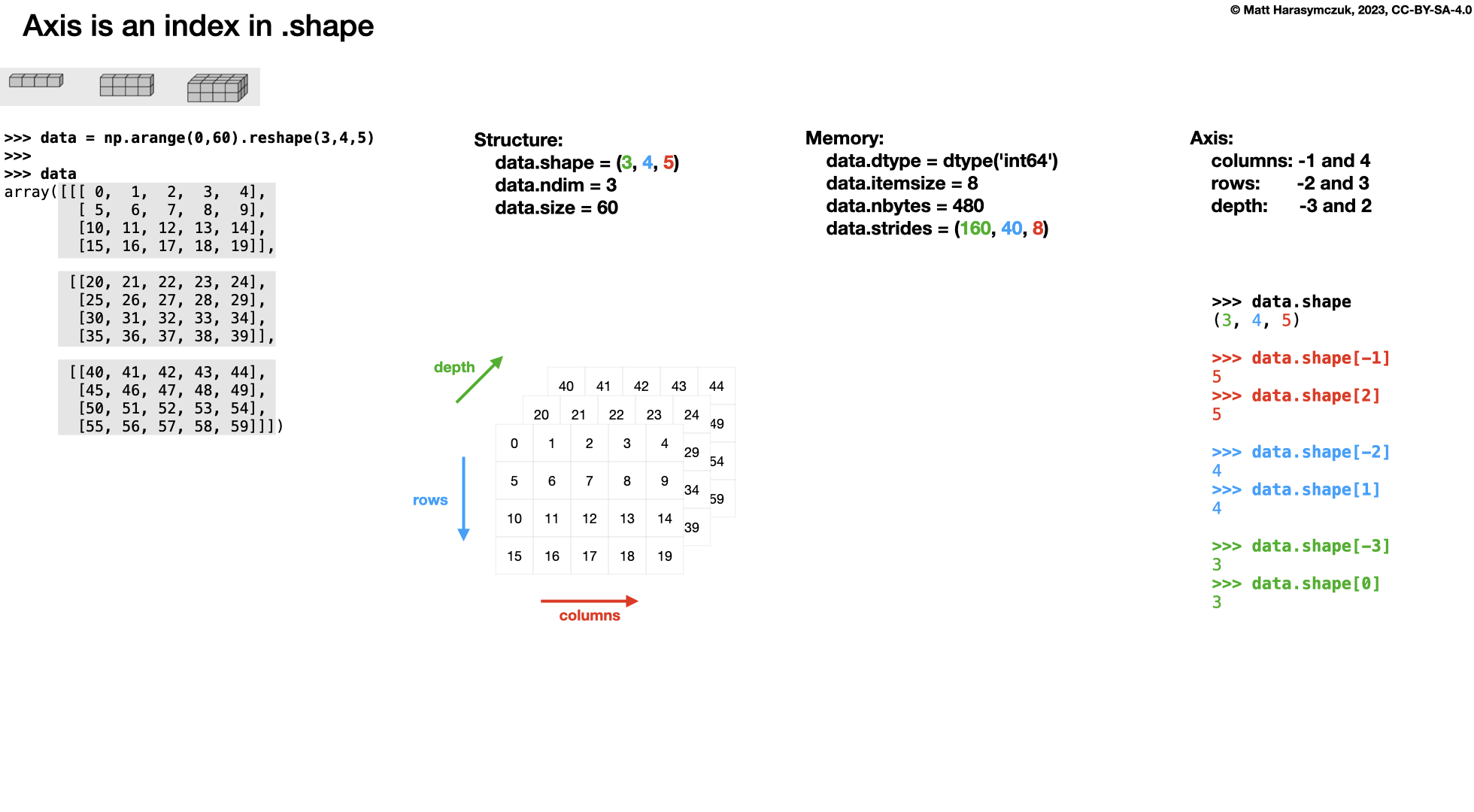
Three Dimensions:
>>> a = np.array([[[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66]]])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(2, 2, 3)
>>>
>>> a.ndim
3
axis=0 # depth
axis=1 # rows
axis=2 # columns
axis=-0 # depth
axis=-1 # columns
axis=-2 # rows
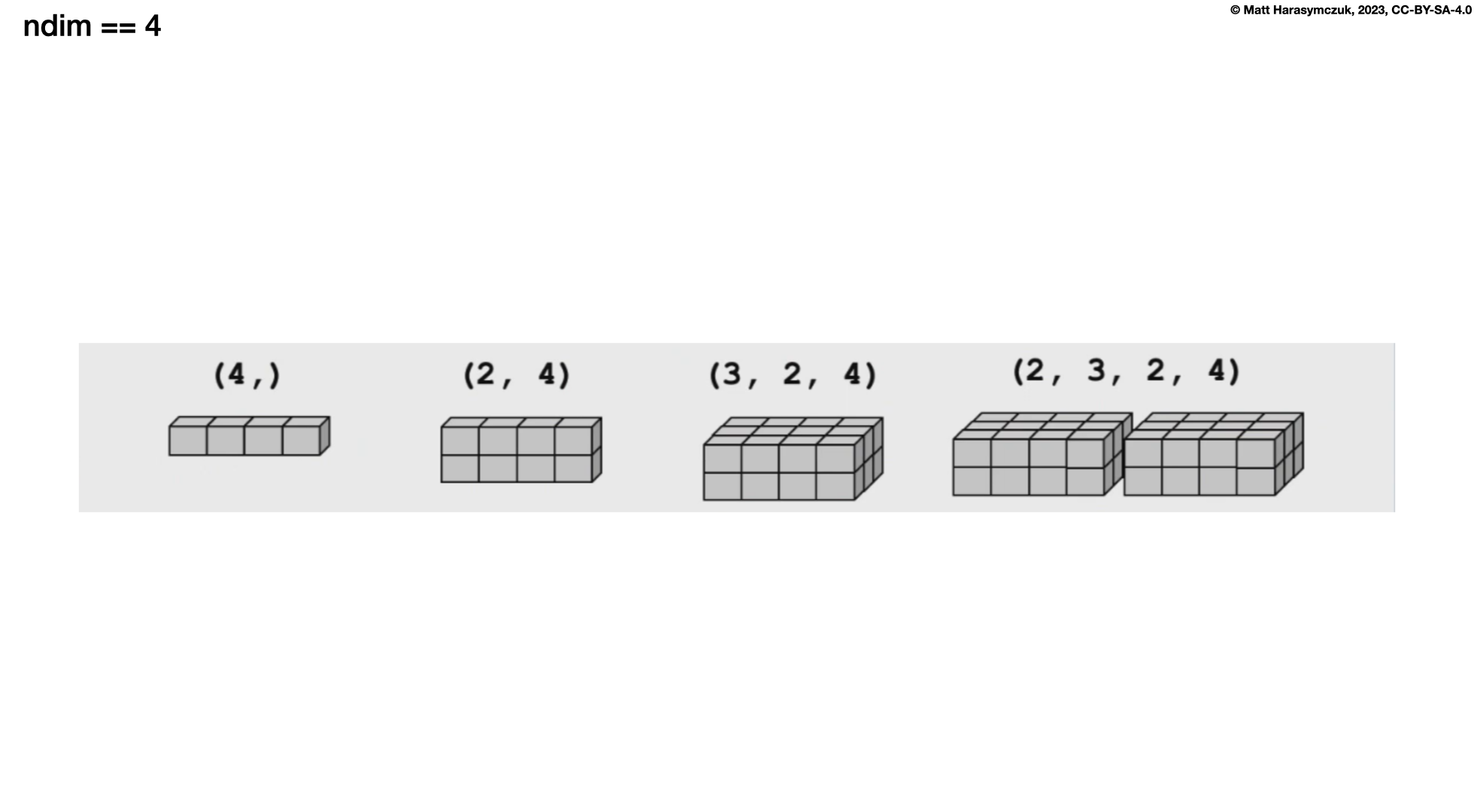
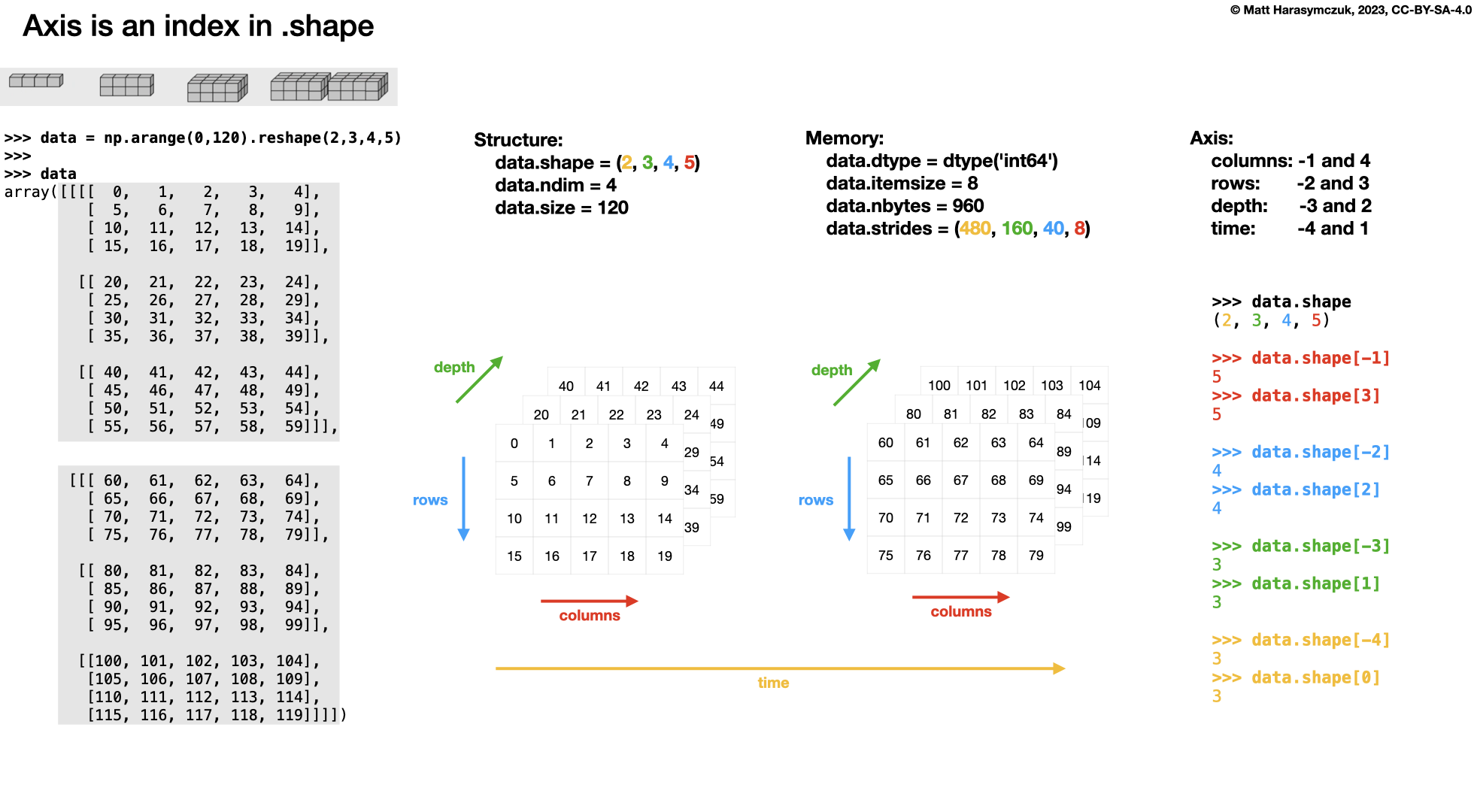
Four Dimensions:
>>> a = np.array([[[[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66]]],
...
... [[[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66]]]])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(2, 2, 2, 3)
>>>
>>> a.ndim
4
axis=0 # depth
axis=1 # rows
axis=2 # columns
axis=-0 # depth
axis=-1 # columns
axis=-2 # rows
6.3.3. Take
One Dimensional:
>>> a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(3,)
>>> a[0]
np.int64(1)
>>>
>>> a[1]
np.int64(2)
>>>
>>> a[2]
np.int64(3)
>>> a.take(0, axis=0)
np.int64(1)
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=0)
np.int64(2)
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=0)
np.int64(3)
>>> a.take(0, axis=-1)
np.int64(1)
>>> a.take(1, axis=-1)
np.int64(2)
>>> a.take(2, axis=-1)
np.int64(3)
>>> a[:, 1]
Traceback (most recent call last):
IndexError: too many indices for array: array is 1-dimensional, but 2 were indexed
>>>
>>> a.take(0, axis=1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
numpy.exceptions.AxisError: axis 1 is out of bounds for array of dimension 1
Two Dimensional - Rows:
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>> a.shape
(3, 3)
>>> a[0, :]
array([1, 2, 3])
>>>
>>> a[1, :]
array([4, 5, 6])
>>>
>>> a[2, :]
array([7, 8, 9])
>>> a.take(0, axis=0)
array([1, 2, 3])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=0)
array([4, 5, 6])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=0)
array([7, 8, 9])
Two Dimensional - Columns:
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
>>> a.shape
(3, 3)
>>> a[:, 0]
array([1, 4, 7])
>>>
>>> a[:, 1]
array([2, 5, 8])
>>>
>>> a[:, 2]
array([3, 6, 9])
>>> a.take(0, axis=1)
array([1, 4, 7])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=1)
array([2, 5, 8])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=1)
array([3, 6, 9])
>>> a.take(0, axis=-1)
array([1, 4, 7])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=-1)
array([2, 5, 8])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=-1)
array([3, 6, 9])
Three Dimensional - Depth:
>>> a = np.array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
... [ 4, 5, 6],
... [ 5, 6, 7]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66],
... [77, 88, 99]]])
>>> a.shape
(2, 3, 3)
>>> a[0, :, :]
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[5, 6, 7]])
>>>
>>> a[1, :, :]
array([[11, 22, 33],
[44, 55, 66],
[77, 88, 99]])
>>>
>>> a[2, :, :]
Traceback (most recent call last):
IndexError: index 2 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 2
>>> a.take(0, axis=0)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[5, 6, 7]])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=0)
array([[11, 22, 33],
[44, 55, 66],
[77, 88, 99]])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
IndexError: index 2 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 2
Three Dimensional - Rows:
>>> a = np.array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
... [ 4, 5, 6],
... [ 5, 6, 7]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66],
... [77, 88, 99]]])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(2, 3, 3)
>>>
>>> a[:, 0, :]
array([[ 1, 2, 3],
[11, 22, 33]])
>>>
>>> a[:, 1, :]
array([[ 4, 5, 6],
[44, 55, 66]])
>>>
>>> a[:, 2, :]
array([[ 5, 6, 7],
[77, 88, 99]])
>>>
>>> a.take(0, axis=1)
array([[ 1, 2, 3],
[11, 22, 33]])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=1)
array([[ 4, 5, 6],
[44, 55, 66]])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=1)
array([[ 5, 6, 7],
[77, 88, 99]])
Three Dimensional - Columns:
>>> a = np.array([[[ 1, 2, 3],
... [ 4, 5, 6],
... [ 5, 6, 7]],
...
... [[11, 22, 33],
... [44, 55, 66],
... [77, 88, 99]]])
>>>
>>> a.shape
(2, 3, 3)
>>>
>>> a[:, :, 0]
array([[ 1, 4, 5],
[11, 44, 77]])
>>>
>>> a[:, :, 1]
array([[ 2, 5, 6],
[22, 55, 88]])
>>>
>>> a[:, :, 2]
array([[ 3, 6, 7],
[33, 66, 99]])
>>>
>>> a.take(0, axis=2)
array([[ 1, 4, 5],
[11, 44, 77]])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=2)
array([[ 2, 5, 6],
[22, 55, 88]])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=2)
array([[ 3, 6, 7],
[33, 66, 99]])
>>>
>>> a.take(0, axis=-1)
array([[ 1, 4, 5],
[11, 44, 77]])
>>>
>>> a.take(1, axis=-1)
array([[ 2, 5, 6],
[22, 55, 88]])
>>>
>>> a.take(2, axis=-1)
array([[ 3, 6, 7],
[33, 66, 99]])
6.3.4. Use Case - 1
>>> shape = (5,)
Positive:
>>> shape[0]
5
Negative:
>>> shape[-1]
5
6.3.5. Use Case - 2
>>> shape = (4, 5)
Positive:
>>> shape[0]
4
>>>
>>> shape[1]
5
Negative:
>>> shape[-1]
5
>>>
>>> shape[-2]
4
6.3.6. Use Case - 3
>>> shape = (3, 4, 5)
Positive:
>>> shape[0]
3
>>>
>>> shape[1]
4
>>>
>>> shape[2]
5
Negative:
>>> shape[-1]
5
>>>
>>> shape[-2]
4
>>>
>>> shape[-3]
3
6.3.7. Use Case - 4
>>> shape = (2, 3, 4, 5)
Positive:
>>> shape[0]
2
>>>
>>> shape[1]
3
>>>
>>> shape[2]
4
>>>
>>> shape[3]
5
Negative:
>>> shape[-1]
5
>>>
>>> shape[-2]
4
>>>
>>> shape[-3]
3
>>>
>>> shape[-4]
2