5.1. Decision Tree
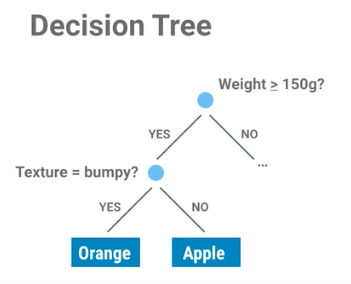
Figure 5.25. Drzewo decyzyjne
from sklearn import tree
# Input to the classifier
# as of Scikit-learn uses real-valued features, we use:
# 0: bumpy
# 1: smooth
#
# features = [
# [140, 'smooth'],
# [130, 'smooth'],
# [150, 'bumpy'],
# [170, 'bumpy'],
# ]
features = [
[140, 1],
[130, 1],
[150, 0],
[170, 0],
]
# Output that we want from classifier
# as of Scikit-learn uses real-valued features, we use:
# 0: apple
# 1: orange
#
# labels = ['apple', 'apple', 'orange', 'orange']
labels = [0, 0, 1, 1]
# create decision tree
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# fit - synonim to "find patterns in data"
clf = clf.fit(features, labels)
# use classifier to predict
result = clf.predict([[160, 0]])
print(result)
# should be: [1]
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
# Features
x = iris.data
# Labels
y = iris.target
# Split dataset into test and training set in half
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.5)
# Create classifier
decision_tree = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# Train classifier using training data
decision_tree.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Predict
predictions = decision_tree.predict(x_test)
# How accurate was classifier on testing set
# Because of some variation for each run, it might give different results
result = accuracy_score(y_test, predictions)
print(result)
# Output: 0.96
Note identical API for classifiers!
5.1.1. Visualizing a Decision Tree
import numpy
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn import tree
iris = load_iris()
# select test indexes
# dataset is ordered so 0, 50, 100 is a first of each kind
test_idx = [0, 50, 100]
# training data
train_target = numpy.delete(iris.target, test_idx)
train_data = numpy.delete(iris.data, test_idx, axis=0)
# testing data
test_target = iris.target[test_idx]
test_data = iris.data[test_idx]
# create and train classifier
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf.fit(train_data, train_target)
print(test_target)
# [0 1 2]
result = clf.predict(test_data)
print(result)
# [0 1 2]
print(test_data[0], test_target[0])
# [ 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2] 0
print(iris.feature_names)
# ['sepal_length (cm)', 'sepal_width (cm)', 'petal_length (cm)', 'petal_width (cm)']
print(iris.target_names)
# ['setosa' 'versicolor' 'virginica']
# Visualization of Decision Tree Classifier
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
import pydotplus
dot_data = StringIO()
tree.export_graphviz(
decision_tree=clf,
out_file=dot_data,
feature_names=iris.feature_names,
class_names=iris.target_names,
filled=True,
rounded=True,
impurity=True
)
graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data.getvalue())
graph.write_pdf('/tmp/iris.pdf')
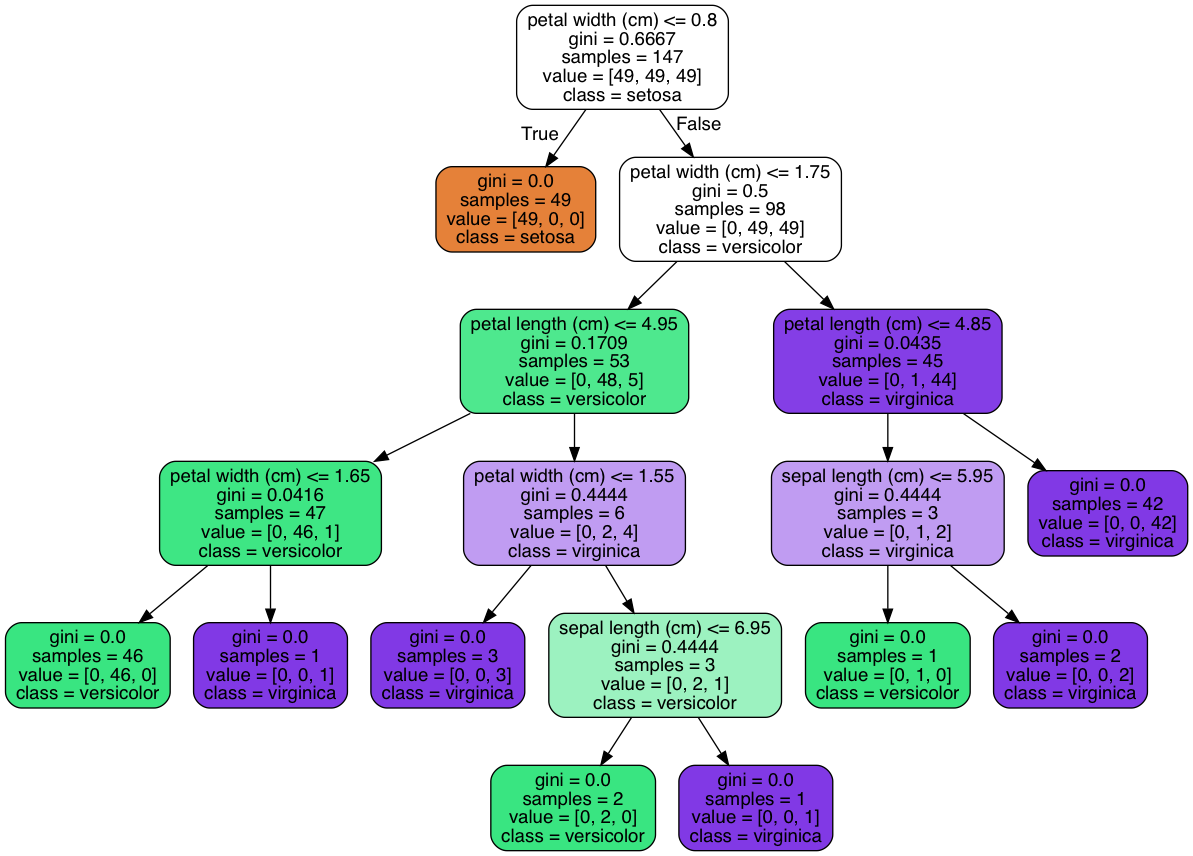
Figure 5.26. Visualization of Decision Tree Classifier