4.3. Numeric Recap
Recap information about
intandfloat
4.3.1. Int
Represents an integer
Could be both signed and unsigned
Default
intsize is 64 bitPython automatically extends
intwhen need bigger numberYou can use
_for easier read especially with big numbersBuiltin function
int()converts argument tointWorks with strings if they have numbers and
+,-,_(underscore)
Definition:
>>> data = 1
>>> data = +1
>>> data = -1
Thousand separator:
>>> million = 1000000
>>> million = 1_000_000
Conversion:
>>> int(1.0)
1
>>>
>>> int('1')
1
4.3.2. Float
Represents floating point number (vide IEEE-754)
Could be both signed and unsigned
Default
floatsize is 64 bitPython automatically extends
floatwhen need bigger number.1- notation without leading zero (0.1)1.- notation without trailing zero (1.0)Engineering notation:
mega = 1e6,micro = 1e-6Scientific notation:
1.23e-4Builtin
float()converts argument tofloat
Definition:
>>> data = 1.0
>>> data = +1.0
>>> data = -1.0
Leading and trailing zero:
>>> data = .1 # 0.1
>>> data = 1. # 1.0
Engineering and scientific notation:
>>> 1.23e-4
0.000123
Conversion:
>>> float(1)
1.0
>>>
>>> float('1.0')
1.0
Decimal separator:
>>> float('1.0')
1.0
>>>
>>> float('1,0')
Traceback (most recent call last):
ValueError: could not convert string to float: '1,0'
Rounding:
>>> pi = 3.14159265359
>>>
>>>
>>> round(pi, 2)
3.14
>>>
>>> print(f'Pi number is {pi:.2f}')
Pi number is 3.14
4.3.3. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Definition
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 5
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Define `mars_highest` with: 20 °C
# 2. Define `mars_lowest` with: -153 °C
# 3. Define `mars_average` with: −63 °C
# 4. Define `moon_day` with: 453 K
# 5. Define `moon_night` with: 93 K
# 6. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Zdefiniuj `mars_highest`: 20 °C
# 2. Zdefiniuj `mars_lowest`: -153 °C
# 3. Zdefiniuj `mars_average`: −63 °C
# 4. Zdefiniuj `moon_day`: 453 K
# 5. Zdefiniuj `moon_night`: 93 K
# 6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> mars_lowest
# -153
#
# >>> mars_average
# -63
#
# >>> moon_day
# 453
#
# >>> moon_night
# 93
# %% Hints
# - `*` - mul operator
# %% References
# [1] Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA).
# Rover Environmental Monitoring Station, Mars Science Laboratory (NASA).
# Year: 2019.
# Retrieved: 2019-08-06.
# URL: http://cab.inta-csic.es/rems/marsweather.html
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert mars_highest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_highest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(mars_highest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_highest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert mars_highest == 20, \
'Invalid value for `mars_highest`, should be 20. Check you calculation'
>>> assert mars_lowest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(mars_lowest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert mars_lowest == -153, \
'Invalid value for `mars_lowest`, should be -153. Check you calculation'
>>> assert mars_lowest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(mars_lowest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert mars_average == -63, \
'Invalid value for `mars_average`, should be -63. Check you calculation'
>>> assert moon_day is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(moon_day) is int, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert moon_day == 453, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid value; expected: `453`.'
>>> assert moon_night is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(moon_night) is int, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert moon_night == 93, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid value; expected: `93`.'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
mars_highest: int
mars_lowest: int
mars_average: int
moon_day: int
moon_night: int
# %% Data
C = 1
K = 1
# %% Result
mars_highest = ...
mars_lowest = ...
mars_average = ...
moon_day = ...
moon_night = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Addition
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 3
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. One Kelvin is equal to 1 Celsius degree (1K = 1°C)
# 2. Zero Celsius degrees is equal to 273.15 Kelvins
# 3. For calculation use round number 273 (0°C = 273K)
# 4. How many Kelvins has average temperatures at surface [1]:
# - Mars highest: 20 °C
# - Mars lowest: -153 °C
# - Mars average: −63 °C
# 5. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Jeden Kelwin to jeden stopień Celsiusza (1K = 1°C)
# 2. Zero stopni Celsiusza to 273.15 Kelwiny
# 3. W zadaniu przyjmij równe 273°C (0°C = 273K)
# 4. Ile Kelwinów wynoszą średnie temperatury powierzchni [1]:
# - Mars najwyższa: 20 °C
# - Mars najniższa: -153 °C
# - Mars średnia: −63 °C
# 5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> mars_highest
# 293
#
# >>> mars_lowest
# 120
#
# >>> mars_average
# 210
# %% Hints
# - `+` - add
# %% References
# [1] Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA).
# Rover Environmental Monitoring Station, Mars Science Laboratory (NASA).
# Year: 2019.
# Retrieved: 2019-08-06.
# URL: http://cab.inta-csic.es/rems/marsweather.html
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert mars_highest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_highest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert mars_lowest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert mars_lowest is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(mars_highest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_highest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(mars_lowest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(mars_lowest) is int, \
'Variable `mars_lowest` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert mars_highest == 293, \
'Invalid value for `mars_highest`, should be 293. Check you calculation'
>>> assert mars_lowest == 120, \
'Invalid value for `mars_lowest`, should be 120. Check you calculation'
>>> assert mars_average == 210, \
'Invalid value for `mars_average`, should be 210. Check you calculation'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
mars_highest: int
mars_lowest: int
mars_average: int
# %% Data
Celsius = 1
Kelvin = 273
MARS_HIGHEST = 20*Celsius
MARS_LOWEST = -153*Celsius
MARS_AVERAGE = -63*Celsius
# %% Result
mars_highest = ...
mars_lowest = ...
mars_average = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Subtraction
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. One Kelvin is equal to 1 Celsius degree (1K = 1°C)
# 2. Zero Kelvin (absolute) is equal to -273.15 Celsius degrees
# 3. For calculation use round number -273 (0K = -273°C)
# 4. How many Celsius degrees has average temperatures at surface [1]:
# - Moon day: 453 K
# - Moon night: 93 K
# 5. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Jeden Kelwin to jeden stopień Celsiusza (1K = 1°C)
# 2. Zero Kelwina (bezwzględne) to -273.15 stopni Celsiusza
# 3. W zadaniu przyjmij równe -273°C (0K = -273°C)
# 4. Ile stopni Celsiusza wynoszą średnie temperatury powierzchni [1]:
# - Księżyca w dzień: 453 K
# - Księżyca w nocy: 93 K
# 5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> moon_day
# 180
#
# >>> moon_night
# -180
# %% Hints
# - `-` - sub operator
# %% References
# [1] Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA).
# Rover Environmental Monitoring Station, Mars Science Laboratory (NASA).
# Year: 2019.
# Retrieved: 2019-08-06.
# URL: http://cab.inta-csic.es/rems/marsweather.html
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert moon_day is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert moon_night is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(moon_day) is int, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(moon_night) is int, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert moon_day == 180, \
'Variable `moon_day` has an invalid value; expected: `180`.'
>>> assert moon_night == -180, \
'Variable `moon_night` has an invalid value; expected: `-180`.'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
moon_day: int
moon_night: int
# %% Data
Celsius = 273
Kelvin = 1
MOON_DAY = 453*Kelvin
MOON_NIGHT = 93*Kelvin
# %% Result
moon_day = ...
moon_night = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Multiplication
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 3
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Define Armstrong line (19 km) in meters
# 2. Define Stratosphere line (20 km) in meters
# 3. Define USAF space boundary line (80 km) in meters
# 4. Define IAF space boundary line (100 km) in meters
# 5. Example: `sea_level = 0*km`
# 6. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Zdefiniuj linię Armstrong line (19 km) w metrach
# 2. Zdefiniuj linię stratosfery line (20 km) w metrach
# 3. Zdefiniuj linię granicy kosmosu wg. USAF (80 km) w metrach
# 4. Zdefiniuj linię granicy kosmosu wg. IAF (100 km) w metrach
# 5. Przykład: `sea_level = 0*km`
# 6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> armstrong_limit
# 19_000
#
# >>> stratosphere
# 20_000
#
# >>> usaf_space
# 80_000
#
# >>> iaf_space
# 100_000
# %% Hints
# - `*` - mul operator
# %% References
# USAF - United States Air Force
# IAF - International Astronautical Federation
# Kármán line (100 km) - boundary between Earth's atmosphere and space
# Armstrong limit (19 km) - altitude above which atmospheric pressure is
# sufficiently low that water boils at the temperature of the human body
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert armstrong_limit is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `armstrong_limit` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert stratosphere is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `stratosphere` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert usaf_space is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `usaf_space` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert iaf_space is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `iaf_space` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(armstrong_limit) is int, \
'Variable `armstrong_limit` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(stratosphere) is int, \
'Variable `stratosphere` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(usaf_space) is int, \
'Variable `usaf_space` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(iaf_space) is int, \
'Variable `iaf_space` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert armstrong_limit == 19_000, \
'Invalid value for `armstrong_limit`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert stratosphere == 20_000, \
'Invalid value for `stratosphere`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert usaf_space == 80_000, \
'Invalid value for `usaf_space`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert iaf_space == 100_000, \
'Invalid value for `iaf_space`. Check you calculation'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
armstrong_limit: int
stratosphere: int
usaf_space: int
iaf_space: int
# %% Data
m = 1
km = 1000 * m
# %% Result
armstrong_limit = ...
stratosphere = ...
usaf_space = ...
iaf_space = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Definition
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 3
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Define variable in meters:
# - Kármán Line Earth: 100_000 m
# - Kármán Line Mars: 80_000 m
# - Kármán Line Venus: 250_000 m
# 2. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Zdefiniuj zmienne w metrach:
# - Linia Kármána Ziemia: 100_000 m
# - Linia Kármána Mars: 80_000 m
# - Linia Kármána Wenus: 250_000 m
# 2. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> karman_line_earth
# 100_000
#
# >>> karman_line_mars
# 80_000
#
# >>> karman_line_venus
# 250_000
# %% Hints
# - `*` - mul operator
# - 1 km = 1000 m
# %% References
# Kármán line (100 km) - boundary between planet's atmosphere and space
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert karman_line_earth is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert karman_line_mars is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert karman_line_venus is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_earth) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_mars) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_venus) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert karman_line_earth == 100_000, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid value; expected: `100_000`.'
>>> assert karman_line_mars == 80_000, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid value; expected: `80_000`.'
>>> assert karman_line_venus == 250_000, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid value; expected: `250_000`.'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
karman_line_earth: int
karman_line_mars: int
karman_line_venus: int
# %% Data
m = 1
km = 1000 * m
# %% Result
karman_line_earth = ...
karman_line_mars = ...
karman_line_venus = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Conversion
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 4
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Calculate altitude in meters:
# - Armstrong Limit: 19 km
# - Stratosphere: 20 km
# - USAF Space Line: 80 km
# - IAF Space Line: 100 km
# 2. Use mul (`*`) operator
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Oblicz wysokości w metrach:
# - Linia Armstronga: 19 km
# - Stratosfera: 20 km
# - Granica kosmosu wg. USAF: 80 km
# - Granica kosmosu wg. IAF 100 km
# 2. Użyj operatora mul (`*`)
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> armstrong_limit
# 19_000
#
# >>> stratosphere
# 20_000
#
# >>> usaf_space
# 80_000
#
# >>> iaf_space
# 100_000
# %% Hints
# - `*` - mul
# - 1 km = 1000 m
# %% References
# USAF - United States Air Force
# IAF - International Astronautical Federation
# Kármán line (100 km) - boundary between Earth's atmosphere and space
# Armstrong limit (19 km) - altitude above which atmospheric pressure is
# sufficiently low that water boils at the temperature of the human body
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert armstrong_limit is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `armstrong_limit` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert stratosphere is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `stratosphere` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert usaf_space is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `usaf_space` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert iaf_space is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `iaf_space` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(armstrong_limit) is int, \
'Variable `armstrong_limit` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(stratosphere) is int, \
'Variable `stratosphere` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(usaf_space) is int, \
'Variable `usaf_space` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(iaf_space) is int, \
'Variable `iaf_space` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert armstrong_limit == 19_000, \
'Invalid value for `armstrong_limit`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert stratosphere == 20_000, \
'Invalid value for `stratosphere`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert usaf_space == 80_000, \
'Invalid value for `usaf_space`. Check you calculation'
>>> assert iaf_space == 100_000, \
'Invalid value for `iaf_space`. Check you calculation'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
armstrong_limit: int
stratosphere: int
usaf_space: int
iaf_space: int
# %% Data
m = 1
km = 1000 * m
ARMSTRONG_LIMIT = 19
STRATOSPHERE = 20
USAF_SPACE = 80
IAF_SPACE = 100
# %% Result
armstrong_limit = ...
stratosphere = ...
usaf_space = ...
iaf_space = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Conversion
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 3
# - Minutes: 2
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Calculate altitude in kilometers:
# - Kármán Line Earth: 100_000 m
# - Kármán Line Mars: 80_000 m
# - Kármán Line Venus: 250_000 m
# 2. Use floordiv (`//`) operator
# 3. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Oblicz wysokości w kilometrach:
# - Linia Kármána Ziemia: 100_000 m
# - Linia Kármána Mars: 80_000 m
# - Linia Kármána Wenus: 250_000 m
# 2. Użyj operatora floordiv (`//`)
# 3. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> karman_line_earth
# 100
#
# >>> karman_line_mars
# 80
#
# >>> karman_line_venus
# 250
# %% Hints
# - `//` - floordiv
# - 1 km = 1000 m
# %% References
# Kármán line (100 km) - boundary between planet's atmosphere and space
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert karman_line_earth is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert karman_line_mars is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert karman_line_venus is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_earth) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_mars) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert type(karman_line_venus) is int, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid type; expected: `int`.'
>>> assert karman_line_earth == 100, \
'Variable `karman_line_earth` has an invalid value; expected: `100`.'
>>> assert karman_line_mars == 80, \
'Variable `karman_line_mars` has an invalid value; expected: `80`.'
>>> assert karman_line_venus == 250, \
'Variable `karman_line_venus` has an invalid value; expected: `250`.'
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
karman_line_earth: int
karman_line_mars: int
karman_line_venus: int
# %% Data
m = 1
km = 1000 * m
KARMAN_LINE_EARTH = 100_000*m
KARMAN_LINE_MARS = 80_000*m
KARMAN_LINE_VENUS = 250_000*m
# %% Result
karman_line_earth = ...
karman_line_mars = ...
karman_line_venus = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Pressure
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Operational pressure of EMU spacesuit: 4.3 PSI
# 2. Operational pressure of ORLAN spacesuit: 40 kPa
# 3. Calculate operational pressure in hPa for EMU
# 4. Calculate operational pressure in hPa for Orlan
# 5. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Ciśnienie operacyjne skafandra kosmicznego EMU (NASA): 4.3 PSI
# 2. Ciśnienie operacyjne skafandra kosmicznego ORLAN (Roscosmos): 40 kPa
# 3. Oblicz ciśnienie operacyjne skafandra EMU w hPa
# 4. Oblicz ciśnienie operacyjne skafandra Orlan w hPa
# 5. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> round(emu, 1)
# 296.5
#
# >>> round(orlan, 1)
# 400.0
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert emu is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `emu` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert orlan is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `orlan` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(emu) is float, \
'Variable `emu` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> assert type(orlan) is float, \
'Variable `orlan` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> round(emu, 1)
296.5
>>> round(orlan, 1)
400.0
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
emu: float
orlan: float
# %% Data
Pa = 1
hPa = 100 * Pa
kPa = 1000 * Pa
psi = 6894.757 * Pa
# %% Result
emu = ...
orlan = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Percent
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Pressure in International Standard Atmosphere (ISA)
# at sea level is: 1 ata = 1013.25 hPa
# 2. Calculate `pO2` - partial pressure of oxygen at sea level in hPa
# 3. To calculate partial pressure use ratio
# 100% --- 1013.25 hPa
# 20.946% --- ? hPa
# 4. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Ciśnienie w Międzynarodowej Standardowej Atmosfera (ISA)
# na poziomie morza wynosi: 1 ata = 1013.25 hPa
# 2. Oblicz `pO2` - ciśnienie parcjalne tlenu na poziomie morza w hPa
# 3. Aby policzyć ciśnienie parcjalne skorzystaj z proporcji
# 100% --- 1013.25 hPa
# 20.946% --- ? hPa
# 4. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> ata
# 101325.0
#
# >>> round(pO2, 1)
# 212.2
# %% Hints
# - 1 hPa = 100 Pa
# - 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
# - 1 ata = 1013.25 hPa
# - ISA - International Standard Atmosphere
# - Nitrogen 78.084%
# - Oxygen 20.946%
# - Argon 0.9340%
# - Carbon Dioxide 0.0407%
# - Others 0.001%
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert ata is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `ata` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(ata) is float, \
'Variable `ata` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> assert pO2 is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `pO2` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(pO2) is float, \
'Variable `pO2` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> ata
101325.0
>>> round(pO2, 1)
212.2
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
ata: float
pO2: float
# %% Data
PERCENT = 100
N2 = 78.084 / PERCENT
O2 = 20.946 / PERCENT
Ar = 0.9340 / PERCENT
CO2 = 0.0407 / PERCENT
Others = 0.001 / PERCENT
Pa = 1
hPa = 100 * Pa
kPa = 1000 * Pa
# %% Result
ata = ...
pO2 = ...
# %% About
# - Name: Numeric Recap Gradient
# - Difficulty: medium
# - Lines: 2
# - Minutes: 3
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. At what altitude above sea level, pressure is equal
# to partial pressure of oxygen
# 2. Print result in meters rounding to two decimal places
# 3. To calculate partial pressure use ratio
# (100% is 1013.25 hPa, 20.946% is how many hPa?)
# 4. Calculated altitude is pressure at sea level minus
# oxygen partial pressure divided by gradient (11.3*Pa/m)
# 5. Mind the operator precedence
# 6. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Na jakiej wysokości nad poziomem morza panuje ciśnienie
# równe ciśnieniu parcjalnemu tlenu?
# 2. Wypisz rezultat w metrach zaokrąglając do dwóch miejsc po przecinku
# 3. Aby policzyć ciśnienie parcjalne skorzystaj z proporcji
# (100% to 1013.25 hPa, 20.946% to ile hPa?)
# 4. Wyliczona wysokość to ciśnienie atmosferyczne na poziomie morza minus
# ciśnienie parcjalne tlenu podzielone przez gradient (11.3*Pa/m)
# 5. Zwróć uwagę na kolejność wykonywania działań
# 6. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Expected
# >>> pO2
# 21223.5345
#
# >>> gradient
# 11.3
#
# >>> round(altitude/m, 2)
# 7088.63
# %% Hints
# - pressure gradient (decrease) = 11.3 Pa / 1 m
# - 1 hPa = 100 Pa
# - 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
# - 1 ata = 1013.25 hPa (ISA - International Standard Atmosphere)
# - Nitrogen 78.084%
# - Oxygen 20.946%
# - Argon 0.9340%
# - Carbon Dioxide 0.0407%
# - Others 0.001%
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> assert gradient is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `gradient` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(gradient) is float, \
'Variable `gradient` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> assert altitude is not Ellipsis, \
'Variable `altitude` has an invalid value; assign result of your program to it.'
>>> assert type(altitude) is float, \
'Variable `altitude` has an invalid type; expected: `float`.'
>>> pO2
21223.5345
>>> gradient
11.3
>>> round(altitude/m, 2)
7088.63
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
gradient: float
altitude: float
# %% Data
PERCENT = 100
N2 = 78.084 / PERCENT
O2 = 20.946 / PERCENT
Ar = 0.9340 / PERCENT
CO2 = 0.0407 / PERCENT
Others = 0.001 / PERCENT
m = 1
Pa = 1
hPa = 100 * Pa
ata = 1013.25 * hPa
pO2 = O2 * ata
# %% Result
gradient = ...
altitude = ...
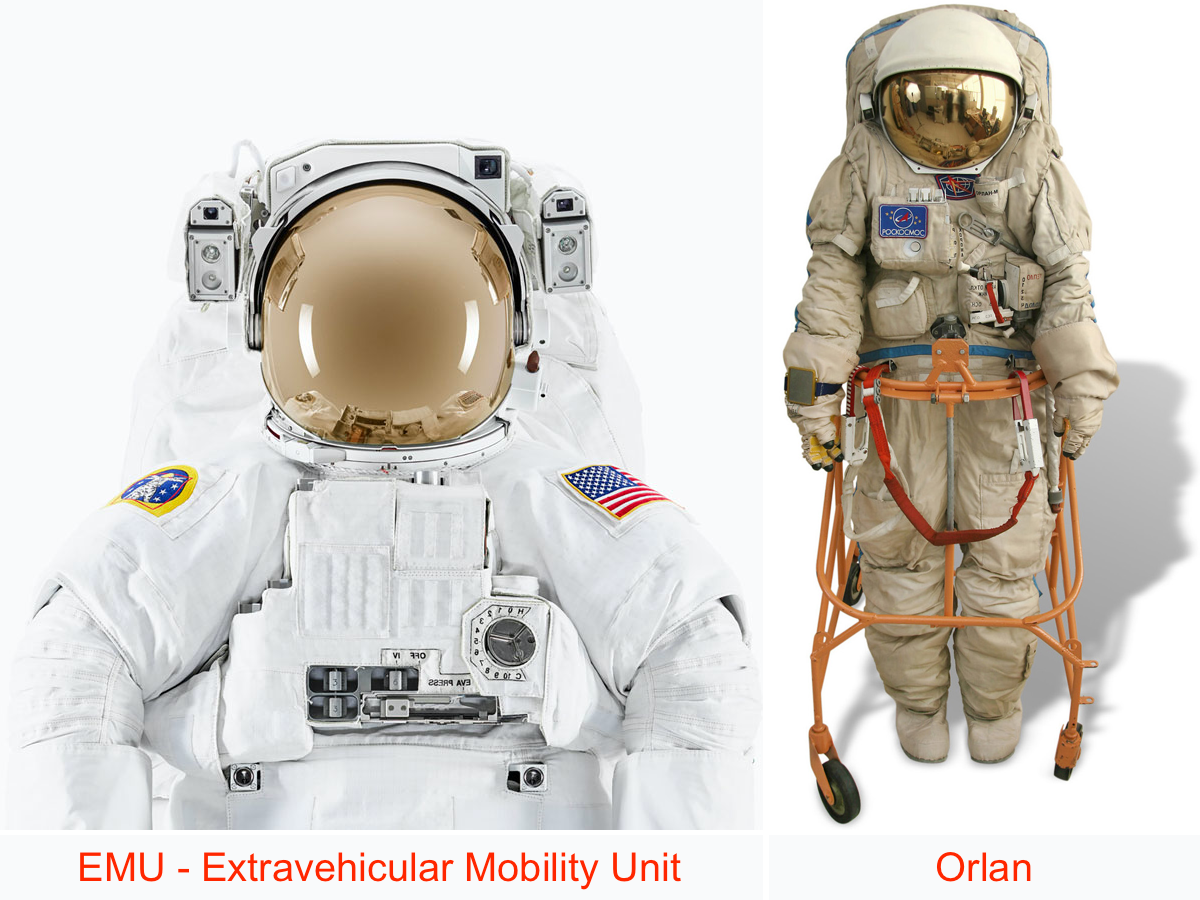
Figure 4.1. EMU and Orlan