4.1. Attributes DType
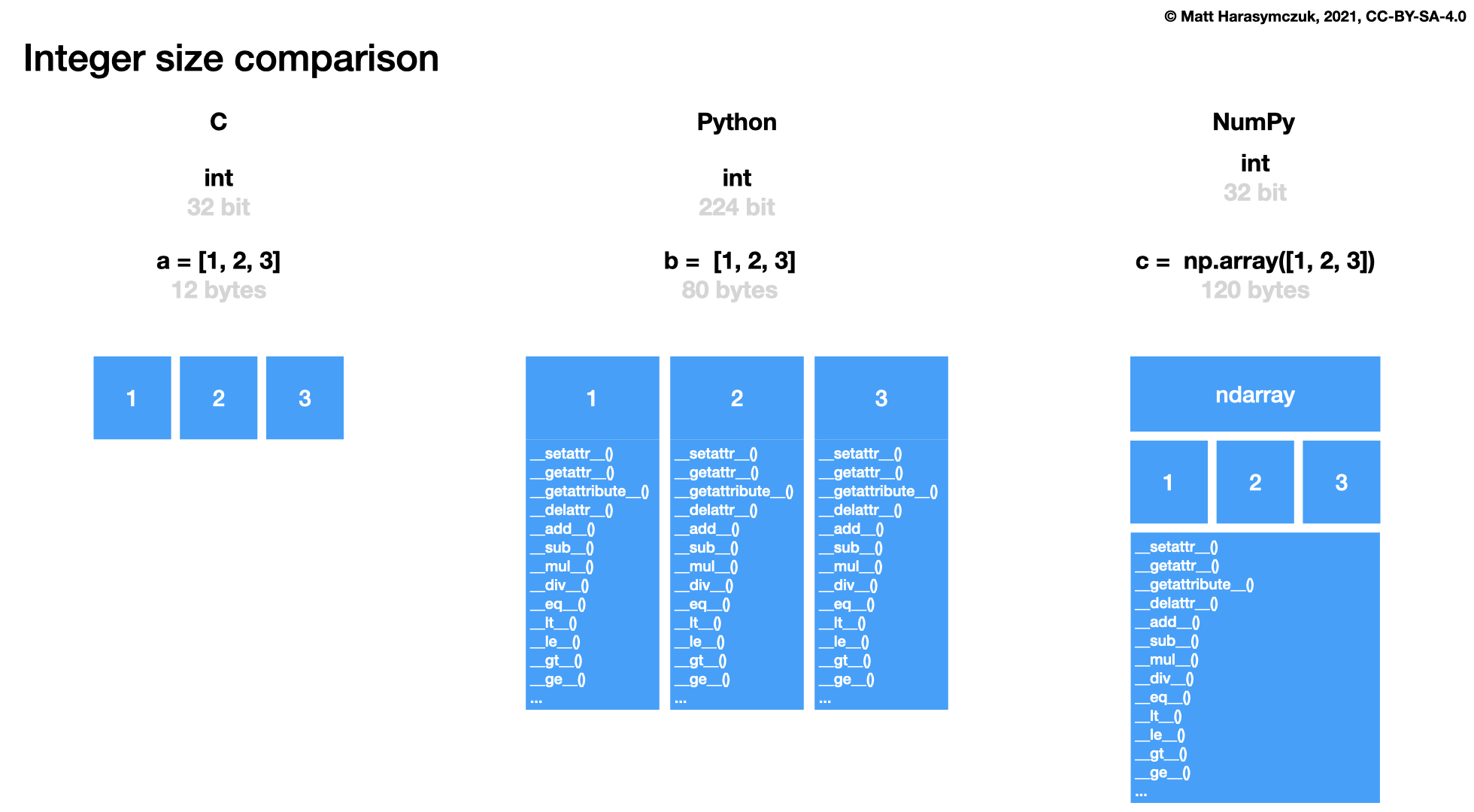
Array can have only one data type (
dtype)Type can be "non-primitive" - any class
4.1.1. SetUp
>>> import numpy as np
4.1.2. Bits and Bytes
Signed and unsigned
Unsigned cannot be negative
For negative signed numbers "Two's complement" is used
1 # unsigned
+1 # signed
-1 # signed
3 bit unsigned integers. Values: 8, minimal: 0, maximal: 8:
0 000
1 001
2 010
3 011
4 100
5 101
6 110
7 111
3 bit signed integers. Values: 8, minimal: -4, maximal: 3:
+0 000
+1 001
+2 010
+3 011
−4 100
−3 101
−2 110
−1 111
8 bit signed integers. Values: 256, minimal: -128, maximal: 127:
+0 00000000
+1 00000001
+2 00000010
+126 01111110
+127 01111111
−128 10000000
−127 10000001
−126 10000010
−2 11111110
−1 11111111
32 bit unsigned int. Values: 2,147,483,647, minimal: 0, maximal: 2,147,483,647:
0 0000000000000000000000000000000000
1 0000000000000000000000000000000001
2 0000000000000000000000000000000010
3 0000000000000000000000000000000011
4 0000000000000000000000000000000100
5 0000000000000000000000000000000101
6 0000000000000000000000000000000110
7 0000000000000000000000000000000111
Calculates a two's complement integer from the given input value's bits:
>>> def twos_complement(value: int, num_bits: int) -> int:
... mask = 2 ** (num_bits - 1)
... return -(value & mask) + (value & ~mask)
>>> np.binary_repr(0, 8) # number 0 using 8-bit integer representation
'00000000'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(1, 8) # number 1 using 8-bit integer representation
'00000001'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(2, 8) # number 2 using 8-bit integer representation
'00000010'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(3, 8) # number 3 using 8-bit integer representation
'00000011'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(-1, 8) # number -1 using 8-bit integer representation
'11111111'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(-2, 8) # number -2 using 8-bit integer representation
'11111110'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(-3, 8) # number -3 using 8-bit integer representation
'11111101'
4.1.3. Comparison
>>> data = 69
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(data, 8) # np.int8
'01000101'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(data, 16) # np.int16
'0000000001000101'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(data, 32) # np.int32
'00000000000000000000000001000101'
>>>
>>> np.binary_repr(data, 64) # np.int64
'0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001000101'
4.1.4. Signed int
Signed (positive and negative)
np.intalias fornp.int64np.int0alias fornp.int64- Integer used for indexingnp.int8np.int16np.int32np.int64
Type |
Bits |
Number of Values |
Minimal |
Maximal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8 |
256 |
-128 |
127 |
|
16 |
65,536 |
-32,768 |
32,767 |
|
32 |
4,294,967,296 |
-2,147,483,648 |
2,147,483,646 |
|
64 |
18,446,744,073,709,551,616 |
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 |
9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
>>> a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
>>>
>>> type(a)
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('int64')
>>> a = np.array([[1., 2., 3.],
... [4., 5., 6.]])
>>>
>>> a.astype(int)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.int8)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]], dtype=int8)
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.int64)
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
4.1.5. Unsigned int
Unsigned (non-negative only)
np.uint0np.uint8np.uint16np.uint32np.uint64
Type |
Bits |
Number of Values |
Minimal |
Maximal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8 |
256 |
0 |
255 |
|
16 |
65,536 |
0 |
65,535 |
|
32 |
4,294,967,296 |
0 |
4,294,967,295 |
|
64 |
18,446,744,073,709,551,616 |
0 |
18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
>>> a = np.array([-1, 0, 1])
>>>
>>> type(a)
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('int64')
>>> a = np.array([-1, 0, 1])
>>>
>>> a.astype(int)
array([-1, 0, 1])
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.uint8)
array([255, 0, 1], dtype=uint8)
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.uint64)
array([18446744073709551615, 0, 1], dtype=uint64)
4.1.6. float
np.floatnp.float16np.float32np.float64np.float128
Type |
Bits |
Minimal |
Maximal |
|---|---|---|---|
|
16 |
-65,504 |
65,504 |
|
32 |
±0.000000×10−95 |
±9.999999×1096 |
|
64 |
±0.000000000000000×10−383 |
±9.999999999999999×10384 |
|
64 |
±0.000000000000000000000000000000000×10−6143 |
±9.999999999999999999999999999999999×106144 |
>>> a = np.array([1., 2., 3.])
>>>
>>> type(a)
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('float64')
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6]])
>>>
>>> a.astype(float)
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.float16)
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]], dtype=float16)
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.float32)
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]], dtype=float32)
>>>
>>> a.astype(np.float64)
array([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
4.1.7. complex
np.complexnp.complex64np.complex128np.complex256
>>> a = np.array([1+2j])
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('complex128')
>>> a = np.array([1.1+2.2j])
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('complex128')
4.1.8. bool
>>> a = np.array([True, False, True])
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('bool')
>>> a = np.array([1, 0, 1], bool)
>>>
>>> a.dtype
dtype('bool')
>>>
>>> a
array([ True, False, True])
4.1.9. str
>>> np.array(['a', 'b', 'c'])
array(['a', 'b', 'c'], dtype='<U1')
>>>
>>> np.array(['one', 'two', 'three'])
array(['one', 'two', 'three'], dtype='<U5')
4.1.10. Comparison
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]], dtype='int8')
>>> a.itemsize
1
>>> a.size
9
>>> a.nbytes
9
>>> b = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]], dtype='int32')
>>> b.itemsize
4
>>> b.size
9
>>> b.nbytes
36
>>> c = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]], dtype='int64')
>>> c.itemsize
8
>>> c.size
9
>>> c.nbytes
72
4.1.11. NBytes
>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
... [4, 5, 6],
... [7, 8, 9]])
...
>>> a.astype('int8').nbytes
9
>>>
>>> a.astype('int16').nbytes
18
>>>
>>> a.astype('int32').nbytes
36
>>>
>>> a.astype('int64').nbytes
72
4.1.12. Iinfo
For
intonly
>>> np.iinfo('int')
iinfo(min=-9223372036854775808, max=9223372036854775807, dtype=int64)
>>>
>>> np.iinfo('int8')
iinfo(min=-128, max=127, dtype=int8)
>>>
>>> np.iinfo('int16')
iinfo(min=-32768, max=32767, dtype=int16)
>>>
>>> np.iinfo('int32')
iinfo(min=-2147483648, max=2147483647, dtype=int32)
>>>
>>> np.iinfo('int64')
iinfo(min=-9223372036854775808, max=9223372036854775807, dtype=int64)
4.1.13. Finfo
For
floatonly
>>> np.finfo('float16')
finfo(resolution=0.001, min=-6.55040e+04, max=6.55040e+04, dtype=float16)
>>>
>>> np.finfo('float32')
finfo(resolution=1e-06, min=-3.4028235e+38, max=3.4028235e+38, dtype=float32)
>>>
>>> np.finfo('float64')
finfo(resolution=1e-15, min=-1.7976931348623157e+308, max=1.7976931348623157e+308, dtype=float64)
4.1.14. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Numpy Dtype Astype
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Given `DATA: np.ndarray` (see below)
# 2. Convert to `int` and save result as `result_int`
# 3. Convert to `bool` and save result as `result_bool`
# 4. What happened in each of those steps?
# 5. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Dany `DATA: np.ndarray` (patrz sekcja input)
# 2. Przekonwertuj do typu `int` i wynik zapisz jako `result_int`
# 3. Przekonwertuj do typu `bool` i wynik zapisz jako `result_bool`
# 4. Co się stało w każdym z tych kroków?
# 5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert 'result1' in globals(), \
'Variable `result1` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result1 is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result1` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert 'result2' in globals(), \
'Variable `result2` is not defined; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert result2 is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `result2` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(result1) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result1` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> assert type(result2) is np.ndarray, \
'Variable `result2` has an invalid type; expected: `np.ndarray`.'
>>> result1
array([[-1, 0, 1],
[ 2, 3, 4]])
>>> result2
array([[ True, False, True],
[ True, True, True]])
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
import numpy as np
# %% Types
result1: np.ndarray
result2: np.ndarray
# %% Data
DATA = np.array([[-1.1, 0.0, 1.1],
[2.2, 3.3, 4.4]])
# %% Result
result1 = ...
result2 = ...