14.4. Generator Inspect
14.4.1. SetUp
>>> from inspect import isgenerator
14.4.2. Is Generator
>>> a = [x for x in range(0,5)]
>>> b = (x for x in range(0,5))
>>>
>>> isgenerator(a)
False
>>>
>>> isgenerator(b)
True
>>> data = range(0, 10)
>>>
>>> isgenerator(data)
False
14.4.3. Introspection
>>> data = (x for x in range(0,10))
>>>
>>>
>>> next(data)
0
>>>
>>> data.gi_code
<code object <genexpr> at 0x..., file "<...>", line 1>
>>>
>>> data.gi_running
False
>>>
>>> data.gi_frame
<frame at 0x..., file '<...>', line 1, code <genexpr>>
>>>
>>> data.gi_frame.f_locals
{'.0': <range_iterator object at 0x...>, 'x': 0}
>>>
>>> data.gi_frame.f_code
<code object <genexpr> at 0x...0, file "<...>", line 1>
>>>
>>> data.gi_frame.f_lineno
1
>>>
>>> data.gi_frame.f_lasti
16
>>>
>>> data.gi_yieldfrom
14.4.4. Memory Footprint
sys.getsizeof(obj)returns the size of anobjin bytessys.getsizeof(obj)callsobj.__sizeof__()methodsys.getsizeof(obj)adds an additional garbage collector overhead if theobjis managed by the garbage collector
>>> from sys import getsizeof
192 bytes for generator in Python 3.13
192 bytes for generator in Python 3.12
200 bytes for generator in Python 3.11
104 bytes for generator in Python 3.10
112 bytes for generator in Python 3.9
112 bytes for generator in Python 3.8
120 bytes for generator in Python 3.7
>>> gen1 = (x for x in range(0,1))
>>> gen10 = (x for x in range(0,10))
>>> gen100 = (x for x in range(0,100))
>>> gen1000 = (x for x in range(0,1000))
>>>
>>> getsizeof(gen1)
200
>>>
>>> getsizeof(gen10)
200
>>>
>>> getsizeof(gen100)
200
>>>
>>> getsizeof(gen1000)
200
>>> com1 = [x for x in range(0,1)]
>>> com10 = [x for x in range(0,10)]
>>> com100 = [x for x in range(0,100)]
>>> com1000 = [x for x in range(0,1000)]
>>>
>>>
>>> getsizeof(com1)
88
>>>
>>> getsizeof(com10)
184
>>>
>>> getsizeof(com100)
920
>>>
>>> getsizeof(com1000)
8856
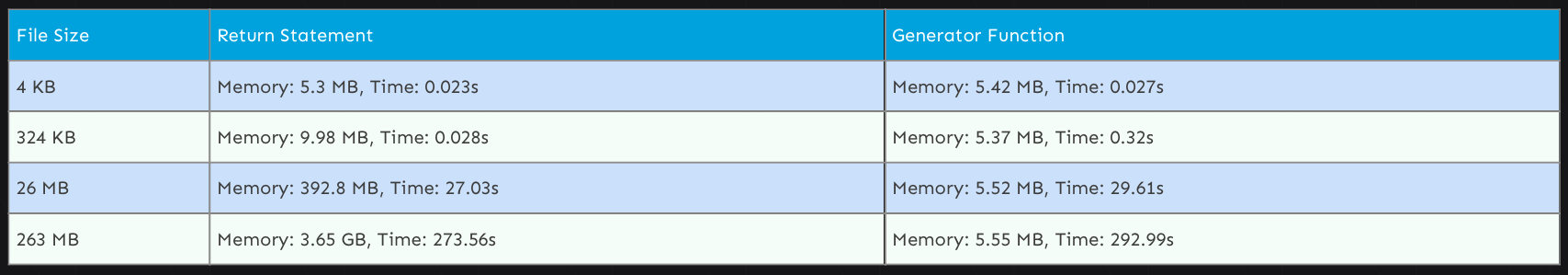
Figure 14.1. Source: https://www.askpython.com/python/python-yield-examples
14.4.5. Assignments
# %% About
# - Name: Generator Function Iris
# - Difficulty: easy
# - Lines: 8
# - Minutes: 5
# %% License
# - Copyright 2025, Matt Harasymczuk <matt@python3.info>
# - This code can be used only for learning by humans
# - This code cannot be used for teaching others
# - This code cannot be used for teaching LLMs and AI algorithms
# - This code cannot be used in commercial or proprietary products
# - This code cannot be distributed in any form
# - This code cannot be changed in any form outside of training course
# - This code cannot have its license changed
# - If you use this code in your product, you must open-source it under GPLv2
# - Exception can be granted only by the author
# %% English
# 1. Write filter for `DATA` which returns `features: list[float]` for given `species: str`
# 2. Implement solution using function
# 3. Implement solution using generator and `yield` keyword
# 4. Compare results of both using `sys.getsizeof()`
# 5. What will happen if input data will be bigger?
# 6. Note, that in different Python versions you'll get slightly
# different values for getsizeof generator and function:
# - 216 for generator in Python 3.13
# - 216 for generator in Python 3.12
# - 224 for generator in Python 3.11
# - 104 for generator in Python 3.10
# - 112 for generator in Python 3.9
# - 112 for generator in Python 3.8
# - 120 for generator in Python 3.7
# 7. Run doctests - all must succeed
# %% Polish
# 1. Napisz filtr dla `DATA` zwracający `features: list[float]` dla danego gatunku `species: str`
# 2. Zaimplementuj rozwiązanie wykorzystując funkcję
# 3. Zaimplementuj rozwiązanie wykorzystując generator i słowo kluczowe `yield`
# 4. Porównaj wyniki obu używając `sys.getsizeof()`
# 5. Co się stanie, gdy ilość danych będzie większa?
# 6. Zwróć uwagę, że w zależności od wersji Python wartości getsizeof
# dla funkcji i generatora mogą się nieznaczenie różnić:
# - 224 dla generator w Python 3.14
# - 216 dla generator w Python 3.13
# - 216 dla generator w Python 3.12
# - 224 dla generator w Python 3.11
# - 104 dla generator w Python 3.10
# - 112 dla generator w Python 3.9
# - 112 dla generator w Python 3.8
# - 120 dla generator w Python 3.7
# 7. Uruchom doctesty - wszystkie muszą się powieść
# %% Doctests
"""
>>> import sys; sys.tracebacklimit = 0
>>> assert sys.version_info >= (3, 9), \
'Python has an is invalid version; expected: `3.9` or newer.'
>>> from sys import getsizeof
>>> from inspect import isfunction, isgeneratorfunction
>>> assert isfunction(function)
>>> assert isgeneratorfunction(generator)
>>> list(function(DATA, 'setosa'))
[[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2], [4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2]]
>>> list(generator(DATA, 'setosa'))
[[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2], [4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2]]
>>> getsizeof(function(DATA, 'setosa'))
88
>>> getsizeof(function(DATA*10, 'setosa'))
248
>>> getsizeof(function(DATA*100, 'setosa'))
1656
>>> getsizeof(generator(DATA, 'setosa'))
224
>>> getsizeof(generator(DATA*10, 'setosa'))
224
>>> getsizeof(generator(DATA*100, 'setosa'))
224
"""
# %% Run
# - PyCharm: right-click in the editor and `Run Doctest in ...`
# - PyCharm: keyboard shortcut `Control + Shift + F10`
# - Terminal: `python -m doctest -f -v myfile.py`
# %% Imports
# %% Types
from typing import Callable, Generator
function: Callable[[list[float|str], str], list[float]]
generator: Callable[[list[float|str], str], Generator[list[float], None, None]]
# %% Data
DATA = [
(5.8, 2.7, 5.1, 1.9, 'virginica'),
(5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2, 'setosa'),
(5.7, 2.8, 4.1, 1.3, 'versicolor'),
(6.3, 2.9, 5.6, 1.8, 'virginica'),
(6.4, 3.2, 4.5, 1.5, 'versicolor'),
(4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2, 'setosa'),
]
# %% Result
def function(data: list, species: str):
...
def generator(data: list, species: str):
...