4.4. Normalization 3rd Normal Form
The Primary Key must fully define all Non-Key columns
Non-Key columns must not depend on any other Key
All fields (columns) can be determined only by the key in the table and no other column
4.4.1. Problem
id (PK) |
firstname |
lastname |
year |
mission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Melissa |
Lewis |
2035 |
Ares3 |
2 |
Mark |
Watney |
2035 |
Ares3 |
3 |
Rick |
Martinez |
2035 |
Ares3 |
Note that pair (2035, Ares3) repeats several times. Knowing the mission name we can determine the year. This should be replaced with a relation (FK) to the database which would store this pair at given primary key. The important fact here is that, if we want to change year of a Ares3 mission, let say it was delayed due to the budget constraints, we have to change it in several places. Leaving one record unmodified will lead to data inconsistency.
4.4.2. Solution
id (PK) |
firstname |
lastname |
mission_id (FK) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Melissa |
Lewis |
3 |
2 |
Mark |
Watney |
3 |
3 |
Rick |
Martinez |
3 |
id (PK) |
year |
mission |
|---|---|---|
1 |
2031 |
Ares1 |
2 |
2032 |
Ares2 |
3 |
2035 |
Ares3 |
Now changing a year for a mission would result in changing it for all astronauts.
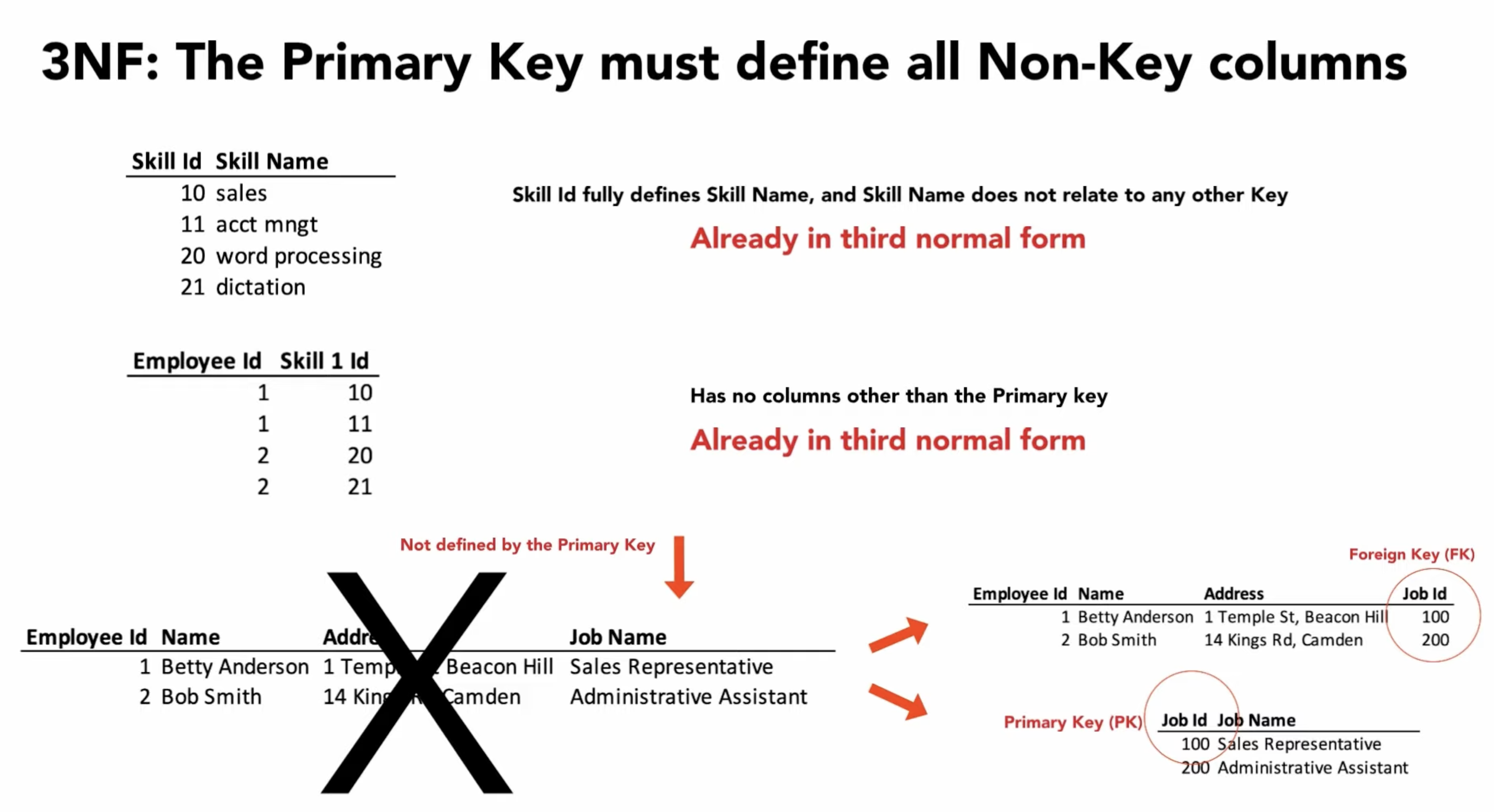
Figure 4.17. The Primary Key must fully define all Non-Key columns Image credit: [1]
4.4.3. Recap
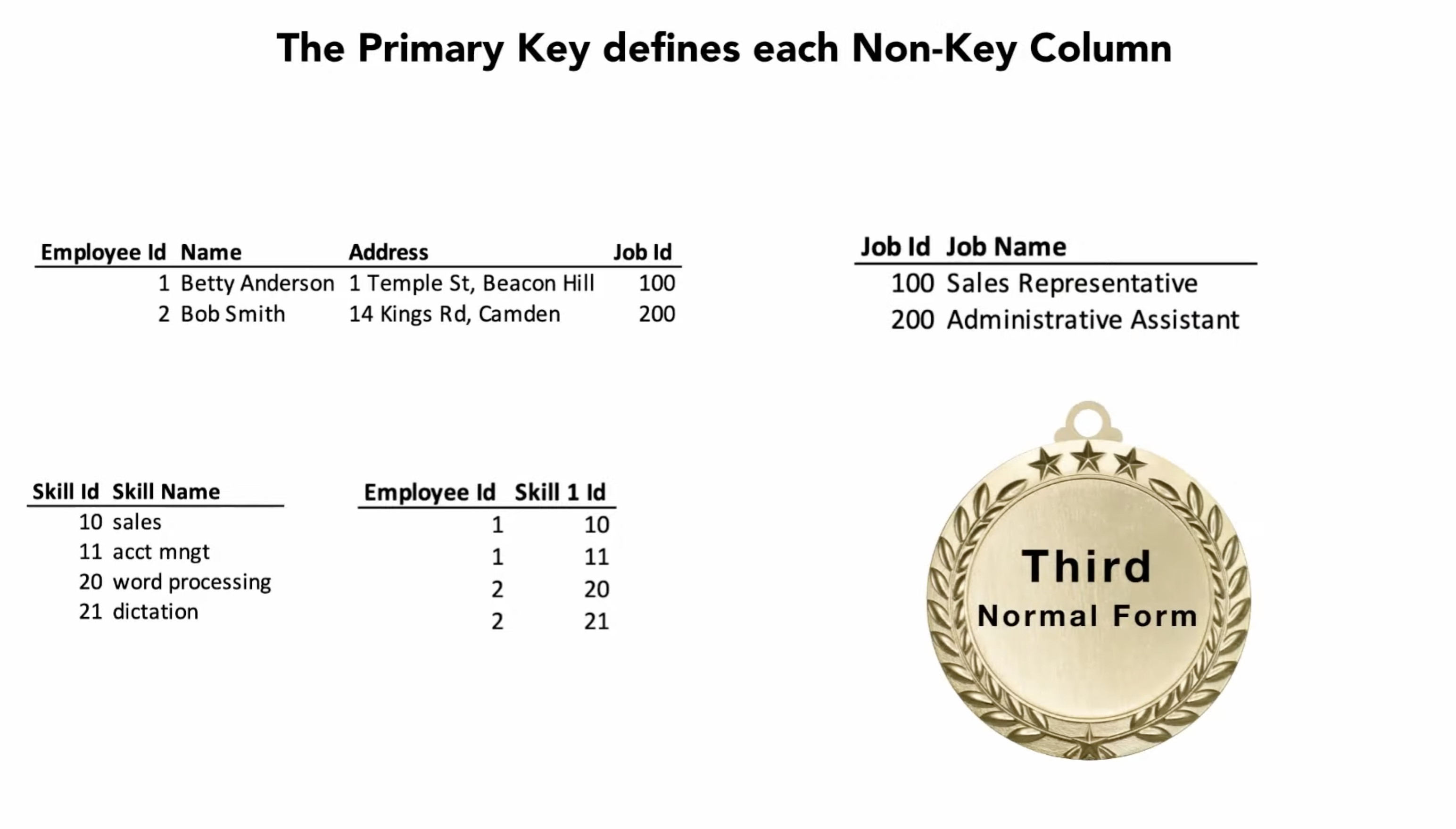
Figure 4.18. If Primary Key fully defines all Non-Key columns and Non-Key columns does not depend on any other Key, the database achieved 3rd Normal Form. Image credit: [1]