4.4. Transport Socket
4.4.1. socket
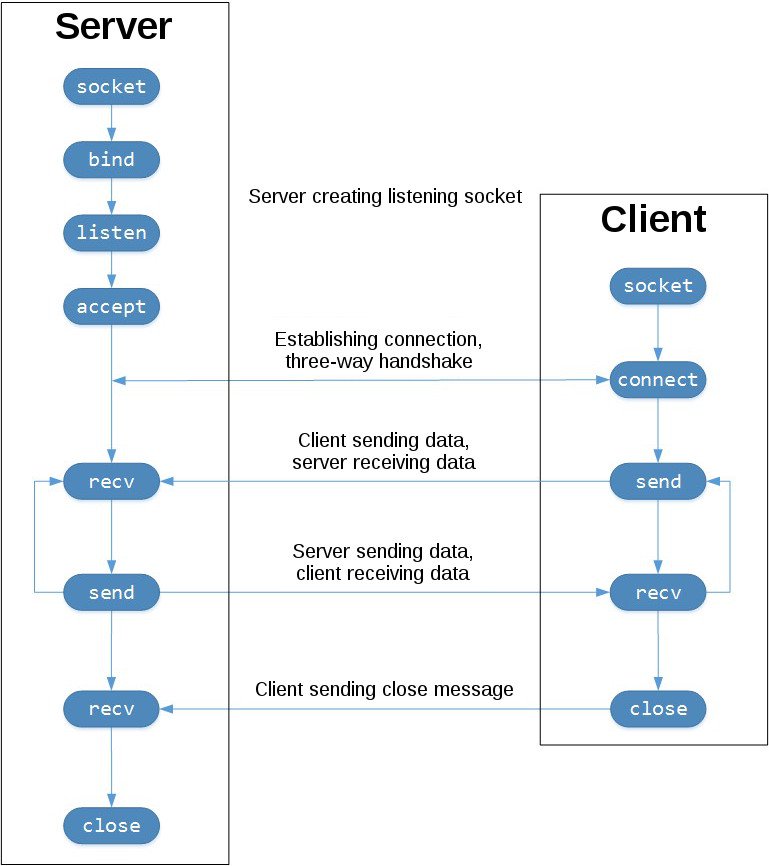
Figure 4.51. Socket Flow
4.4.2. Protocols
IPv4 -
socket.AF_INETIPv6 -
socket.AF_INET6UDP -
socket.SOCK_DGRAMTCP -
socket.SOCK_STREAMBroadcast -
socket.SO_BROADCAST
4.4.3. API
The
bufsizeargument of 1024 used above is the maximum amount of data to be received at onceaccept(),connect(),send(), andrecv()are blockingBlocking calls have to wait on system calls (I/O) to complete before they can return a value
Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.4.4. TCP
Server:
import socket
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock:
print(f'Listening on {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/TCP...')
sock.bind((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT))
sock.listen(1)
while True:
conn, addr = sock.accept()
received = conn.recv(1024).decode()
print(f'From: {addr}, received: "{received}"')
response = 'Thanks'
conn.sendall(response.encode())
if not received:
print(f'Client {addr} disconnected.')
conn.close()
Client:
import socket
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock:
print(f'Connecting to {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/TCP')
sock.connect((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT))
payload = 'Hello World'
sock.sendall(payload.encode())
data = sock.recv(1024).decode()
print(f'Received: "{data}"')
4.4.5. UDP
Server:
import socket
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) as sock:
print(f'Listening on {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/UDP...')
sock.bind((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT))
while True:
received, addr = sock.recvfrom(1024)
received = received.decode()
print(f'From: {addr}, received: "{received}"')
Client:
import socket
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM) as sock:
print(f'Connecting to {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/UDP')
sock.connect((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT))
payload = 'Hello World'
sock.sendall(payload.encode())
received = sock.recv(1024).decode()
print(f'Received: {received}')
4.4.6. Multicast
import socket
def send(data, port=50000, addr='239.192.1.100'):
"""send(data[, port[, addr]]) - multicasts a UDP datagram."""
# Create the socket
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Make the socket multicast-aware, and set TTL.
s.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_IP, socket.IP_MULTICAST_TTL, 20) # Change TTL (=20) to suit
# Send the data
s.sendto(data, (addr, port))
def recv(port=50000, addr="239.192.1.100", buf_size=1024):
"""recv([port[, addr[,buf_size]]]) - waits for a datagram and returns the data."""
# Create the socket
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
# Set some options to make it multicast-friendly
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
try:
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEPORT, 1)
except AttributeError:
pass # Some systems don't support SO_REUSEPORT
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_IP, socket.IP_MULTICAST_TTL, 20)
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_IP, socket.IP_MULTICAST_LOOP, 1)
# Bind to the port
s.bind(('', port))
# Set some more multicast options
iface = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname())
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_IP, socket.IP_MULTICAST_IF, socket.inet_aton(iface))
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_IP, socket.IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, socket.inet_aton(addr) + socket.inet_aton(iface))
# Receive the data, then unregister multicast receive membership, then close the port
data, sender_addr = s.recvfrom(buf_size)
s.setsockopt(socket.SOL_IP, socket.IP_DROP_MEMBERSHIP, socket.inet_aton(addr) + socket.inet_aton('0.0.0.0'))
s.close()
return data
4.4.7. socketserver
4.4.8. TCP
Server:
from socketserver import BaseRequestHandler, TCPServer
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
class RequestHandler(BaseRequestHandler):
def handle(self):
received = self.request.recv(1024).decode()
print(f'From: {self.client_address}/TCP, received: "{received}"')
response = 'Thanks'
self.request.sendall(response.encode())
with TCPServer((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT), RequestHandler) as server:
print(f'Accepting connections on {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/TCP...')
print(f'To stop the server use `Ctrl-C`\n')
server.serve_forever()
Client:
import socket
SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SERVER_PORT = 1337
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock:
print(f'Connecting to {SERVER_HOST}:{SERVER_PORT}/TCP')
sock.connect((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT))
payload = 'Hello World'
sock.sendall(payload.encode())
data = sock.recv(1024).decode()
print(f'Received: "{data}"')
4.4.9. Asynchronous
- Threaded:
socketserver.ThreadingTCPServersocketserver.ThreadingUDPServer
import socket import threading from socketserver import ThreadingTCPServer, BaseRequestHandler SERVER_HOST = '127.0.0.1' SERVER_PORT = 1337 class RequestHandler(BaseRequestHandler): def handle(self): received = self.request.recv(1024).decode() print(f'From: {self.client_address}/TCP, received: "{received}"') response = 'Thanks' self.request.sendto(response.encode(), self.client_address) def send_message(server_host, server_port, message): with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as sock: sock.connect((server_host, server_port)) sock.sendall(message.encode()) response = sock.recv(1024).decode() print(f'Received: {response}') with ThreadingTCPServer((SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT), RequestHandler) as server: # Start a thread with the server -- that thread will then start one more thread for each request server_thread = threading.Thread(target=server.serve_forever) # Exit the server thread when the main thread terminates server_thread.daemon = True server_thread.start() print(f'Server loop running in thread: {server_thread.name}') send_message(SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT, 'Hello World 1') send_message(SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT, 'Hello World 2') send_message(SERVER_HOST, SERVER_PORT, 'Hello World 3') server.shutdown()
Forking:
socketserver.ForkingTCPServer
socketserver.ForkingUDPServer
4.4.10. References
4.4.11. Assignments
4.4.11.1. Heartbeat
- About:
Name: Heartbeat
Difficulty: medium
Lines: 20
Minutes: 21
- License:
Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
This code can be used only for learning by humans (self-education)
This code cannot be used for teaching others (trainings, bootcamps, etc.)
This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
This code cannot be distributed in any form
This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
This code cannot have its license changed
If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
Exception can be granted only by the author (Matt Harasymczuk)
- English:
Create a Heart Beat client and server
Both the client and the server are to be run in threads
The server is to accept UDP/IPv4 messages on port 1337
Communication is to be done using the JSON protocol
The client is to have information about its IP and PORT
The client is to send information to the server every 5 seconds about its IP and PORT
Print:
UTC date of packet arrival,
IP and PORT sent by the client.
Run doctests - all must succeed
- Polish:
Stwórz klienta i serwer Heart Beat
Zarówno klient jak i serwer ma być uruchamiany w wątkach
Serwer ma przyjmować komunikaty UDP/IPv4 na porcie 1337
Komunikacja ma odbywać się za pomocą protokołu JSON
Klient ma mieć informację o swoim adresie IP i PORT
Klient ma co 5 sekund wysyłać informację do serwera o swoim IP i PORT
Wypisz:
datę UTC przyjścia pakietu,
IP i PORT przesłany przez klienta.
Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
- Hints:
threading.Timer(frequency: int, fn: Callable).start()socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)socketserver.ThreadingUDPServer
4.4.11.2. Backdoor
- About:
Name: Backdoor
Difficulty: medium
Lines: 150
Minutes: 34
- License:
Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
This code can be used only for learning by humans (self-education)
This code cannot be used for teaching others (trainings, bootcamps, etc.)
This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
This code cannot be distributed in any form
This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
This code cannot have its license changed
If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
Exception can be granted only by the author (Matt Harasymczuk)
- English:
Create a TCP server running in a thread
The server is to be run on a random port in the range 1025-65535 (why this range of ports?)
Extract information about the IP address and PORT on which the server is listening
The server expects messages in JSON format:
date: datetime(UTC),command: str,timeout: int.
The server executes the command saved in
commandin the operating system, taking into accounttimeoutSend the sender JSON with the result of the command execution, i.e.:
date: datetime(UTC),host: str,port: int,stdout: str,stderr: str,exit_code: int
Run doctests - all must succeed
- Polish:
Stwórz uruchamiany w wątku serwer TCP
Serwer ma być uruchamiany na losowym porcie z przedziału 1025-65535 (dlaczego taki zakres portów?)
Wyciągnij informację o adresie IP i PORT na którym nasłuchuje serwer
Serwer oczekuje na komunikaty w formacie JSON:
date: datetime(UTC),command: str,timeout: int.
Serwer wykonuje polecenie zapisane w
commandw systemie operacyjnym uwzględniająctimeoutPrześlij nadawcy JSON z wynikiem wykonania polecenia, tj.:
date: datetime(UTC),host: str,port: int,stdout: str,stderr: str,exit_code: int
Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
- Hints:
random.randint()socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)socketserver.ThreadingTCPServersubprocess.run(cmd: str, timeout: int, shell: bool = True)json.dumps(obj: Any)json.loads(s: str)