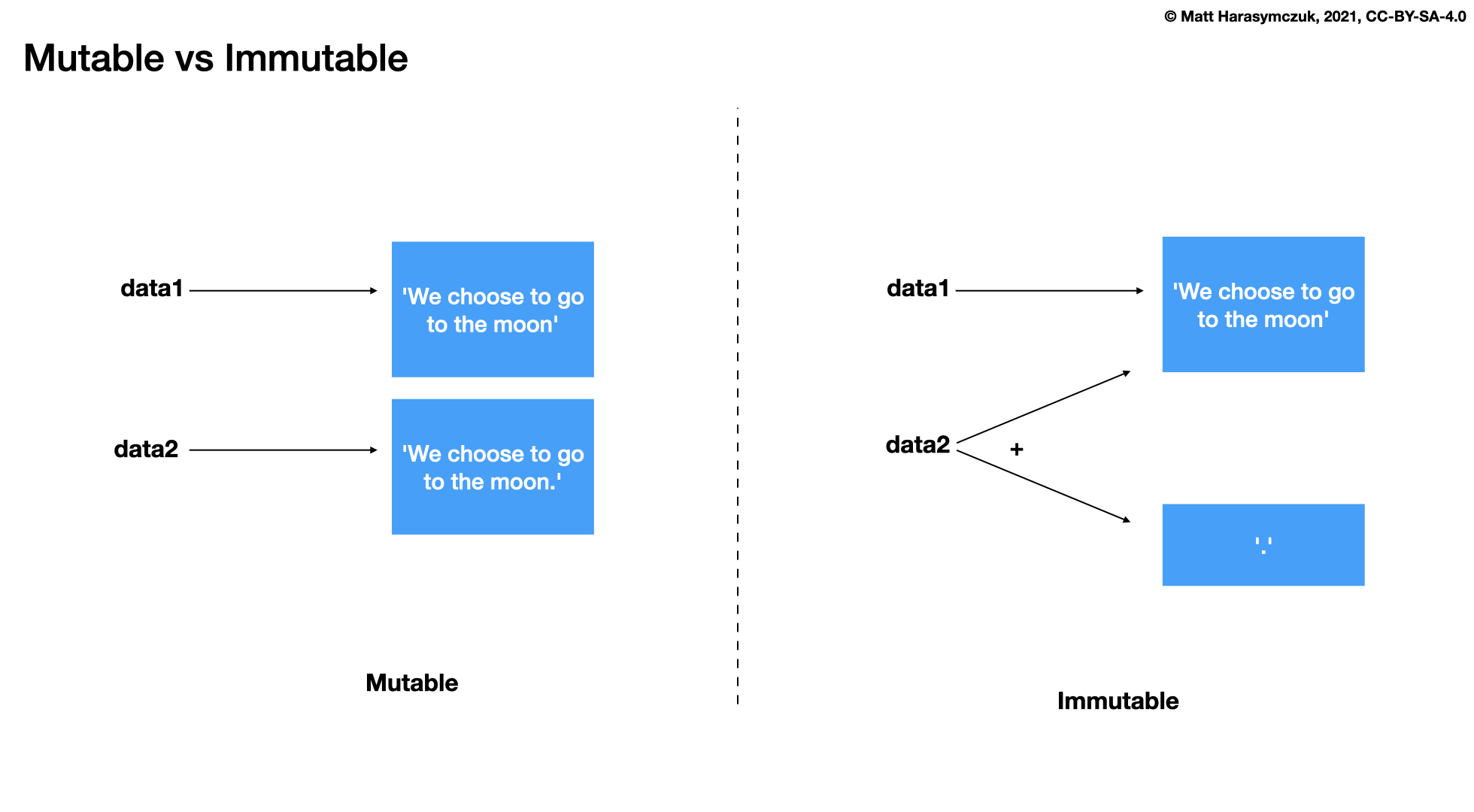
5.3. String Immutable
stris immutablestrmethods create a new modifiedstr
Whenever you call a method on string, it will not change that string, but it will generate a new one. You can capture this newly generated string:
>>> text = 'Alice'
>>> result = text.upper()
>>>
>>> print(result)
ALICE
>>>
>>> print(text)
Alice
You can also assign to the same variable, which will give you an impression
that this modified string, but in fact that is a new object to which
text identifier will point:
>>> text = 'Alice'
>>> text = text.upper()
>>>
>>> print(text)
ALICE
5.3.1. Memory
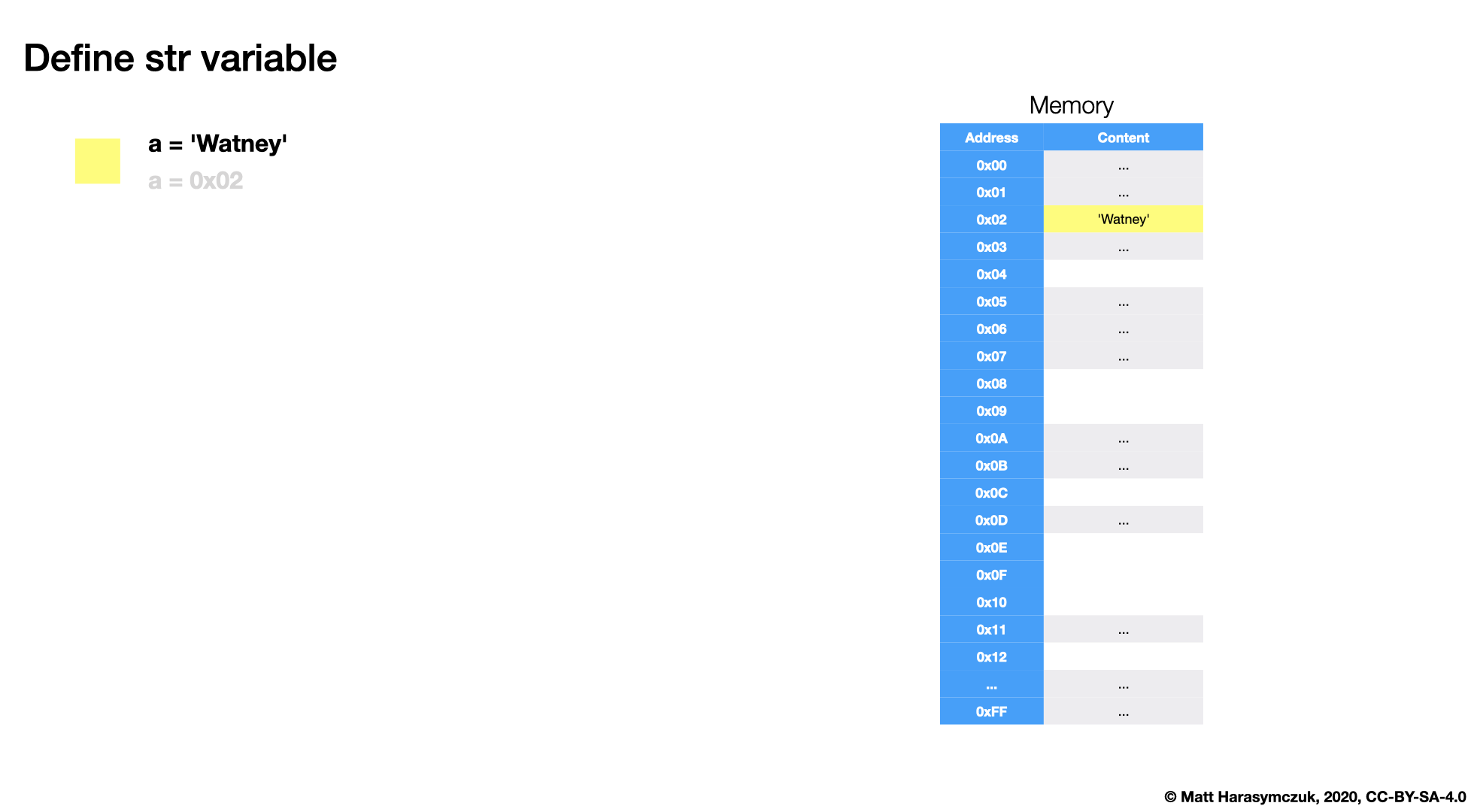
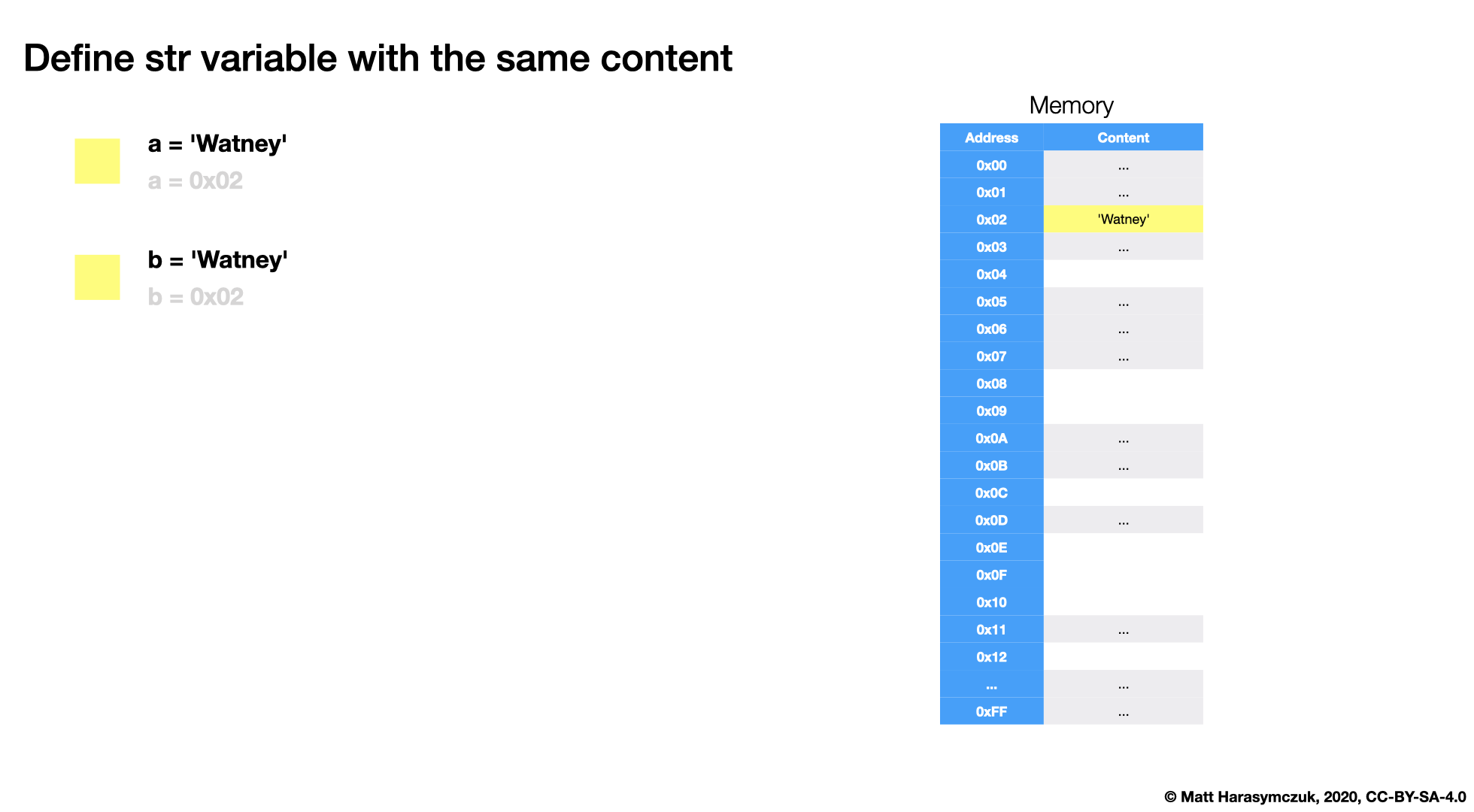
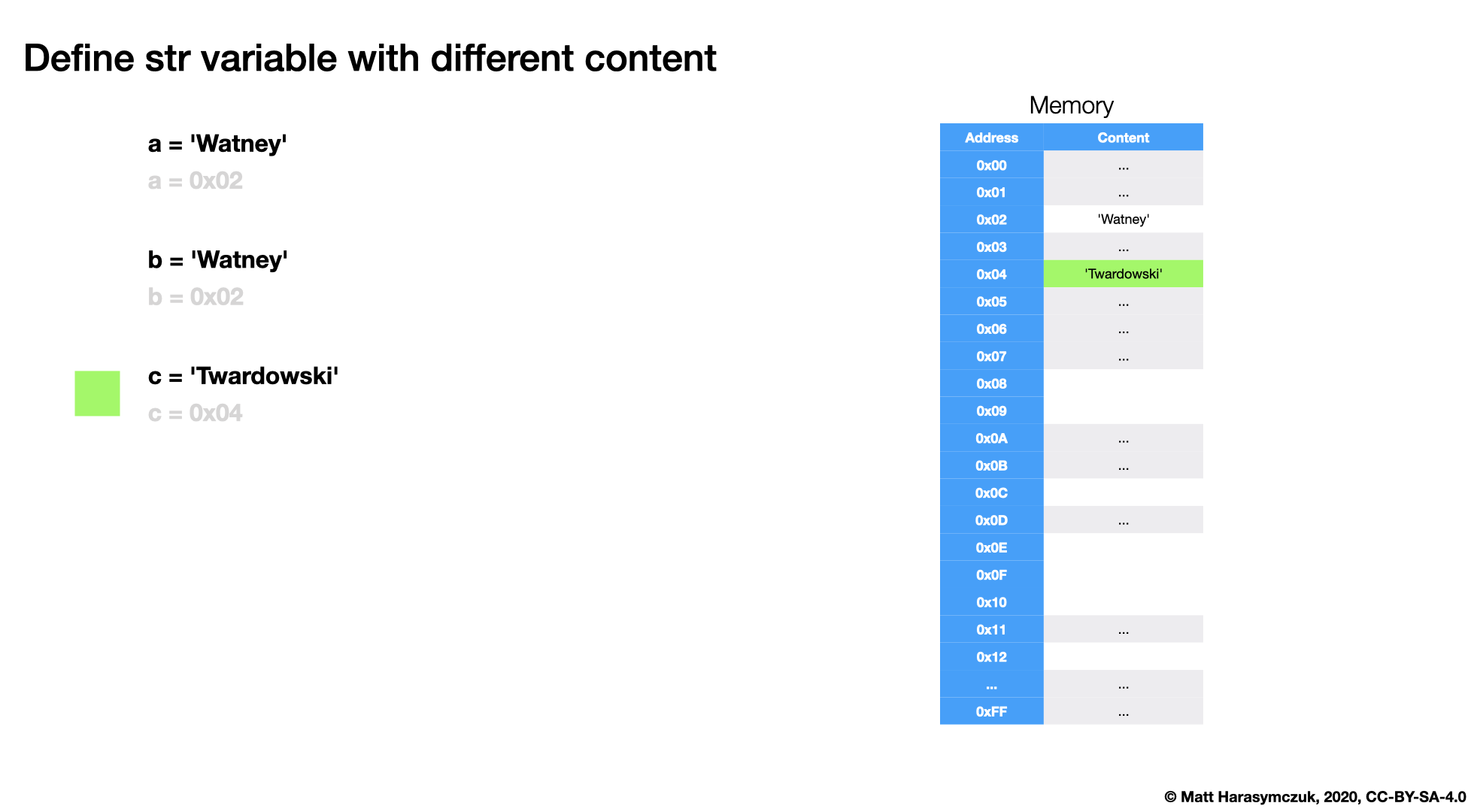
5.3.2. Value Check
Use
==to check if strings are equal
This is valid way to check str value:
>>> name = 'Alice'
>>>
>>> name == 'Alice'
True
5.3.3. Length
Builtin
len()returns the length of a string
>>> len('Alice')
5
5.3.4. Concatenation
Concatenation - joining two or more strings
You can concatenate using
+operator or withf-stringSince Python 3.6
f-stringconcatenation is preferred (it is also faster)
>>> username = 'alice'
>>> domain = 'example.com'
>>>
>>> username + '@' + domain
'alice@example.com'
>>>
>>> f'{username}@{domain}'
'alice@example.com'
5.3.5. Concat Numbers
>>> name = 'Alice'
>>> age = 30
>>>
>>> 'User ' + name + ' has ' + str(age) + ' years'
'User Alice has 30 years'
>>>
>>> f'User {name} has {age} years'
'User Alice has 30 years'
5.3.6. Concat Multiply
>>> 'ha' * 3
'hahaha'