5.3. Random Distributions
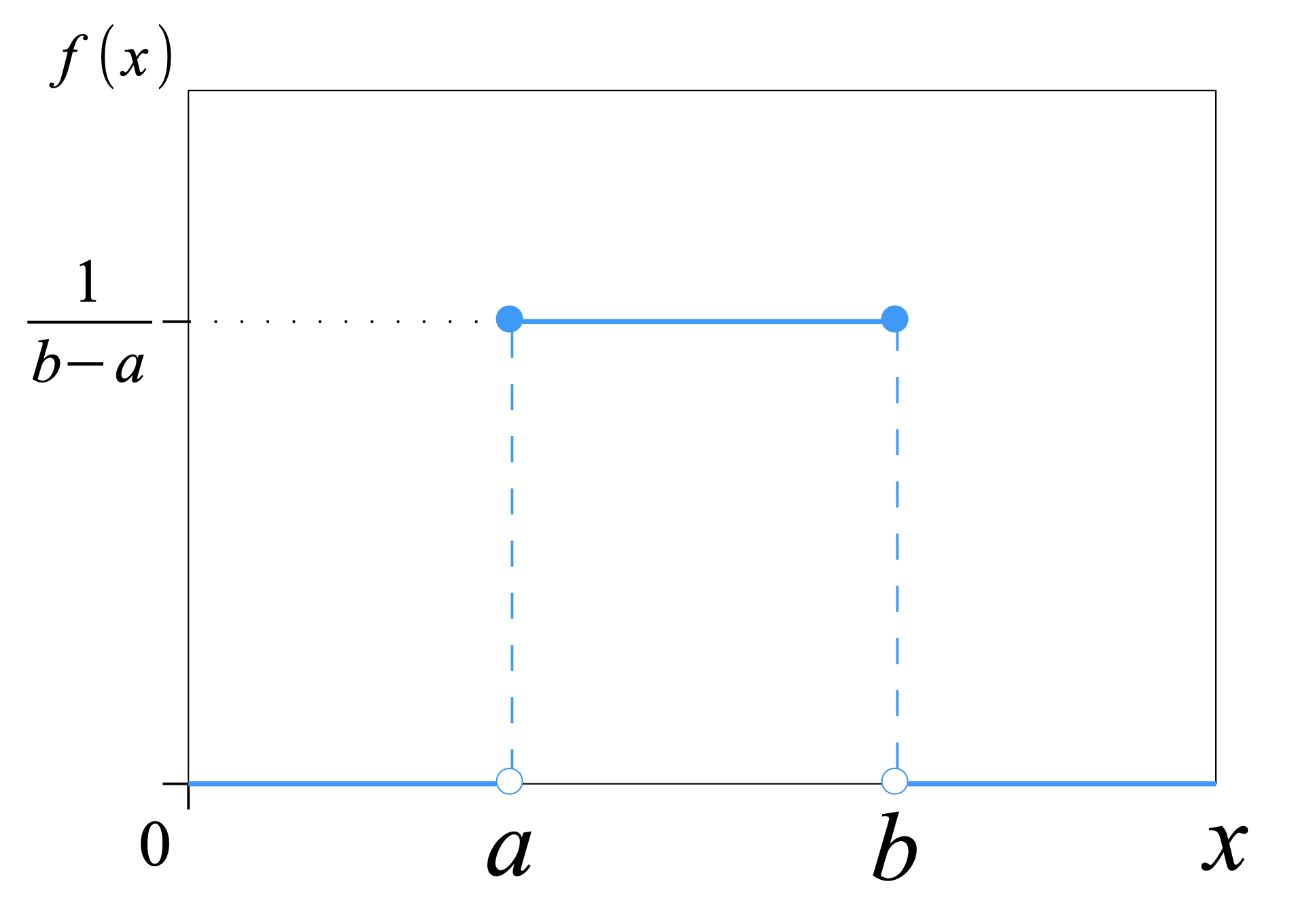
5.3.1. Continuous Uniform Distribution
Results are from the "continuous uniform" distribution over the stated interval
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.random.seed(0)
Random float in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0):
>>> np.random.rand(5)
array([0.5488135 , 0.71518937, 0.60276338, 0.54488318, 0.4236548 ])
>>> np.random.rand(2,3)
array([[0.64589411, 0.43758721, 0.891773 ],
[0.96366276, 0.38344152, 0.79172504]])
>>> np.random.rand(3,2)
array([[0.52889492, 0.56804456],
[0.92559664, 0.07103606],
[0.0871293 , 0.0202184 ]])
5.3.2. Normal (Gaussian) Distribution
Draw pseudorandom samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution
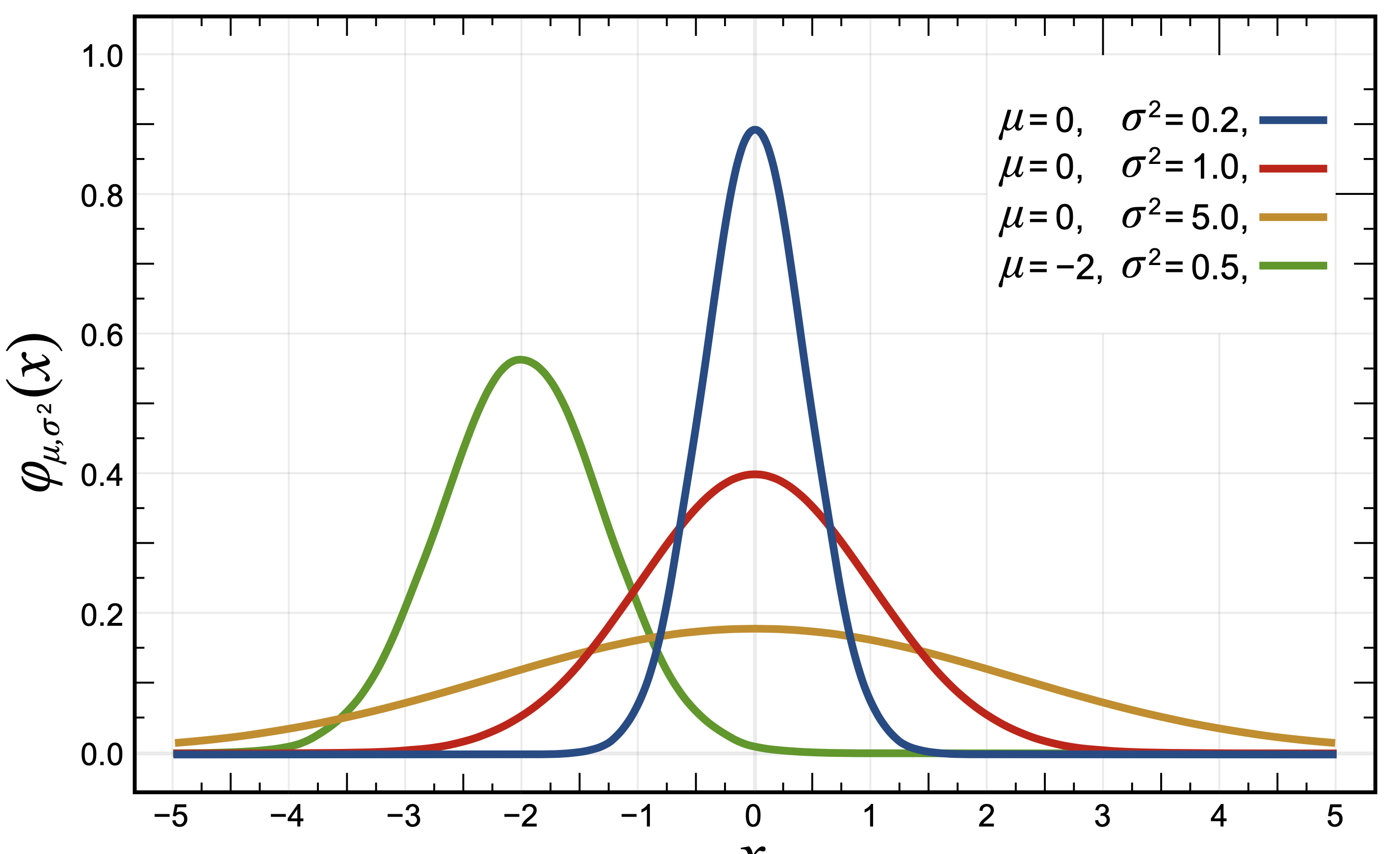
Defaults:
μ -
loc=0.0σ -
scale=1.0
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.random.seed(0)
Draw pseudorandom samples from a normal (Gaussian) distribution:
>>> np.random.normal()
1.764052345967664
>>> np.random.normal(0.0, 1.0)
0.4001572083672233
>>> np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
0.9787379841057392
>>> np.random.normal(size=5)
array([ 2.2408932 , 1.86755799, -0.97727788, 0.95008842, -0.15135721])
>>> np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(2,3))
array([[-0.10321885, 0.4105985 , 0.14404357],
[ 1.45427351, 0.76103773, 0.12167502]])
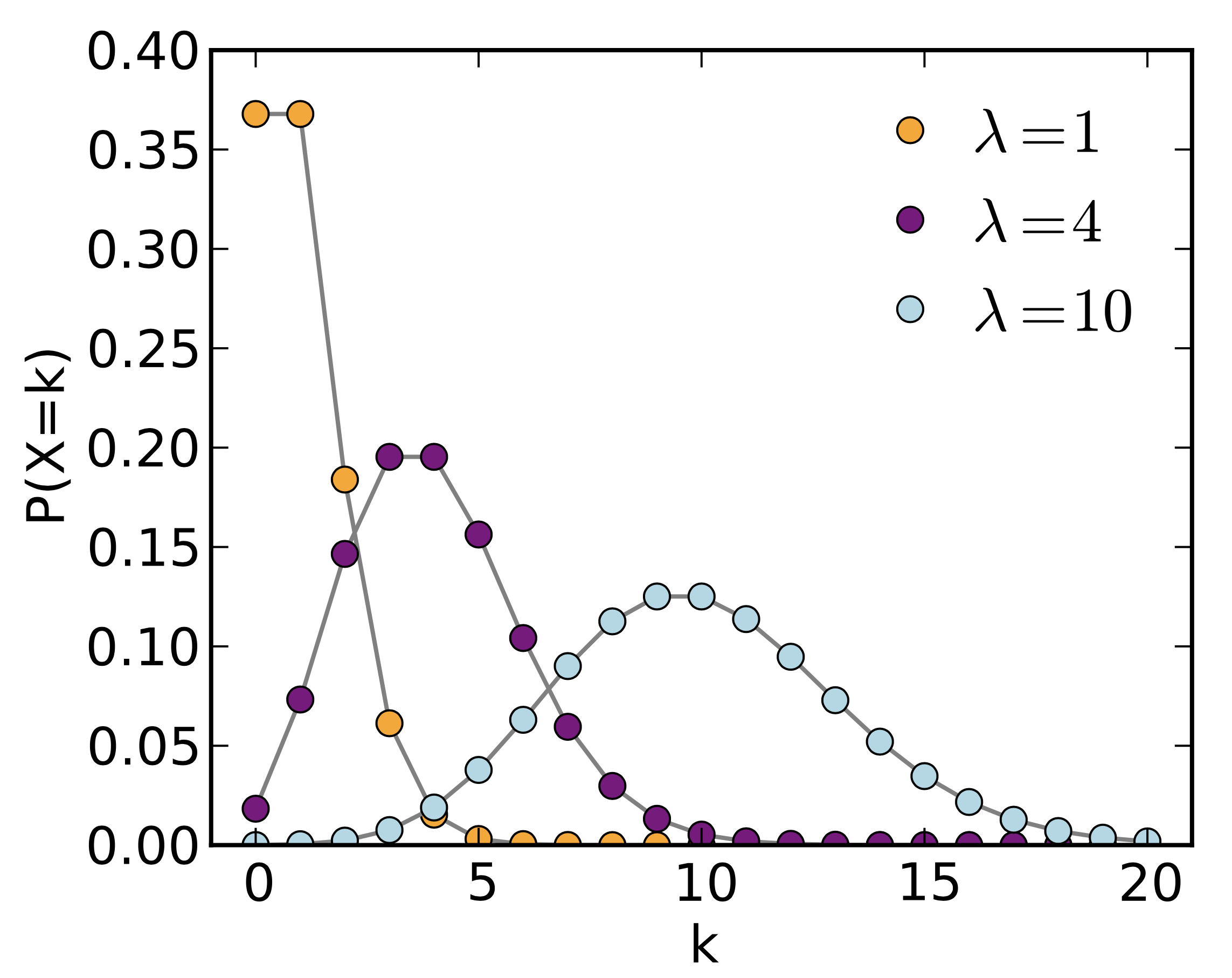
5.3.3. Poisson Distribution
Draw samples from a Poisson distribution
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.random.seed(0)
Draw samples from a Poisson distribution:
>>> np.random.poisson(6.0)
11
>>> np.random.poisson(lam=6.0)
4
>>> np.random.poisson(lam=6.0, size=5)
array([9, 7, 8, 5, 5])
>>> np.random.poisson(lam=6.0, size=(2,3))
array([[5, 5, 7],
[3, 5, 6]])
5.3.4. References
5.3.5. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Random Float
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Set random seed to zero
# 2. Define `result: np.ndarray` of 10 random floats
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Ustaw ziarno losowości na zero
# 2. Zdefiniuj `result: np.ndarray` z 10 losowymi liczbami zmiennoprzecinkowymi
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert 'result' in globals(), \
'Variable `result` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> result
array([0.5488135 , 0.71518937, 0.60276338, 0.54488318, 0.4236548 ,
0.64589411, 0.43758721, 0.891773 , 0.96366276, 0.38344152])
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result: np.ndarray
# %% Data
np.random.seed(0)
# %% Result
result = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Random Int
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Set random seed to zero
# 2. Define `result: np.ndarray` of size 16x16 with random integers `[0;9]` (inclusive)
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Ustaw ziarno losowości na zero
# 2. Zdefiniuj `result: np.ndarray` o rozmiarze 16x16 z losowymi liczbami całkowitymi `<0,9>` (włącznie)
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert 'result' in globals(), \
'Variable `result` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> result
array([[5, 0, 3, 3, 7, 9, 3, 5, 2, 4, 7, 6, 8, 8, 1, 6],
[7, 7, 8, 1, 5, 9, 8, 9, 4, 3, 0, 3, 5, 0, 2, 3],
[8, 1, 3, 3, 3, 7, 0, 1, 9, 9, 0, 4, 7, 3, 2, 7],
[2, 0, 0, 4, 5, 5, 6, 8, 4, 1, 4, 9, 8, 1, 1, 7],
[9, 9, 3, 6, 7, 2, 0, 3, 5, 9, 4, 4, 6, 4, 4, 3],
[4, 4, 8, 4, 3, 7, 5, 5, 0, 1, 5, 9, 3, 0, 5, 0],
[1, 2, 4, 2, 0, 3, 2, 0, 7, 5, 9, 0, 2, 7, 2, 9],
[2, 3, 3, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 9, 1, 4, 6, 8, 2, 3, 0],
[0, 6, 0, 6, 3, 3, 8, 8, 8, 2, 3, 2, 0, 8, 8, 3],
[8, 2, 8, 4, 3, 0, 4, 3, 6, 9, 8, 0, 8, 5, 9, 0],
[9, 6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 0, 4, 9, 6, 5, 7, 8, 8, 9, 2],
[8, 6, 6, 9, 1, 6, 8, 8, 3, 2, 3, 6, 3, 6, 5, 7],
[0, 8, 4, 6, 5, 8, 2, 3, 9, 7, 5, 3, 4, 5, 3, 3],
[7, 9, 9, 9, 7, 3, 2, 3, 9, 7, 7, 5, 1, 2, 2, 8],
[1, 5, 8, 4, 0, 2, 5, 5, 0, 8, 1, 1, 0, 3, 8, 8],
[4, 4, 0, 9, 3, 7, 3, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 2, 5, 5]])
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result: np.ndarray
# %% Data
np.random.seed(0)
# %% Result
result = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Random Choice
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 1
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Set random seed to zero
# 2. Define `result: np.ndarray` with 6 random numbers
# without repetition from `DATA`
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Ustaw ziarno losowości na zero
# 2. Zdefiniuj `result: np.ndarray` z 6 losowymi
# liczbami bez powtórzeń z `DATA`
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert 'result' in globals(), \
'Variable `result` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> result
array([30, 5, 27, 31, 33, 38])
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result: np.ndarray
# %% Data
np.random.seed(0)
DATA = np.arange(1, 50)
# %% Result
result = ...